Abstract
The article discusses the problem of increasing the influence of physical culture and sports on political, socio-economic and cultural processes. The scientific novelty of the study lies in defining the principles of health-saving education and health-saving environment; in revealing and describing theoretical and methodological grounds underlining the necessity to prepare bachelors within the line with health-saving policy of higher education of the Republic of Iraq. It is substantiated that the modern society more and more consciously concludes that it is necessary to form a new worldview of a self-developing personality in the context of creating a sustainable motivation for health protection. The attention of the researchers was focused on the fact that today HE institutions of the Republic Iraq use approaches based on the principles of ensuring the quality of vocational education in educational activities, which corresponds to the current development trends going in the national educational system in the state and conforms with the Bologna process recommendations. The experiment was complemented by the expert assessments aimed at studying theoretical and methodological approaches targeting the technologies responsible for physical culture acquisition among the bachelors in Iraqi universities. The generalized results of the research are presented, which testify to the effectiveness of the developed model, which showed up itself in a positive dynamics for all selected structural components. However, it is noted that the specificity of the physical development of the bachelors requires such technologies to be used that are capable to purposefully influence different aspects of personality development.
Keywords: Healthy lifestylehealth-saving environmentmodeltechnology
Introduction
The most important theoretical prerequisite for the recovery of the nation by means of physical culture is the binary nature of physical culture of an individual. Physical culture is introduced in HE institutions as an academic discipline and the most important basic component coming into the general construction of the young people culture. Its essence lies in the consistency of the parties and components of the physical culture of an individual. It contributes to harmonization of physical and spiritual unity; ensure the formation of such important human values as health, physical and mental well-being, physical development of the youth.
Understanding the importance given to the physical development a bachelor-student personality as a value can be an effective factor in developing various types of physical culture, progressive tendencies in the development of the state, the needs to rerate the values of sports.
Based on understanding the specificity of physical culture, health protection technologies, we suggest some pedagogical methods, techniques, approaches directed to students’ health protection and support, inter alia, to form the value-based attitude to own health.
Of particular relevance is the process of forming a healthy lifestyle among bachelor degree students of the Republic of Iraq, including the implementation of appropriate techniques, methods, and approaches, a set of tools, both organizational and methodological.
Within the framework of the problem being studied, a healthy lifestyle is step-by-step and manageable process dealing with giving information to the bachelor students about the components of the healthy lifestyle, negative risk factors that prevent from being in the healthy lifestyle, and the importance of physical culture and sports in development, preservation and strengthening the health, involvement into active physical culture and sports events, characterized by development of motivational-need and cognition spheres of personality, implemented with a view of adaptive capacity and health state of an individual.
This is largely due to the fact that the health system includes and, accordingly, activates (apart physical activities and training), some potential components: the power supply system, psycho-regulation, rehabilitation factors affecting the body (massage, hardening, etc.), diagnosis methods, control and self-control.
The problem is becoming shaper in the context of the need to construct a health-life style model for undergraduate students of the Republic Iraq in line with eve-changing labour market.
The modern development of the economy requires a new approach to the challenge dealing with the professional culture of an Iraqi specialist, in whose competence zone there are included the concepts of an employee’s physical health, allowing him to adapt well to working and living conditions.
The overall increase in body’s functional capabilities, strengthening of the health, the resistance to adverse impacts achieved through the use of physical culture factors has the positive effect on any kind of professional activity and on its subsequent effects on a performer.
At the same time, frequent diseases, the pathological psycho-emotional state of a person reduce the level of work efficiency, and therefore one of the most important pedagogical tasks, has not yet been solved at a university level, is to provide the future bachelor with a motivated approach to the basics of a healthy lifestyle, physical culture and sport.
Theoretical analysis within the topic we are discussing has shown that among the reasons for irresponsible attitude that the students have to physical culture and, consequently, to own health can be pointed out the lack of anatomy knowledge, low level of physical skills and healthy life style, the absence of systematic targeted education within the physical culture as an academic subject. Therefore, the students have poor awareness in habits supporting the healthy life style that can actively lead to health loss.
It promotes the status quo and the abandonment of the centuries-old traditions of the East in maintaining a healthy life style towards development own health and health of their families.
Problem Statement
Within the problem under study, as fundamental we have taken into account both the works devoted in general to methodologies describing approaches towards healthy lifestyle, to some pedagogical technologies used in the educational space to shape physical culture among students, and the works that consider certain aspects of the physical culture as part innovative technologies implementation. Thus, there are research studies with the focus to searching for new pedagogical technologies in higher education, The interesting works are: Adolf (2005), Adolf and Iliina (2007), Al-Battauiy (2013, 2015), etc. In the studies of Davidenko (2008) and others. In their research Davidenko (2008) justify that the health-saving function in the modern system of vocational education is very important. This involves students’ participation in so-called marathon targeted at strengthening and preserving their health with the help of a sustainable motivation towards the healthy lifestyle.
The challenge of modernization of environmental and physical education at the university in the context of anthropoecological and acmeological approaches is studied in the research by Artemyev and Shutov (2004), Glazacheva (2011), etc. Some publications of Afanasyev (2011) others are devoted to the issues relating a) searching for ways to improve the mechanisms to transfer physical culture knowledge, ways to preserve and promote health through a special education itself, b) management of physical activity of students with the aim at ncreasing their motivation to physical education and a healthy lifestyle. Iraqi scientists contributed to the development of health keeping problems in the Arab world (Abdelmunem, 2004; Al-Khatib, 2001, 2003; Alatas, 2007). One of the most studied questions is the history of physical culture development in Iraq, as well as the introduction of the world experience to the Olympic movement. We can also note the thesis that studies the problems connected with organization and mechanisms of physical culture management in Palestine. The socio-cultural and pedagogical aspects of physical education and sports in Iraqi universities are also considered.
With all the great theoretical and practical significance of the research it should be noted that in the scientific literature of Iraq there are actually no data that reveal the contribution of physical culture to the dynamics of students' physical and psychosomatic health, to formation of motivational and axiological aspect of personal physical culture, and conscious acceptance of it by students. There is no special comprehensive study towards the problem, targeted at systemic training of bachelors on the basis of health-saving technologies, and therefore, there are some contradictions:
- between the adoption by the Higher School of Iraq of the subject-developmental ideas and values of the Bologna process and the insufficient development in the pedagogical science of theoretical and methodological ideas relating to the education and development of bachelor students within the health-saving technologies.
- between the need to implement the state order encompassing the health-saving education in universities in Iraq, taking into account the specific conditions of internal development and the external situation of the country and the insufficient development of technologies helping to support a healthy lifestyle for bachelor students in the educational process of HE institutions.
Research Questions
The subject of the research is a set of educational conditions, means and methods helping to organize all means to support a healthy lifestyle for the bachelor students in the educational settings of HE of the Republic of Iraq.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the research is theoretical substantiation and experimental application of the technology supporting a healthy lifestyle for the bachelor students in the educational settings of HE of the Republic of Iraq.
Research Methods
In organizing and conducting the study, the following methods were used: general theoretical methods of scientific knowledge (analysis, synthesis, comparison, generalization, systematization, grouping-clustering, and others); general pedagogical methods (literature review, analysis on the study results by phases); prognostic methods (training modeling programs designing); empirical methods
Findings
At the diagnostic stage of the experiment, the initial critical analysis conducted towards the accumulated empirical experience was of great importance, which predetermined understanding some aspects of the field that we are researching (Afanasyev, 2008). Thus, in the context of health preservation issue in the educational settings of a university, the experimental data obtained by Glazacheva (2011) were very important for our study. The researcher studied the phenomenon of burnout syndrome among students, which is considered as a process of gradual loss of emotional, cognitive and physical energy, expressed in the symptoms of emotional, mental and physical exhaustion.
According to our study, before the exam 42% of the students complained of increased heart rate, 36% reported about sleep disturbances, 23% had impaired normal skeletal muscle tone (trembling, restricted movement), 11% of the respondents reported about unpleasant feelings in the chest, and 6% had headaches. In this case, the answers to questions about the knowledge, and most importantly, the use of methods targeted at emotional self-regulation, relaxation before an exam were distributed as follows (Figure
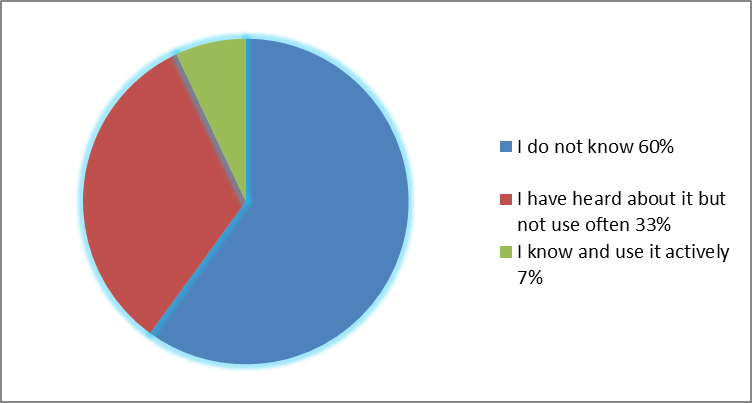
In addition, we have checked the degree of comprehension and interpretation by the students towards the concept of "health" as a prerequisite for acknowledging of high significance in the individual hierarchy of values and identifying the degree of motivation development in terms of preserving and strengthening health. The content analysis procedure was used to interpret the answers. When determining the concept “health”, obtained with the experimental group, as the semantic units – the elements of content – were examined the essential signs of health, and also the frequency of their occurrence. The most frequently used characteristics of health, when answering the question «
Thus, it is possible to note that the majority of the respondents (37,3%) define health as the state, which is characterized by a good health and mood (for example, “health – this is calmness and confidence for tomorrow” or “health – this is cheerfulness and a good mood”); health is defined also by the students as that which does not be required to comprehend and to take care of until appearing the symptoms of its worsening (health – this is absence of diseases and fear before them” or “this is when nothing it aches”) the respondents answered 23,8% and 20,3% respectively. 18.6% of the respondents consider one of the characteristics of health to be a harmonic state in a person of spiritual and physical origins.
In the context of presented understanding what health is, we were also interested in the degree of understanding by the respondents towards the personal responsibility for their own health, considering it as a necessary condition for achieving success in various fields of activity and future profession. To this end, they were asked to express their attitude to the question-reasoning "
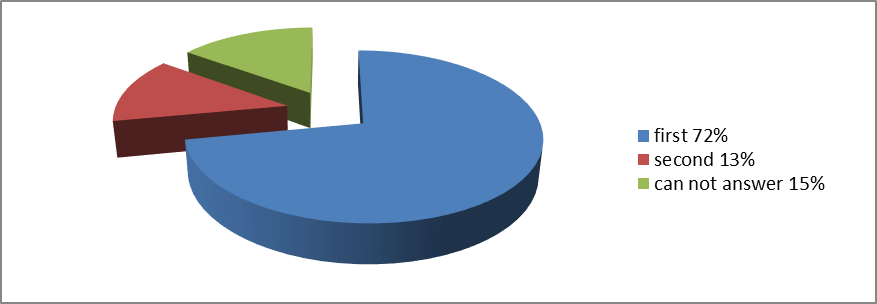
Among the reasons were also named: “conditions are not created”, “lack of willpower”, “no time for sports”, etc. Indicative for us there were also some generalized empirical data on the motivational and axiological attitude to own health in the students' environment. Thus, the majority of the respondents participating in the survey believe that they adhere to a healthy way of life, however, as a rule, only 17% to 20% of boys and girls say that they adhere to the correct diet; also most of them eat cold snacks (only 31.6% of the guys take liquid food once a day, whereas, 16.8% do not eat it at all). The girls have a bit different situation - they like “liquid food” (53%) more than “dry ration” (24.5%). Despite the fact that a young body constantly requires recuperation after a school day, 54% of the girls and 37% of the boys spend no more than 6-7 hours to rest.
In the frames of our study, among the reasons for violating health indicators, the following are identified as the main ones (Table
A significant number of the students believe that they lead the healthy lifestyle, but at the same time they have bad habits, do not adhere to a diet, sleep, spend a lot of time at a computer, etc., which can lead to negative consequences (mental disorder, body diseases). It is also necessary to note the increased self-esteem by the students towards their own health, because they do not coincide with the objective data that characterize the state of morbidity of the student contingent, the level of their physical and functional readiness.
The lack of desire to fully use physical activities and sports for physical qualities and skills development suggests that the possibilities of physical culture in terms of updating health-saving technologies in the educational settings of the university have not yet received proper development. Within the framework of the personality-developing component as part of the methodologically-informative block that constructs the model responsible for developing health-saving technologies in bachelors' training in the universities of the Republic of Iraq, we were interested in the respondents' attitudes toward self-development, their personal focus on health preservation in terms of gaining success in the society and future professional activity. To compare with the results obtained within our research, we, first, turned to the already existing studies addressing the values and life-meaning orientations of the students of Islamic and secular-status higher educational institutions. As follows from the research materials, the most significant values for the students of Islamic universities are "health", "happy family life", "and peace in the country, “life wisdom”, “having good and true friends".
It should be noted that the desire to achieve success and self-affirmation is not significant for the faith-based (religious) youth. The students going to the secular-status higher education institutions are more aware of the need to exercise some physical activity, which expresses better in an atmosphere of calm, social, political and economic stability. We paid the special attention to the study devoted to the life values of Iraqi youth, in which more than 600 university students from the Kurdistan region of Iraq took part. The importance of studying the value system among students is associated with a change in the situation in the Kurdistan region of Iraq and with little knowledge that is available on this problem and its current state in universities. The task of the study was to identify the place of values in the general hierarchy among students of different courses in terms of their importance in a given combination. The results showed the absolute importance for the students of such values as "interpersonal relations" and "professional self-realization." It is interesting to note that, according to Alukaily (2009), among insights of the majority of students, the “interpersonal relations” value block is equated to the concept of “collective relations”, which indicates the Iraqi youth’s disagreement with purely individualistic values of the Bologna process as indicators of the life success.
Thus, the ascertaining stage of the experimental work showed that the majority of the respondents demonstrate low (38.7%) and medium (46.6%) levels of motivation for conscious health care; understanding the basics of self-organization and self-development towards the topic we consider. They generally lack the ability to set goals in terms of health and physical education (the list of goals was a chaotic set of near and far prospects, while the respondents had difficulty in identifying some obstacles to goals implementation and assessing the own resources). Only 17% of the respondents presented more or less clear and coordinated program. The study also demonstrated the overestimated level to assessment of own functional state (an objective assessment of the functional state turned out to be lower than subjective opinion) and, on the contrary, some underestimation towards body's resources.
Conclusion
The development of the Higher School of the Republic of Iraq is correlated with the need to prepare students, young people, with taking into account the health-saving technologies, which, in essence and content, are the only possible way of generalizing and structuring knowledge and skills that can be applied in taking care of individual health and supporting/organizing special conditions for the healthy lifestyle; in skillful implementing the capabilities of a human body (Kryazh, 2005). The bachelors' training in the conditions of the high school with health environment showed a significant reorientation of the goals and objectives of the physical education and revealed the formation of certain physical qualities, vital motor skills, and the bachelors in-depth knowledge of their bodies.
Organizational and pedagogical conditions in bachelors' preparation on the basis of health-saving technologies have shown their effectiveness in solving issues and challenges of physical education. The technology oriented to shaping the healthy lifestyle for the bachelor students of the Republic of Iraq provides the effective training for the bachelors on the basis of the health-saving technologies; allows to visualize the educational process with a multi-variation of all its components that helps to orient the students to choose the healthy life style, to exercise physically as life norms, social adaptation and future professional competitiveness as the desire to self-development and life-long learning.
References
- Abdelmunem, M. Sh. (2004). Physical culture in Iraq. Baghdad.
- Adolf, V. A. (2005). Modernization towards teachers’ training based on modeling professional activities. Krasnoyarsk: KSPU.
- Adolf, V. A., & Iliina, N. F. (2007). Innovation activity of a teacher in professional career development. Kransnoyarsk: Policom.
- Afanasyev, V. G. (2008). System and society. Moscow: Academia.
- Afanasyev, V. V. (2011). Factors and prerequisites to social-pedagogical support to learners. Secondary vocational education, 1, 16–18.
- Alatas, S. H. (2007). Intellectuals in Developing Societies. L.s Cass.
- Al-Battauiy, G. A. (2013). Experience of foreign countries towards physical education system development in Iraq. Physical culture and halth, 1(43), 43–45.
- Al- Battauiy, G. A. (2015). National percularities of physical system development in Iraq. Tambov.
- Al-Khatib, M. H. (2001). Die entwicklung Von korperkulter und sport in Irak von 1917 bis in die gegenwart. Der philosophischer Fakultat des wissenschaltlichen Rats der Martin-Luther Universitat Halle-Wittenberg ZurErlangung des Akademischen Grades Doktereines Wissenschaftszweiges.
- Al-Khatib, M. H. (2003). Der Studentensportan der Baghdad Universitat und seine Zukunftigeentwicklung. Diplomarbeitan der Martin-Luther-Universitat Halle Wittenberg.
- Alukaily, G. (2009). Development of manpower for the petroleum and related industries in Iraq. – Science and technology in developing countries. Cambrige: At the Univ.-ty press.
- Artemyev, V. P., & Shutov, V. V. (2004). Theory and methodology of physical education: motion qualities. Mogilev: MSU.
- Davidenko, D. N. (2008). Motitoring on university discipline ‘physical culture’. Science notes, 12, 15–20.
- Glazacheva, E. V. (2011). Syndrom of emotional exhaustion among students: search for methods to optimize the processes. Vestnik of International Science Academy (Russian section). Special iss., 26–45.
- Kryazh, V. N. (2005). Physical Education in the Republic of Belarus. International Comparison of Physical Education. Concepts. Problems. Prospects. Marcus Gerber. Oxford: Meyer & Meyer.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Demkina*, E., & Fadel Saad, A. (2019). Healthy Lifestyle For Bachelor Students Of The Republic Of Iraq: Problem Statement. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 677-684). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.92
