Abstract
The research is aimed to reveal opportunities to optimize processes of formation and development of socially-cultural competence of students, while using socially-cultural environment of St. Petersburg. The study analyzed the tourism resource potential of St. Petersburg for the youth sightseeing and educational tourism development. Considered using sightseeing and educational activities as a possibility for the general students cultural competencies development, provided by state standards, technology features of designing student audience excursion programs with the direct students participation in the excursion routes development have been determined. The authors found out that St. Petersburg socio-cultural environment, as well as student audience experience on drawing up their own excursion routes, that organize youth leisure, makes the process of common cultural competences formation more effective. Authors noted a very well-developed excursion activity in the Northern capital researching St. Petersburg excursions variety. Museums, theaters, palaces and historical architectural structures created by great architects and sculptors. All this has a beneficial effect on the new excursion routes and various types of excursions creation. Active cooperation between the university and the different areas of the urban socio-cultural environment, using higher education resources and city potential with current training requirements may be used to work with the students, since the formation of student modern thinking requires strengthening the personal developmental approach of student as an educational and professional activities subject.
Keywords: Professional educationgeneral cultural competenceseducational tourismcamping designexcursion activitytourist-resource potential
Introduction
The modern model of higher education involves such organization, which is, above all, would ensure successful adaptation to the existing community and developing civilization, as well as high quality of universal preparation and a deep specialization in the future professional activity field for readiness for creative exploration and the development of advanced and modern technology at this stage of society development. This, of course, applies equally to both the direct learning processes and the students development outside of school time.
One of main tasks that a student must decide during his stay at a higher education organization is the task of his self-development and reflexive culture formation: attaining self- analyze and self-esteem ability, learn and acquire new necessary knowledge based on self-control, understand and properly use self-development, self-education, self- upbringing methods and mechanisms.
The study required a wide variety of sources in the following areas: philosophy and educational theory (Shipunova & Berezovskaya, 2018); provisions reflecting the new educational paradigm problems: fundamentalization and humanization, informatization, greening, educational availability and continuity, its advanced and innovative character (Nikiforova, Bylieva, Lobatyuk, & Petrova, 2017; Zeleneva, Matveevskaya, & Ermolina, 2017); activity approach to learning (Gashkova, Berezovskaya, & Shipunova, 2018); competence-based approach (Trostinskaya, Pozdeeva, Evseeva, & Tanova, 2018; Volkova, Golubev, Mitenkova, & Evseev 2018); approaches to the development of the regional education system.
The study was also based on innovative ideas of education using electronic communication technologies (Bylieva, Lobatyuk, & Nam, in press), including for the development of tourism and the effective implementation of tourism activities (Matveevskaya, & Pogodin, 2018; Vasileva, 2018).
Problem Statement
One of the central tasks of the university's educational process is to create conditions for self-development and the formation of a reflexive culture in a student: mastering the ability to self-analyze and self-appraise, learn and acquire new necessary knowledge based on self-control, understand and properly use the methods and mechanisms of self-development, self-education, self-education.
Research Questions
The tourism resource potential of St. Petersburg for the youth sightseeing and educational tourism development.
Excursion and educational activities as a possibility for the general students cultural competencies development, provided by state standards.
Technology features of designing student audience excursion programs with the direct students participation in the excursion routes development.
Purpose of the Study
Educational tourism excursion is activity which can be seen as a form of educational process organization, the kind of learning activities and learning technology.
Research Methods
The methodological basis of the study was a system analysis and synthesis of philosophical, psychological, pedagogical, didactic, methodical literature and Internet materials on the research problem, theoretical and pedagogical analysis (retrospective, systemic, inductive-deductive, comparative-comparative) universities excursion-educational activities (analysis curricula and plans, educational complexes for individual disciplines), a summary of pedagogical experience, survey methods, interviews, questionnaires, visualization, peer review.
Findings
St. Petersburg tourism and resource potential for youth sightseeing and educational tourism development
St. Petersburg has an impressive historical and cultural heritage. Cultural tourism is a priority type in the city in its two components - heritage tours and event tours. The historical and cultural heritage of St. Petersburg invariably attracts a significant number of guests to the city. Tourist interest forms an individual's motivation for consuming a tourist product and making a tourist trip. It determines peoples choice of particular vacation place.
Tourist interest is a prospect of obtaining objective information by the tourist, positive emotions and/or the potential opportunity to meet planned tourist needs for a particular tourist service, goods and products based on a specific set of tourist resources, acting as objects of tourist interest (Weil, 2006). The city, with its sights, historical and socio-cultural objects is the subject of tourist interest. After the publication in 1993 of the book D. Heider, F. Kotler and I. Reyna "Marketing of territories" established the concept that in today's world, citizens are consumers and territory (city, region and country) - the goods (New Holland, n. d.).
Consuming tourist product, is actually a tourist meeting with city officials subject to its tourist interest, tourist consumes the city itself, that is, its socio-cultural environment. Travel helps to get maximum visuals formed by the different socio-cultural environments.
It happens in the shortest amount of time during the tours, which becomes a certain model of environmental perception in modern society. Modern tourists are willing to penetrate into a different socio-cultural city environment and its semantic system (State Museum of History and Religion, n. d.).
In 2013, the Russian-German branding agency DammundLandl launched a large-scale marketing research «Petersburg in the 21st Century. In search of identity» (Travel Agency Arina, n. d.).
The project aims to find those unique qualities that distinguish the city and form its unique and recognizable image.
Based on the results of the study, it is possible to form a recognizable brand of the city and position it on the tourist market as an attractive destination.
Svetlana Landl, the founder of DammundLandl, who developed the brand of the Mikhailovsky Theater and «Night of Museums”, expressed her opinion about the image that exists in the Northern capital today: «St. Petersburg obviously needs a brand».
City of St. Petersburg identity evolved over time, in the historical, geographical, social and cultural contexts. From the point of view of complexity and richness of meanings, Petersburg is a special city with many meanings, often contradictory.
This makes it complicated for branding. The search for urban identity is useful not only for attracting tourists, but also for the residents themselves. Literacy campaign can reduce the flow of emigrating talented young people (St. Petersburg City Guide, n. d.).
The brand is directly related to the associations that people have when the city is mentioned. Thoughts and associations that are associated with the city name, have great financial, political and social value.
In order to find out which associations people link to St. Petersburg, the research team S. Landl survey was conducted among local residents and foreign experts.
The survey results were as follows: the prevailing view was that «modern culture is suppressed by city image of high culture and history. This static image does not allow to position St. Petersburg as a modern city, opened to creativity» (Kopylova, 2013, Research, para. 1).
Accordingly, one of the significant elements of a possible brand Northern capital should be a combination of innovation and classic. The innovation theme in culture is especially important for St. Petersburg, which unofficially is the status of "cultural capital" of Russia.
The city has a rich cultural heritage. St. Petersburg culture is a unique phenomenon. Authenticity of most cultural heritage objects preserved in St. Petersburg.
There is a systematic approach to the museum collections formation that have been created over the centuries, significant contribution to the St. Petersburg artistic life makes the activities of many institutions within ballet, drama theater, opera and performing arts field (Gdalin, Pogodina, & Shulga, 2013).
St. Petersburg holds an unofficial title of «Russian tourism capital»: the city ranked among the «25 best tourist destinations – Europe» popular European destinations according to the well-known portal Trip Advisor in 2019 (Trip Advisor, n. d.).
World importance cultural values, which are the national treasure of Russian people are concentrated in St. Petersburg. Suffice it to say that in the list of World Natural and Historical and Cultural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO included the entire central part of St. Petersburg and the palace and park necklace city suburbs.
One of the categories of tourism in St. Petersburg is educational sightseeing tourism. It is an integral part of the educational and educational process in educational organizations, both middle and top level. Tourism is an effective tool that mobilizes students' cognitive activity, attaches them to independent creative activity, develops the initiative, skills and self-education.
According to the law of the Russian Federation «About bases of tourist activity in the Russian Federation» dated 24.11.1996 №132-FZ (as amended. From 03.05.2012 number 47-FZ) internal tourism and social types are treated as a priority. Youth, student tourism is focused on the socially unprotected population segment, therefore, by definition, it is a social tourism type.
Educational tourism excursion is a trip (hiking), committed to fulfill tasks defined by educational organization curriculum. This type of activity can be seen as a form of educational process organization, the kind of learning activities and learning technology (Pogodina, & Tarakanova, 2014).
Innovative activity in a field of tourism and sightseeing activities is developing in different directions. New tourist products are being developed and introduced, first of all, excursions of various forms and themes, such as excursions to ostrich farms or innovative enterprises.
Developers constantly conduct market research on a new socio-cultural level, arranging the program "approach to the client", taking into account the individual demand of the potential client.
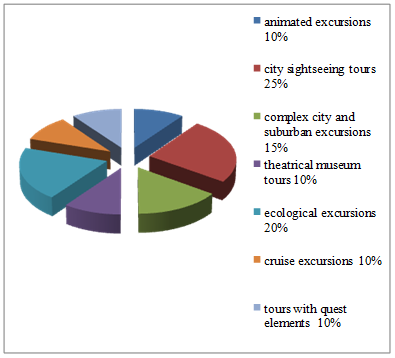
With the help of a survey in 2018, studies were conducted, aimed at learning the preferences of citizens in the excursion activity field. More than 200 people of different ages, gender, wealth and fields of activity were surveyed (Figure
Survey data showed that traditional excursions are more popular than new interactive routes. For tourists to receive unforgettable impressions, excursions developers use a variety of techniques. Techniques, meaning excursion programs that use computer equipment and animation, as well as technologies that provide the effect of presence.
Formation possibility of students common cultural competence in extracurricular activities
A tour is primarily an educational activity in the acquisition of new knowledge and is a type of travel. As you know, the journey is one of the most exciting and interesting acts performed by man.
Thus, an excursion is a route determined by the purpose, as it proceeds, objects located in the natural environment are visited and considered, presented in real and immediate form. This is one of the unique opportunities to see everything as it is.
Indeed, in most cases, training, in particular school, does not imply a direct demonstration of the objects being studied. In order to acquire certain knowledge, all students have perceive it trough a story. This greatly reduces possibilities of perception. During the excursion trip, you can clearly demonstrate the object and get the necessary information empirically.
Indeed, as the development of excursion activity gradually added thematic tours, in particular of course - scientific orientation.
Currently ecological excursions are particularly relevant, especially among students, because in today's world there are many urgent environmental problems of a global scale, that younger generation has to fight. Ecological tours allow to not only learn about various environmental issues in more detail, but also to learn how to solve them, and teach respect for the nature.
The knowledge that received by sightseers must, first of all, reflect a certain holistic picture of the world around us, a place for certain objects. In terms of sightseeing techniques chosen sights are impractical to show to the tourists in isolation from the environment. In addition, the active perception of such objects leads to not only their comprehension, but also to personal, individual assessment.
All this leads us to the fact that the modern excursion technique is a set of instruments aimed at active development of new knowledges, implemented in the process of practical, direct perception of the objects of our world.
Excursion methodic is one of the main instruments in sightseeing, it helps to share information and opinions, broaden horizons and solves some upbringing and educational issues. The excursion methodic is normally divided in three parts:
-methodic of choosing and developing new concepts for excursions.
-methodic of preparation for excursions.
-methodic of giving an excursion.
Culture and service are constantly developing, which affects the demand for excursions. New requirements appear due to society development, new technologies, fashion and services.
As a result, excursion topics change as well as forms of its organization. One of the newest forms of excursions are quests.
Looking at quest-excursions as a new way to experience sightseeing, we can point out that it is a very interesting and fast-developing way to learn about culture. Adventurous excursion would be interesting for both adults and kids, St. Petersburg locals and visitors. The main difference of this experience is its interactivity. Most of the information regarding chosen topic is not provided by a tour guide, but collected by participants themselves. It boosts motivation due to competitive game form, making exciting, and with beautiful city landscapes gives an opportunity to make the excursion an unforgettable emotional experience.
Features of organization and holding of excursion as an educational technology
Nowadays Russian education is experiencing active reformation wave. In accordance with the State educational standard, students master a number of necessary competences that correspond to the disciplines studied during their course.
Competence approach determines a target base of students training at universities. The educational standards also define a general cultural and professional competencies, that a future graduate should master. In this regard, extracurricular activities organized in the form of educational tourism would be useful.
One of important excursion pedagogy concepts is a concept of educational excursion. This term should denote educational trips lasting no more than a day, carried out in order to form universal, general professional and specialized student competencies. The functional essence excursion pedagogy is organization form of educational process carried out outside the main educational institution.
Important elements of the educational tours are both a foreword and conclusion, that act as independent parts of the tour. Tour start is largely determined by the character and excursion training. It is desirable that the dialogue between the organizer and the excursionists takes place at this stage. During the introductory interview, it is important to strengthen the cognitive interest of the participants. Mastering the technique of the right mix of display and the story, can achieve high performance tours.
To assimilate the excursion material by the participants (and later to discuss it), it is of great importance to take notes during the excursions, the objects observed, as well as their personal impressions. Such registration of observations is possible, however, requires to use special teaching methods. In this regard, it is highly desirable for the student to create a “guide” for each particular excursion.
For example, it can be a small booklet, that can be a start of preparation for future tourists for an excursion, or the “Excursion diary” for a particular excursion route. It is important that students start working with “diaries” at the pre-touring stage, getting acquainted with the course of the excursion and the main tasks that they will have to perform. Directly on the route, the excursionists only point out what they have observed and what results they have achieved.
Another important task in the preparation of a study tour is to select the most interesting visually and most informative objects from a variety. Thoughtful, methodically reasonable selection of excursion sites provide a visual perception of the base materials and the most profound revelation of the tour theme. While selecting objects to display, it is important to consider educational value, artistic value, safety, effects etc.
In the course of educational work with students, excursion work is important. Moreover, at the beginning of training, students take part as passive sightseers. But their activity changes with each trip.
It is desirable to build a sightseeing work in such way that at the end students could not only hold their own tour cycle, but also design their own tour, for example, for foreign conference participants. To do this, they are given an instruction in accordance with what they present their own version of the methodical development of their own excursion to their tutor.
In the course of methodical preparation for a study tour, it is necessary to consider how to organize an excursion in order to keep the participants in a good mood, that will contribute to the effectiveness of the material studied. It is important to remember that the novelty of visual material is of interest, emotions that support the cognitive activity of tourists.
Conclusion
Student years coincide with the first period of maturity and are characterized by reaching the top in mental qualities development, functions, rights and personal properties emergence.
Formation of student modern thinking requires the strengthening of personal-developmental approach, the learning growth as educational and professional activities subject.
Education performs two main functions: on the one hand, it responds to the state and society social request, and on the other hand, it corresponds to the goals, interests, and inclinations of the individual.
Only a harmonious combination of these features can provide education optimization. We can say that over the years of training in high school young person must receive two degrees: professional and personal.
Humanization, modernization of higher professional education is closely connected with the development of the future specialist's personality, his cognitive, value-motivational and volitional sphere, with mastering the personality not just with new knowledge, but also with ways of acquiring and creating new information, ensuring conditions for self-knowledge, self-development , self-organization and self-realization.
Attracting young students to participate in cultural and educational activities of educational and self-development, and guided tours by students contribute to cognitive activity development, high level of culture formation, education and personal qualities of improving the professional competence of the future graduates.
Technology of sightseeing and educational activities organization for students ensures success of such activities as: information, advertising, management, communication and creative, socio-psychological, analytical, reference, cultural and educational, organizational, sociological, scientific and research.
References
- Bylieva, D. S., Lobatyuk, V. V., & Nam, T. A. (in press). Academic Dishonesty in e-Learning System. In Soliman K.S. (ed.), Proceedings 33th International Business Information Management Association Conference. Granada, Spain: IBIMA.
- Gashkova, E. M., Berezovskaya, I. P., & Shipunova, O. D. (2018). Models of self-identification in digital communication environments. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 35, 374-382.
- Gdalin, D. A, Pogodina, V. L., & Shulga, I. I. (2013). Designing tourist-excursion educational programs. Novosibirsk: NSPU
- Kopylova, D. (2013, January 28). Pryamaya rech': Svetlana Landl' — o tom, pochemu u Peterburga net Brenda [Direct speech: Svetlana Landl - why St. Petersburg has no brand]. The Village. [in Rus]. Retrieved from https://www.the-village.ru/village/city/city/119412-pryamaya-rech-svetlana-landl-o-brendirovanii-sankt-peterburga
- Matveevskaya, A., & Pogodin, S. (2018). Professional Orientation of The Future Specialist Through The Organization Of Industrial Tourism. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 51, 1055-1062. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.02.114
- New Holland. Cultural urbanization (n. d.). Retrieved from https://www.newhollandsp.ru
- Nikiforova, N., Bylieva, D., Lobatyuk, V., & Voronova, L. (2017). The problem of “sign field” creation for the Russian national technology initiative. 4th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference on Social Sciences and Arts SGEM2017. Book6, Vol.1, 117 – 127.
- Pogodina, V.L., & Tarakanova, T. S. (2014). Metodika ispol'zovaniya kvest-tekhnologiy v organizatsii gorodskikh ekskursiy shkol'nikov. [The method of using quest technologies in the organization of urban excursions of students]. In V.P. Solomin, V.V. Rumyantsev, D.A. Subetto, & N.V. Lovelius. (Eds.), Geography: traditions and innovations in science and education. LXVII Herzen readings (pp. 345-349). St. Petersburg: Russian State Pedagogical University. A.I. Herzen. [in Rus].
- Shipunova, O. D., & Berezovskaya I. P. (2018). Formation of The Specialist's Intellectual Culture In The Network Society. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 51, 447-455. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.02.48
- St. Petersburg City Guide. (n. d.). Retrieved from https://www. hellopiter.ru
- State Museum of History and Religion. (n. d.). Retrieved from https://www.gmir.ru
- Travel Agency Arina. (n. d.). Retrieved from https://www. arina-tour.ru
- Trip Advisor. (n. d.). Retrieved from https://www. tripadvisor.ru
- Trostinskaya, I. R., Pozdeeva, E. G., Evseeva, L. I., & Tanova, A. G. (2018). The Problem Of Developing Students’ Analytical Competence. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 51, 1439-1446. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.02.153
- Vasileva, O. O. (2018). Network Environment of Business Activity. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 51, 1046-1054.
- Volkova, L. M., Golubev, A. A., Mitenkova, L. V., & Evseev, V. V. (2018). Physical education in civil aviation experts communicative competence formation. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 35, 1396-1403. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.02.163
- Weil, P. (2006). Genius of the place. Moscow: Kolibri
- Zeleneva, I. V., Matveevskaya, A. S., & Ermolina, M. A. (2017). Dialogue of Civilizations - New Model Of World Politics. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 35, 829-836.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
02 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-072-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
73
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-986
Subjects
Communication, education, educational equipment, educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), Study skills, learning skills, ICT
Cite this article as:
Tarakanova, T., Vasileva, O., Pogodina, V., & Evseev, V. (2019). Technology Of Sightseeing And Educational Activities Organization For Students. In N. I. Almazova, A. V. Rubtsova, & D. S. Bylieva (Eds.), Professional Сulture of the Specialist of the Future, vol 73. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 917-925). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.96
