Abstract
This article is aimed at revealing the essence of the pedagogical potential in the professional self-development of the future teacher in the conditions of educational institutions of various types. The leading method in the study of this problem was the method of questioning conducted among 180 teachers and revealing the content of the pedagogical potential of an educational institution that ensures successful professional self-development of the future teacher. The article reveals that modern pedagogical potential brings the student's professional self-development to a new level. It was clarified that the pedagogical potential of an educational institution is the established traditions, real possibilities and trends in the development of pedagogical education. The factors of pedagogical potential are revealed and justified. It is proved that the student's professional self-development is promoted by the integration of the capacities of educational institutions, immersion into the professional environment in which interaction with practicing teachers is organized. The materials presented in the article demonstrate the formation of the qualities necessary for the successful implementation of conscious professional activities aimed at self-improvement in accordance with professional requirements. The model developed by the authors of the interaction of practicing teachers and students, focused on joint professional self-development in the process of professional activity, contributes to the formation of motivation, the development of initiative, creativity, info-communicativeness of students and is a targeted process of professional self-development.
Keywords: Self-developmentinstitution's potentialself-improvementprofessional development
Introduction
In this problem, the content of the pedagogical potential of an educational institution as a set of opportunities and resources that ensure the successful professional self-development of the future teacher is of considerable interest. The concept of “potential” is interpreted by researchers as a source, opportunity, reserve, means that can be mobilized to achieve certain goals and solve specific tasks of carrying out activities (Golovey & Krulova, 2003; Timonin, 2008). As a qualitative characteristic, the potential reflects the presence of real possibilities associated with the preservation, functioning, and development of the system.
Hence, by potential we understand the totality of opportunities for the implementation of current activities and future development, the strategic balance for a certain point in time, the reserve in the process of training and self-development of students.
Consequently, modern pedagogical potential brings to the new level the student's professional self-development. Let us specify that the pedagogical potential of an educational institution is the established traditions, real possibilities and trends in the development of pedagogical education.
Current researches of A. F. Amirov, A. A. Derkach, E. F Zeer, R. S. Nemov, V. A. Slastenin testify at the actualization of the problem of professional self-development, the determination of pedagogical conditions and factors accompanying this phenomenon.
Under the student's professional self-development, researchers understand: progressive self-change, forming the qualities necessary for successful implementation of professional activity (Nemov, 2007); conscious activity aimed at self-improvement in accordance with professional requirements (Slastenin, 2000); integration of vocational training, defining content and the personal meaning of self-development (Zeer, 2009); a high level of professionalism and professional achievements (Derkach & Sayko, 2010); the intensity of professional development in productive professional socialization (Amirov, Garanina, & Garanin, 2014).
Problem Statement
Based on the analysis of the theory and practice of pedagogical education, a contradiction has been established between the recognition of the fact that the pedagogical potential of the professional self-development of a person is present and the lack of work devoted to the study of the influence of this phenomenon on the process of professional development of a teacher. This contradiction determined the topic of this study, the problem of which is to determine the nature and characteristics of the phenomenon of the pedagogical potential of the professional self-development of personality, and its influence on the professional development of the future teacher in the process of professional training in the conditions of educational institutions of various types.
The actualization of the pedagogical potential of professional self-development of personality in the process of vocational training and professional activity ensures the formation of the professional competence of the future teacher.
Research Questions
To solve this problem it is necessary to solve the following questions to:
1) determine the nature and content of the phenomenon “pedagogical potential of professional self-development of personality”;
2) reveal the determining role of the pedagogical potential of the professional self-development of personality in the process of professional development of the future teacher;
3) develop a model of interaction between practicing specialists (teachers) and students (future teachers), focused on joint professional self-development, actualizing the pedagogical potential.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the research is to reveal the essence of the pedagogical potential of professional self-development of the future teacher in the conditions of educational institutions of various types.
Research Methods
During the research, theoretical methods were used (analysis, synthesis, specification, generalization, analogy method, modeling); diagnostic (questioning, testing, method of tasks and assignments); empirical (study of the work experience of educational organizations, regulatory and educational documentation; pedagogical observation); experimental (stating, forming, control experiments); methods of mathematical statistics and graphical images of the results.
The experimental base of the research was the Artek International Children's Center, the Crimean Engineering and Pedagogical University, the Kursk State University, the Vyatka State University, Kirov city.
The study of the problem was carried out in three stages:
At the first stage, a theoretical analysis of the existing methodological approaches in philosophical, psychological and pedagogical scientific literature, dissertation works on the problem, as well as the theory and methodology of pedagogical research was carried out; the problem, purpose, and research methods were highlighted, a plan of experimental research was worked out;
The second stage is connected with experimental work on the identification of the psychological and pedagogical conditions for the development of the potential of future teachers, with the development and implementation in the system of professional education of a model for developing the potential of students, allowing the implementation of a non-standard approach to pedagogical creativity; at the third stage, the analysis and synthesis of the results of the study were performed, the basic theoretical principles of the study were clarified, conclusions were formulated, the experiment was described and the text of the study was finalized.
Findings
The structure and content of the model
The model of the interaction of practiсing specialists and students focused on joint professional self-development in the process of professional activity can serve as the specifics of the work of the teaching staff of the International Children's Center Artek and educational institutions of the Russian Federation. This is reflected in the management of the educational process, the integration of the educational work of student counselors, the organization of student internship and curatorial counselors working in “Artek”, the formation of a culture of communication for counselors, their preparation for work with different age groups of children, creation of pedagogical conditions for professional development and personal development of all subjects of professional interaction.
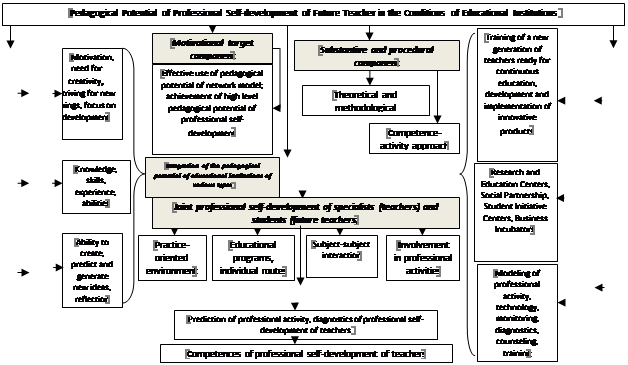
On the basis of the competence-activity approach (Tarkhan, 2008), a structural-functional model of interaction between practicing specialists and students focused on joint professional self-development was developed in the course of professional activity, including motivational-targeted, substantive-procedural, productive-evaluative structural components (Figure
The motivational-target component of the interaction model envisages the process of forming value orientations for the implementation of training of new-generation teachers in terms of the effective use of the pedagogical potential of the network model; increase their motivation, interest in the use of network model resources; awareness of the importance of the professional formation and development of teaching staff through the use of the resources of partner universities; satisfaction with the activity; awareness of the importance of professional growth; ensure readiness for continuous professional and personal self-development.
The substantive-procedural component characterizes the system of knowledge, skills, ways of creative activity, educational modules, designed to ensure the qualitative formation of the professional competencies of counselors in the course of their educational, research, independent activities in the context of the implementation of the network model. The component is aimed at developing counselors' abilities to analyze situations of professional interaction based on the effective use of the pedagogical potential of interaction between partner universities and the International Children’s Centre “Artek”, on mastering the ways to solve professional problems; on the formation of counselors skills to design their professional future, taking into account the inter-regional (interdisciplinary) dominant; on the formation of their skills to use the resources of the network model for professional and personal self-development.
Effectively-evaluative component included the assessment and self-assessment of the effectiveness of the implementation of the network model, ensuring the formation and development of basic skills and competencies of teaching staff of the International Centre “Artek”, contained not only a qualitative assessment of the formation of competencies, but also statistical data processing, which confirms the effectiveness of the work done.
Stages of implementation of the model
First of all, it was necessary to define the essence and content of the notion “pedagogical potential” of educational institutions included in the network model as a set of opportunities and resources ensuring successful professional self-development of a future teacher using the methods of testing, questioning, pedagogical observation and self-observation of teachers, statistical results processing research and the following stages of experimental work.
In order to solve the problems posed during the ascertaining stage of the experiment, all students were divided into two groups: control and experimental with approximately equal number of participants (64 people each).
To assess the effectiveness of the use of the pedagogical potential of the network model of interaction between educational organizations, survey methods were used. The object of attention was the professionally significant knowledge and skills that we considered from the position of adequacy used by students in the process of implementation of educational tasks for inclusion, including in project activities; skills evaluated from the point of view of compliance of the means used to the tasks.
Analysis of the results of the initial student survey allowed us to formulate the following conclusions: the level of external and internal motivation of students to perform the tasks meets the requirements for the organization of project activities (58.8 %), their ability to self-assessment, self-reflection, and self-control of the work done is well developed (47 %);
the level of formation of knowledge and skills of active participation in project activities is also quite high (63.4 %), as indicated by the following facts: the presentation of the results of team work on design does not cause students difficulties;
sufficiently formed level of self-awareness, responsibility for the results of their work (64.2 %).
According to 76 % of the surveyed, the effectiveness of the formation of motivation, competence and creativity of students in the network model is influenced by the resources of various educational organizations that allow them to be used productively in solving educational problems.
When processing the results of the questionnaire proposed by teachers working in networked conditions, it turned out that the majority of respondents consider the work on the use of the pedagogical potential of various educational organizations necessary not only from the point of view of strengthening students' professional knowledge and skills, but also to increase their motivation to study, development of abilities to self-analysis, reflection, self-control. At the same time, about 73 % of teachers say that it is not always possible to effectively organize interdisciplinary classes (webinars) due to the lack of free time, didactic and methodological materials, special literature and electronic teaching aids; 42 % of respondents, as it turned out, have the most general ideas about the organization of work on the use of the pedagogical potential of the network interaction model for solving educational problems on an interdisciplinary basis.
In the course of the ascertaining experiment, educational and methodological complexes developed by teachers were analyzed; network educational modules developed on the basis of integration, evaluation tools for academic disciplines and participation in students' project activities were studied. As a result, it was concluded that only 69 % of the analyzed educational and methodological complexes contain tasks for the organization of training sessions, taking into account the interdisciplinary dominant. Many teachers (47 %) do not include students in the joint design of business, role-playing games for the formation of professional experience based on interdisciplinary.
In the course of analyzing the results of the ascertaining experiment, it was confirmed that it was necessary to use a specially developed pedagogical model and its technological support. The results of the ideas about the content of the pedagogical potential of the educational institution are shown in Figure
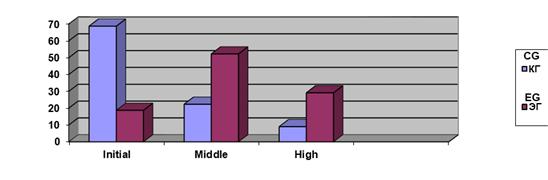
In total, the study covered 128 teachers, 67 teachers became direct participants in the experiment. An analysis of the results of the diagnostic examination led to the conclusion that the majority of teachers have an initial (68.7 %) and medium (22.3 %) level of understanding of the content of the pedagogical potential of an educational institution as a set of opportunities and resources that ensure successful professional self-development of the future teacher.
The logic of the formative stage of the experiment was to create for one of the groups of students an experimental situation in which, based on the relevant pedagogical conditions, it is possible to trace the severity and sustainability of the results of the implementation of the proposed pedagogical model. The goal of the formative experiment was to determine and verify the pedagogical conditions and the effectiveness of the implementation technology of the pedagogical model we developed. We regard efficiency as the degree of conformity of the results obtained and the expected results, as well as the ratio of the results obtained and the amount of money spent.

During the experimental work, the natural conditions of the educational process were preserved under the conditions of the implementation of the network model. At this stage, an experimental program was developed that was tested in the course of the formative experiment and had a phased nature, involving teachers participating in the functioning of the network model in interaction with other teachers and methodological service to create and implement a step-by-step algorithm for pedagogical interaction. Each teacher chose a meaningful educational route of a specific orientation (adaptive type, developing and creative orientation) depending on the stage of the model implementation. The potential of the integration of theory and practice, personalized in the pedagogical resources of teachers, successfully combining scientific, teaching and work experience, implemented in the practice bases, was used.
At the first stage (conceptualization), the goals and tasks of teachers and students were defined when developing a conceptual concept of using the pedagogical potential of network interaction based on a dialogue. This work made it possible to verify the legitimacy of involving the students themselves in the development of an innovative solution to this problem. In addition, this was facilitated by a developing, innovative, and technologically rich environment of research and educational centers, laboratories of educational institutions included in the network model.
At the second stage (modeling), the idea of introducing into the educational process the pedagogical conditions and the technology for implementing the constructed pedagogical model was developed. An important feature of pedagogical modeling was that it was aimed at the self-development of all participants in the educational process in the course of working together through a sustainable partnership (Abakumova, Godunov, & Belova, 2017).
During the third stage (designing), the following tools were developed: methods, tools, and forms of organization of training aimed at the successful implementation of the initial plan; network educational modules were formed, and a complex of pedagogical technologies, forms and methods was developed that ensure the development of students' motivation, competence and creativity.
The fourth stage (parameterization) was devoted to assessing the level of formation of students 'skills to enter into discussion, create monologues, conduct a dialogue on professionally important issues, and create a fund of assessment tools to determine the level of formation of students' skills of self-assessment.
At the fifth stage (implementation), an organizational technology was introduced into the educational process, tools and teaching methods were tested, teachers worked individually with students, intermediate and final controls were implemented. This stage included the organizational-activity game “The components of the success of the professional activity of the future teacher”. The participants of the game, taking into account the results of diagnostics of the level of formation of motivation, competence and creativity, developed generalized modules, determined the step-by-step logic of their implementation. The scheme of the generalized module was aimed at the successful development of professional skills necessary for their activities; achievement of goals through communication.
And finally, the sixth stage (reflection) was aimed at self-assessment of the effectiveness of the implementation of organizational technology, ensuring the formation and development of students' motivation, competence and creativity. The stage included not only a qualitative assessment and statistical data processing, which confirms the effectiveness of the work done.
The results of the formative experiment were compared with the data obtained during the study of the initial level of formation of motivation, competence and creativity in the control and experimental groups. During the first stage of the formative experiment, the author's educational materials were tested, including a selection of video materials, network educational modules, which were created by teachers together with students in group work.
The data obtained as a result of the experimental work, allow us to conclude that the motivation, competence and creative components of the experimental group have a higher level of formation, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed pedagogical model and its technological support.
Despite the fact that students in the control group also showed an increase in the level of development of motivation, competence and creativity after training in the traditional methodology, the positive dynamics of development in the experimental group is significantly higher. For example, the level of development of competence among students in the control group increased by 6 %, and among students of the experimental group – by 12.4 %. The quantitative and qualitative interpretation of the results of the control phase of a pedagogical experiment in comparison with the indicators of the ascertaining experiment suggests positive dynamics in the development of motivation, competence and creativity for all selected parameters, which confirms the effectiveness of the developed pedagogical model.
The quantitative and qualitative analysis of the results of the formative experiment allowed the following conclusion to be drawn: the pedagogical model of using the pedagogical potential of network interaction will be effective provided that the complex pedagogical conditions that ensure a positive result in this process are observed.
The data obtained allow us to confirm the hypothesis put forward by the research, to prove the effectiveness of the use of the designed pedagogical model and the objectivity of the pedagogical conditions for its implementation.
In the course of experimental work, diagnostic sections were carried out using the same methods as at the ascertaining stage of the experiment. The control slice data showed changes in comparison with the measurements of the ascertaining stage for all criteria, however, these changes were significant only in the experimental group, where there was a shift in the number of teachers with an average (52.1 %) and high (30.2 %) levels of interaction with students in joint professional self-development. In the control group, no significant changes occurred (Figure
Conclusion
The study of psychological and pedagogical literature allows us to state the absence of special studies devoted to the problem of the content of the pedagogical potential of an educational institution in the context of real practical pedagogical activity. At the same time, it should be noted that researchers interpret the concept of “potential” as a source, opportunity, reserve, means that can be mobilized to achieve certain goals and solve specific tasks of carrying out activities (Golovey & Krulova, 2003; Timonin, 2008) . As a qualitative characteristic, “potential” reflects the existence of real opportunities associated with the design, preservation, operation and development of the system (Novikov & Novikov, 2004).
It is established that the pedagogical potential of an educational institution, for the student's professional self-development, is manifested in the following:
a set of established traditions, real opportunities and trends in the development of teacher education;
the integration of theory and practice, personalized in the pedagogical resources of teachers, successfully combining scientific, teaching and work experience, implemented in the practice bases;
developing, innovative and technologically rich environment of scientific and educational centers, laboratories of an educational institution;
active implementation of information educational technologies as a source of the latest knowledge in the field of pedagogy for professionally mobile, in-demand, qualified specialist;
variability and the possibility of continuous intensive professional and personal growth of a teacher throughout his career.
The student's professional self-development will be carried out successfully, with the organization of the integration of the capacities of educational institutions, immersion in the professional environment in which interaction with practicing teachers is organized.
References
- Abakumova, I. V., Godunov, M. V., & Belova, E. V. (2017). The development of ideas about the personality-forming strategies of the individual in modern society. Humanities, socio-economic and social sciences, 5, 3-16.
- Amirov, A. F., Garanina, R. M., & Garanin, A. A. (2014). Activation of the personal-development potential of independent work of university students as a condition for the development of their subjective position. Samara: Etching.
- Derkach, A. A., & Sayko, E. V. (2010). Self-realization – the basis of acmeological development. Moscow: MPSI.
- Golovey, L. A., & Krulova, A. A. (2003). The intellectual potential of the subject of the activity. Intellectual potential of a person: problems of development. SPGU Publishing St. Petersburg State University.
- Nemov, R. S. (2007). Psychology. In 3 books. Educational Psychology. Book 2. Moscow: Vlados.
- Novikov, A. M., & Novikov, D. A. (2004). Educational project (methodology of educational activity). Moscow: Egves.
- Slastenin, V. A. (2000). Axiological foundations of general and vocational education. Lipetsk: Publishing house of Lipetsk University.
- Tarkhan, L. Z. (2008). Didactic competence of an engineer-teacher: theoretical and methodological aspects: monograph. Simferopol: KRP "Krymuchpedgiz Publishing House".
- Timonin, A. I. (2008). Socio-pedagogical support of the professional development of students of humanitarian faculties of the university. Kostroma.
- Zeer, E. F. (2009). Psychology of professional development. Moscow: Academy.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
23 January 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-077-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
78
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-838
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques
Cite this article as:
Saveleva-Rat, E. A., & Tarkhan*, L. Z. (2020). Pedagogical Potential In Future Teacher`s Professional Self-Development. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education- IFTE 2019, vol 78. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 205-214). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.01.26
