Interdisciplinary Integration For Developing Professional Responsibility Of The Future University Teacher
Abstract
The modern school system requires universities to solve a complex social problem connected with the preparation of teachers. The future specialist should be well-educated, understand the depth of connections between phenomena and processes, and have a holistic view of the world. Therefore, the future teacher as a specialist in the humanitarian field has to master the basics of various academic disciplines. The use of interdisciplinary integration of academic disciplines in the educational process of the university meets the stated goal. The interrelation and interaction of concepts, objects, phenomena, processes, the integration of various subject areas leads to the formation of a holistic picture of future professional activity. The purpose of the research is the theoretical substantiation and experimental verification of the use of interdisciplinary integration of educational disciplines in the formation of the future professional responsibility of the university teacher. The research methods are theoretical (analysis and synthesis of regulatory documents, study of psychological and pedagogical literature, content analysis of educational and methodical materials), and pedagogical experiment (stating, forming, control stages). The authors have developed a modular program which uses interdisciplinary integration of humanitarian and economic disciplines. The qualitative and quantitative analysis of the pedagogical experiment allows to state that the interdisciplinary integration of educational disciplines makes it possible to form a subject of responsibility, namely, it contributes to the formation of professional responsibility.
Keywords: Interdisciplinary integrationintegrative approachprofessional responsibilityfuture teacher
Introduction
The subject disunity of academic disciplines in the university does not allow forming a holistic picture of the future professional activity, understanding the depth of connections, phenomena and processes representing it. Therefore, the worldview of future teachers is quite limited while the modern education system needs specialists with a high level of intelligence, a holistic picture of the world, which integrates knowledge and ideas of economic, political, cultural and informational nature.
These factors create serious difficulties in formation of future teacher’s professional responsibility. The use of interdisciplinary integration of academic disciplines in the process of preparing a future teacher is one of the most important contemporary problems of the educational process. Therefore, an integrative approach developed by Berulava (1998), Galiczkix, (1999), Makhmutov (1989) is getting popular. The interrelation and interaction of concepts, objects, phenomena of processes, integration of various subject areas lead to the formation of a holistic picture of future professional activity; and the teacher will be responsible for the results of his/her activity to various subjects of the educational process. According to modern requirements, the future specialist of the humanitarian field needs to master the basics of economic, managerial knowledge and information technology in order to initiate and implement educational projects.
The relevance of the research is also due to the contradiction between the requirements of the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” and the federal state educational standard on the use of interdisciplinary connections in the implementation of educational programs and the substantive aspect of the educational and methodical materials that are not sufficiently consistent to solve this problem.
Problem Statement
In Russian psychology responsibility is considered in the context of self-consciousness of the person and is included in the macrostructure of self-relation (Asmolov, 2001; Leont`ev, 2002; Rubinshtejn, 1989). Responsibility is manifested in a variety of life situations and in professional activities. A person is responsible before the formal organizations (educational organization) and informal ones (other people, himself) (Muzdybaev, 2010).
Rubinshtejn (1989) defines responsibility as one of the personality traits included in the directional structure, it determines his or her activity and selectivity in relation to reality, determines the behavior of a person in changing external conditions. Under these conditions, a person is responsible for his or her actions and, as a result, is capable of internal control. Responsibility, which is a characteristic of a mature person, acts as a single mechanism of self-regulated voluntary meaningful activity (Rubinshtejn, 1989).
Responsibility as a personal trait is formed through the processes of socialization and individualization. These processes are organized in the special university space during educational activities (Bim-Bad, 1995). Thanks to the inclusion of the future teacher in the educational process, professional responsibility is developed. Accordingly, the process of forming the professional responsibility of a future teacher is the result of university education, which uses the integration of subject areas, in particular academic disciplines of the humanitarian and economic field. The interaction of economic and humanitarian disciplines must be considered at the paradigm level. At present, it is legitimate to talk about the convergence of the paradigms of the humanities and economic sciences at the level of understanding the role of the subject of activity and determinism (Novikova, 2017).
Many Russian teachers study the problem of the relationship of academic disciplines. A great contribution to the development of interdisciplinary research and their integration was made by Yakovlev (1980). He has identified general integration trends for higher education, developed models of an “integral profile” specialist. Zagvyazinskij (1984) has developed a concept for the integration of pedagogical knowledge, its main point is the importance of creating an integrative knowledge system in the educational process. For the formation of a knowledge system and the development of integrated courses it is necessary to apply the following types of interdisciplinary relationships: teaching and disciplinary direct; research and interdisciplinary direct; mentally indirect; indirectly applied links (Pashchenko, 2006). The use of interdisciplinary connections in a higher educational institution enhances cognitive interest, activates professional and pedagogical thinking and develops the personal qualities of a specialist, including professional responsibility (Plugina, 2009; Xasanov & Mamatkarimov, 2016; Himmataliev, Fajzullaev, Safarova, Madazizova, & Sobirzhonova, 2016).
Thus, Russian researchers have revealed the essence of the concept of responsibility as a psychological phenomenon, underlined the importance of its formation through the integration of subject areas and within a single training course (Zagvyazinskij, 1984). However, less attention is paid to the use of economic disciplines in the preparation of a future specialist.
The problem of the implementation of interdisciplinary links acquires greater significance as schools expect from universities not just professionally trained teachers, but specialists with different competencies who are able to integrate the knowledge of different sciences.
In foreign psychology, responsibility is included in the problematics of studying the self-concept, along with the concept of freedom (Jonas, 2004; Rychlak, 1984; Yaspers, 1994). Freedom or responsibility is always a question of choice between the implementation of plans and taking into account the internal perspectives of other people, between action and inaction. Studying the relationship of freedom and responsibility from the standpoint of the target nature and human behavior, Rychlak (1984) came to the conclusion that the person participates in the selection and establishment of predicates, “his laws”, on the basis of which a person can choose his dependencies and evaluate his behavior.
Ericson (1974) has analyzed the development of the person throughout his life, including the transition from one step to another, passing through crises. The formation of responsibility as a personal trait falls on the fifth and sixth stages of development which corresponds to the period of university studies (Ericson, 1974).
Many foreign researchers consider various aspects of formation of professional responsibility of future teachers. Lauermann and Karabenick (2013) analyze the subjects of responsibility, namely, who is responsible for what which organization checks the performance of professional duties. Researchers come to the conclusion that it is important to form professional responsibility due to the fact that this quality motivates teachers to perform professional activities of high quality.
Some foreign scientists (Matteucci & Helker, 2018; Edling & Frelin, 2013) study distribution of responsibility between different subjects (parents, students, teachers). Daniels, Radil, and Goegan (2017) underline that the proper distribution of responsibilities between them improves the quality of education.
Teacher’s professional duties are determined by the level of professional responsibility. Robinson, Phillips, and Quennerstedt (2018) discuss the importance of respecting students’ rights, including educational work in order to explain them their rights. Chatelier and Rudolph (2018) reveal teacher’s professional ability to work and teach students with special educational needs.
The use of interdisciplinary integration in the educational process is considered in foreign studies in different contexts. Cezarino, Liboni, Oliveira, and Caldana (2016) solve the problem of integrating academic disciplines from the perspective of managing this process. The authors attempt to connect academic disciplines by changing the structure of the curriculum, organizing the educational process and teaching methods.
Other researchers consider it important to connect the relationship of the learning process with educational activities. For example, López Castellano, García-Quero, and García-Carmona (2018) and Misiaszek (2017) reveal the potential of eco-pedagogy to form an environmentally competent citizen. Shumer, Lam, and Laabs (2012) examine the relationship of academic education with the education of specialist’s personal qualities, which are necessary for the implementation of professional activities.
Baranova and Valeev (2015) study the development of creative cognitive activity of students through the use of interdisciplinary connections in the educational process at the university. The authors identify options for the relationship of subject areas: the logical relationship of educational topics in various subjects; one subject as a tool for solving the issues and tasks of another subject. These options directly affect the development of students' cognitive activity, presentation of the unity of the material world, formation of their worldview.
Kress and Lake (2017) consider excursion as one of the forms of the subject of study. It allows to integrate several academic subjects, to combine theoretical knowledge and practical experience of the student.
Thus, foreign researchers have defined the place of professional responsibility in the system of human behavior, shown the possibilities of personal development through formation of a holistic picture of the world. Formation of professional responsibility of the future teacher is possible through the definition of subjects of responsibility and the distribution of specific responsibilities between them.
Foreign researchers consider interdisciplinary integration in a broad context: starting with the management of this process by the director / manager, interrelation of the education process, influence of interdisciplinary connections of educational disciplines on the development of personal qualities.
Research Questions
Is the use of interdisciplinary integration of academic disciplines effective in the process of formation of professional responsibility of the future university teacher?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is the theoretical justification and experimental verification of the use of interdisciplinary integration of academic disciplines in formation of professional responsibility of the future university teacher. The main tasks of the research are: the study of regulatory and scientific-methodical literature; development of a modular program using interdisciplinary connections of academic disciplines; diagnostics of the level of formation of professional responsibility of the future teacher.
Research Methods
-
Analysis and synthesis of normative documents, study of psychological and pedagogical literature, content analysis of educational and methodical materials allowed to develop a modular program of the academic discipline and exercises using interdisciplinary integration.
-
Pedagogical experiment (stating, forming, control stages).
Experimental research base
The research was held at Vyatka State University in 2017-2018. 130 students of the 3d year pursuing "Pedagogical education" (bachelor degree) took part in the research.
Stages of research
The study had three stages. At the theoretical stage the authors studied and formulated the research problem; defined goal, research hypotheses; made a study plan. At the experimental stage they conducted a pedagogical experiment; developed a modular program and exercises using interdisciplinary integration. The third stage included qualitative, quantitative analysis and synthesis of results.
Findings
Stating stage of the experiment
To assess the development of professional responsibility of future teachers, we used the methodic of “Responsibility” (Pryadein, 2012), “Moral-legal reliability of a person” (Strizhov, 2008).
Evaluation criteria
High level. Value points are the basic universal human and pedagogical values that regulate the interaction between subjects of activity. Responsibility is a guideline and value, connected with a sense of duty while performing professional duties, desire to help other people and earn their respect. The student is able to regulate his emotional behavior, show balance, behavioral activity, perseverance in achieving the goal.
Middle level. Universal and pedagogical values, regulating the interaction between the subjects of activity, are determined by the value points. Responsibility is a value connected with a sense of duty while performing professional duties, but it is not always manifested in the desire to help other people to earn their respect. The student can regulate his/her emotional behavior, show balance, but does not always show behavioral activity, perseverance in achieving the goal.
Low level. Value points as separate universal and pedagogical values that regulate the interaction between the subjects of activity. Responsibility is not a stable value; it is connected with a sense of duty while performing professional duties, but not manifested in the desire to help other people to earn their respect. The student is not always able to regulate his/her emotional behavior, show balance, does not show behavioral activity, perseverance in achieving the goal.
Forming stage of the experiment
A modular program have been developed using interdisciplinary integration of academic disciplines of a humanitarian and economic fields: academic disciplines “Legal support of education” and “Theory and methods of education. Psychological and pedagogical workshop "(humanitarian field) and" Economics of education "(economic field). Modular learning technology was used (Yuczyavichenya, 1989) while creating a modular program.
The purpose of the program is to deepen students' knowledge in the context of disciplines, to form a holistic picture of future professional activities, which contributes to the formation of professional responsibility, an important professional quality.
The integrative content of the program is presented in completed independent modules, the assimilation of which is carried out in accordance with a specific goal. The purpose of each module formulates professional responsibilities, for which the teacher will be responsible in future activities.
As an example, let us present one of the modules of the academic discipline "Regulatory and legal support of education" (estimated time to be spent on the module 8 hours (2 hours - lectures, 2 hours - seminar, 4 hours - independent work).
The topic of the lecture is “Children’s rights and forms of their legal protection”.
The objective is to form student’s professional responsibility for the observance of children’s rights in the framework of educational activities.
Lecture plan:
International documents on the protection of children's rights. UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Children’s rights and forms of their legal protection.
A student chooses independently the level of mastering educational material on the topic (each level is determined by a different number of educational elements).
1 level: УЭ0-УЭ1-УЭ3-УЭ4-УЭ7-УЭ8
2 level: УЭ0-УЭ1-УЭ2-УЭ3-УЭ4-УЭ5-УЭ7-УЭ8
3 level: УЭ0-УЭ1-УЭ2-УЭ3-УЭ4-УЭ5-УЭ6-УЭ7-УЭ8
It is intended to connect classroom and extracurricular independent work within the framework of the developed module.
Table
On the example of the presented content of the module, let us consider the integration of two academic disciplines “Regulatory and legal support of education” and “Theory and methods of education. Psychological and pedagogical workshop" (humanitarian field). As part of the educational element (UE6), students were asked to develop and conduct an educational event on the topic “The rights of the child in modern Russia”. Knowledge of the regulatory framework governing the rights of the child allowed future teachers to prove themselves as a competent specialist in this field, to present this material in the context of the educational function of the educational process.
Integration of knowledge of humanitarian and economic fields is considered through the content of the discipline "Economics of Education". It is aimed to study mechanisms of regulation of various relations (economic, legal, social) in the field of education. In the process of studying the module, corresponding types of professional responsibility are formed: civil, labor and financial. The formation of civil responsibility is focused on the social attitudes of the future specialist, aimed at the desire to carry out their activities, based on a sense of civic duty, the development of students’ social activity. Labor responsibility presupposes the conscientious fulfillment of one's labor duties, the observance of the rules of internal labor regulations and labor discipline. Financial responsibility arises from the infliction of material damage in the performance of work duties or as a result of administrative misconduct. The importance of using interdisciplinary integration eliminates the one-sided perception of future professional activities.
In general, the implemented modular program allows to include students in an active independent professional activity, to work at an individual pace of study, which, of course, increases their responsibility for learning results. It creates optimal conditions for the quality training of the future specialist and the formation of professional responsibility.
Control stage of the experiment
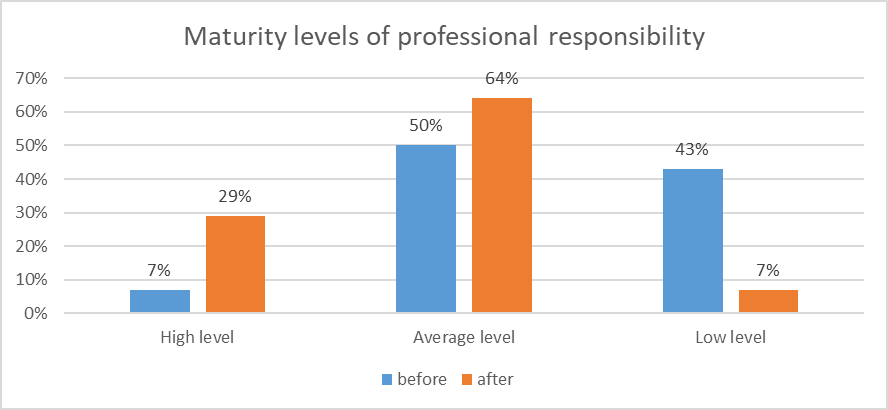
At this stage of the experiment, the authors carried out diagnostic sections to determine the level of professional responsibility of future teachers in the course of the experimental work, using the same methods as at the stating stage of the experiment. A comparison of the results of the stating and control experiments showed that the level of development of professional responsibility increased: the number of students with a high level increased by 22%, with an average level by 14%, and with a low level decreased by 36% (Figure
To determine the level of statistical significance of the studied parameters, we used the Fisher multifunctional criterion. In our research the Fisher criterion is used when comparing the distributions of quantitative traits (Ermolaev, 2003).
We use the basic calculation formula for calculations:
φemp –number which determines levels of significance.
φ1 - value taken from the table corresponding to a larger percentage;
φ2 - value taken from the table corresponding to a smaller percentage;
n1 - number of observations in sample 1;
n2 - number of observations in sample 2.
According to the change in the data of a high level of professional responsibility for 29%, the corresponding value φ1 = 1,137, and for 7% the value φ2 =0,536. n1 = 130, n2 = 130. Substituting the data into formula (1), we get φэмп = 4,844. Critical values for this criterion are:
Analyzing the location of φэмп on the “axis of significance,” we can say that the obtained value φэмп = 4,844 falls into the zone of significance of the studied measurements. In other words, obtained measurements are statistically significant at the significance level of р=0,01.
According to the change in the data of an average level of professional responsibility for 64%, the corresponding value φ1 = 1,855, and for 50% the value φ2 = 1,571. n1 = 130, n2 = 130. Substituting the data into formula (1), we get φэмп = 2,289. Analyzing the location of φэмп on the “axis of significance” relative to critical values for the Fisher criterion, we can say that the obtained value φэмп = 2,289 falls into the zone of significance of the studied measurements. In other words, obtained measurements are statistically significant.
According to the change in the data of an average level of professional responsibility for 43%, the corresponding value φ1 = 1,430, and for 7 % the value φ2 = 0,536. n1 = 130, n2 = 130. Substituting the data into formula (1), we get φэмп = 7,206. Analyzing the location of φэмп on the “axis of significance” relative to critical values for the Fisher criterion, we can say that the obtained value φэмп = 7,206 falls into the zone of significance of the studied measurements. In other words, obtained measurements are statistically significant.
Thus, we can conclude that there are statistically significant changes in the dynamics of levels of professional responsibility of future teachers in the process of experimental work.
In the course of experimental work, we came to the conclusion that the integration of humanitarian and economic academic disciplines, which discuss the professional activities of the teacher, purposefully forms the subject of responsibility. Namely, it contributes to the formation of professional responsibility.
Conclusion
Currently, there is a problem of subject disunity of academic disciplines, which does not allow forming a holistic picture of future teacher’s professional activities. It leads to low-quality training of the future specialist, who doesn’t understand the depth of connections, phenomena and processes within the educational process. It causes difficulty in performing professional duties while teaching.
The future teacher, as a specialist in the humanitarian sphere, needs to master the basics of economic knowledge in order to perform certain activities related to the economic side of the educational process. Therefore, the authors have created a modular program that integrates academic disciplines “Legal and regulatory support for education”, “Theory and methods of education. Psychological and pedagogical workshop" (humanitarian field) and “Economics of education” (economic field). The purpose of the modular program is to deepen students' knowledge in the context of disciplines, form a holistic picture of future professional activities, which contributes to the formation of an important professional quality - professional responsibility. The purpose of each module formulates specific professional responsibilities, for which the teacher will be responsible in future activities. The integrative content of the program is presented in complete independent modules, the level and rate of assimilation of which the student chooses independently according to his/her needs.
A comparison of the results of stating and control experiments demonstrated that the level of professional responsibility development increased after the implementation of the modular program (the number of students with a high level increased by 22%, with an average level by 14%, and with a low level the number decreased by 36%). The conclusion about statistically significant changes in the dynamics of professional responsibility levels of future teachers in the process of experimental work was confirmed using the method of mathematical statistics - Fisher criterion.
In the course of experimental work, we came to the conclusion that the integration of humanitarian and economic academic disciplines, which discuss the professional activities of the teacher, purposefully forms the subject of responsibility. Namely, it contributes to the formation of professional responsibility.
References
- Asmolov, A. G. (2001). Psychology of a person: principles of general psychological analysis. Moscow: Smysl.
- Baranova, A. R., & Valeev, A. A. (2015). Development of creative cognitive activity of university students by means of interdisciplinary connections. Social Sciences, Pakistan, 10(7), 2094-2097.
- Berulava, M. N. (1998). Theoretical foundations of education integration. Moscow: Sovershenstvo.
- Bim-Bad, B. M. (1995) Anthropological foundations of educational theory and practice. Pedagogy, 5, 3-10.
- Cezarino, L. O., Liboni, L. B., Oliveira, M. F., & Caldana, A. C. F. (2016). Soft systems methodology and interdisciplinarity in management education. Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 33(2), 278-288. https://doi.org/10.1002/sres.2383
- Chatelier, S., & Rudolph, S. (2018). Teacher responsibility: Shifting care from student to (professional) self? British Journal of Sociology of Education, 39(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01425692.2017.1291328
- Daniels, L. M., Radil, A. I., & Goegan, L. D. (2017). Combinations of personal responsibility: Differences on pre-service and practicing teachers' efficacy, engagement, classroom goal structures and wellbeing. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00906
- Edling, S., Frelin, A. (2013). Doing good? Interpreting teachers given and felt responsibilities for pupils well-being in an age of measurement. Teachers and Teaching: Theory and Practice, 19(4), 419-432. https://doi.org/10.1080/13540602.2013.770234
- Ericson, E. H. (1974) Childhood and Society. N.Y.
- Ermolaev, O. Yu. (2003). Mathematical statistics for psychologists: Textbook. Moscow: Flinta.
- Galiczkix, E. O. (1999). An integrative approach to the professional development of a teacher at the stage of university preparation. Vestnik VyatGGU – VSUH Bulletin, 2, 34-37.
- Himmataliev, D. O., Fajzullaev, R. X., Safarova, S. O., Madazizova, D. R., & Sobirzhonova, N. R. (2016). Content of interdisciplinary connections in the system of vocational education. Higher School Pedagogy, 2(5), 25-27. Retrieved from https://moluch.ru/th/3/archive/32/1101/
- Jonas, G. (2004). The principle of responsibility. Experience of ethics for technological civilization. Moscow: Ajris-press.
- Kress, T. M., Lake, R. (2017). The strong poetry of place: A co/auto/ethnographic journey of connoisseurship, criticality and learning. Cultural Studies of Science Education, 3(15), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11422-016-9804-y
- Lauermann, F., & Karabenick, S. A. (2013). The meaning and measure of teachers' sense of responsibility for educational outcomes. Teaching and Teacher Education, 30(1), 13-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2012.10.001
- Leont`ev, D. A. (2002). The inner world of a personality. Saint Petersburg: Liter.
- López Castellano, F., García-Quero, F., & García-Carmona, M. (2018). Perspectives on human and social capital theories and the role of education: An approach from mediterranean thought. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 51(1), 51-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131857.2018.1449106
- Makhmutov, M. I. (1989). Production and the problem of integration in vocational education of students. Moscow: APN SSSR.
- Matteucci, M. C., & Helker, K. (2018). Who is responsible for educational outcomes? responsibility ascriptions for educational outcomes in a sample of italian teachers, parents, and students. Learning and Individual Differences, 61, 239-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.12.009
- Misiaszek, G. W. (2017). Educating the global environmental citizen: Understanding ecopedagogy in local and global contexts. New York: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315204345
- Muzdybaev, K. (2010). The psychology of responsibility. Moscow: LIBROKOM.
- Novikova, E. Yu. (2017). Problems of interaction of humanitarian and economic disciplines in the education system. Theory and practice of modern science, 1, 1276-1278. Retrieved from https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=29036899
- Pashchenko, K. A. (2006). Interdisciplinary communication of educational disciplines in the professional-personal technology of training public relations specialist, aimed to formation of corporate values. In International Conference of Intellectual Information Systems. Voronezh, Russia.
- Plugina, N. A. (2009). Interdisciplinary connections in the development of integrative natural science concepts among university students. Bulletin of the Mordovian State University, 2, 126-131. Retrieved from https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=15001705
- Pryadein, V. P. (2012). Definitions of responsibility, effort and will as objects of Pedagogical and Psychological research. Pedagogy. Psychology, 1, 32-45.
- Robinson, C., Phillips, L., & Quennerstedt, A. (2018). Human rights education: Developing a theoretical understanding of teachers’ responsibilities. Educational Review, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2018.1495182
- Rubinshtejn, S. L. (1989). Fundamentals of general psychology (Vol. 1). Moscow: Pedagogika.
- Rychlak, J.F. (1984). The nature and challenge of teleological psychological theory. Annals of theoretical psychology, 2, 115-150.
- Shumer, R., Lam, C., & Laabs, B. (2012). Ensuring good character and civic education: Connecting through service learning. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 32(4), 430-440. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188791.2012.741768
- Strizhov, E. Yu. (2008). Psychological analysis of the personality of fraudster using the concept of Moral-legal reliability. Bulletin of TGU, 4(60), 163-171.
- Xasanov, A. A., & Mamatkarimov, K. Z. (2016). Interdisciplinary communication as a didactic condition for improving the efficiency of the educational process. Young scientist, 20, 738-741. Retrieved from https://moluch.ru/archive/124/33275/
- Yakovlev, I. P. (1980). Integration processes in higher education. Saint Petersburg: LGU.
- Yaspers, K. (1994). Philosophical Faith. Moscow: Respublika.
- Yuczyavichenya, P. (1989). Basics of modular learning. Vilnius: Minvuz LitSSR.
- Zagvyazinskij, V. I. (1984). Intra-subject integration of pedagogical knowledge. Soviet pedagogy, 12, 45-50.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
23 January 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-077-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
78
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-838
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques
Cite this article as:
Kuvaldina, E. A., & Bykova*, S. S. (2020). Interdisciplinary Integration For Developing Professional Responsibility Of The Future University Teacher. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education- IFTE 2019, vol 78. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 477-488). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.01.53
