Abstract
Modern digital platforms transform relations in the society interaction and integration process of economics in international, national and regional level. Digitalization affects all spheres of life and not only does it allow us to use personal devices. Digital globalization is creating more efficient markets in developing countries, broadening its participation in small companies and start-ups. The era of digital globalization allows more than ten million enterprises worldwide to export goods within e-commerce markets and large companies to control their international business in more economical and efficient way. Nowadays digitalisation creates the most convenient ways for business development, as well as for state and municipal authorities to reach the economy stability in regions. The new era of global flows make entrepreneurs analyse their company structures, the quality of the goods, their assets, and competitor positions as well as the state and regional formations are to be affected by global changes. In contrast to the long-term practice of foreign countries, Russia has recently introduced a digital regulation system in the domestic economy. As a result of globalization, the digital economy and computing technology is growing significantly and being developed by many people. On this basis, Russian regions must develop policies that will allow them to take advantage of the digital revolution, while minimizing losses both in individual regions and throughout the territory of the Russian Federation.
Keywords: GlobalizationdigitalizationeconomyregionsInternet
Introduction
The digital economy is a modern stage in the economic relations evolution in Macro, Meso and Micro approaches (Dyatlov, Lobanov, & Zhou, 2018; Bin & Shuhua, 2017). Moreover, its powerful development is affected by the globalization factors (Nosova, Semenova, Redin, Tarakanova, & Makarenko, 2018). Globalization is connected with diverse types of related phenomena: political, sociological, economic and business. It refers to the growing interdependence of national economies, international business competition, and markets (Pankov, 2011). The characteristic features are the international integration of information, labor, technology, goods and asset (Khizbullin et al., 2017).
There main actors in economic globalization are transnational corporations supported by governments of industrialized countries, international financial organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Trade Organization, the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation. However, now they deal with the small and midsize regional enterprises that have grown significantly over the past decade. These enterprises actively take part in global business operations as mobile partners.
Globalization is a significant international phenomenon, which affects national economic systems and meso-level economic entities in the aspects of politics, economics, education, society and environment. Therefore, the development of regional aspects of globalization becomes one of the main issue. As a result of globalization, the digital economy and computing technology is growing significantly and being used by individuals to learn, find work and build personal networks. On this basis, Russian regions must develop policies that will allow them to take advantage of the digital revolution, while minimizing the displacement of jobs in some of the most developed territories (Betelin, 2018; Tsvetkov, Shutkov, Dudin, & Lyasnikov, 2018).
Problem Statement
Nowadays globalization process has stalled. But although the global goods trade has flattened and cross-border capital flows have declined sharply, globalization is not heading into reverse. Rather it is entering a new phase defined by soaring flows of data and information.
According to the world statistics provided by the global agency Hootsuite for 2019 (Brown, 2019), there are several indicators:
1. There are 5.11 billion unique mobile users in the world today, up 100 million (2 percent) in the past year.
2. There are 4.39 billion internet users in 2019, an increase of 366 million (9 percent) versus January 2018
3. There are 3.48 billion social media users in 2019, with the worldwide total growing by 288 million (9 percent) since this time last year.
4. 3.26 billion people use social media on mobile devices in January 2019, with a growth of 297 million new users representing a year-on-year increase of more than 10 percent.
Obviously, digital transformation will cause the change in business technology of any industry: from sales to telecommunications. At the same time, there is an obvious increase of some globalization instruments in economics. There is a good chance for changing the specifics of work, interaction and economic development in the Russian Federation (Danchikov, Gureva, Polozhentseva, Chernenko, & Varavenko, 2017).
According to the statistics, there are 109.6 million internet users in Russia. Study notes rising rates of internet penetration in Russia stands at 76% of the population. At the same time, 85% of all online users in Russia use Internet every day, and 11% at least once a week (Kuzmina, 2018). There is an obvious development of digital technologies indicators in Russia (Figure

At the same time, there are factors affecting the digitalization development process in certain regions of the Russian Federation. The main problems affecting the uneven development of digitalization at the level of Russian regions are:
1. The lack of qualified staff and the need of educational adjustment programs (Sadovaya, 2018; Vasilyeva, 2018).
2. The lack of funding. It is especially difficult to allocate funds for digitalization to the regions of the Russian Federation having more serious economic problems (Dagayev, 2018).
3. The problem of digital inequality. It is impossible to use either the E-Government or the “Smart City” services without Internet. Only a third of cellular base stations have an access to 4G and LTE networks which are considered as the modern standard of mobile Internet. The development of 5G communication has been postponed until 2022.
4. Slow formation of a new regulatory environment, which cause the emergence digital technologies development. This process is still relevant in most regions of Russia (Popova, 2018).
Obviously, the country is undergoing positive transformations, yet they are time-consuming. Therefore, there is a need to use digital economy tools to solve regional development problems.
Research Questions
First of all, it is necessary to clearly distinguish the main globalization competencies. The factors depicted in Figure
1. Policy: the government removes barriers to trade and foreign investment. International firms export and build production facilities for new markets.
2. Technologies: customers learn more about foreign goods. They will have more options to choose variations of technologies, connections and interactions. Small companies are becoming global competitors using Internet and network computing, which also leads to an increase in the number of companies making transactions with electronic commercial systems.
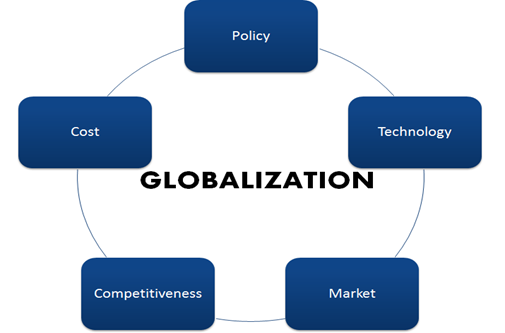
3. Market: companies globalize; therefore, they deal with global customs. When firms saturate domestic markets, they begin to create branch companies in foreign markets.
4. Cost: economy of scale reduces cost due to the globalization of product lines. These costs include production, development and stockpiling costs. A company can promote a product or sales chain to an “inexpensive” country.
5. Competitiveness: Globalization leads to the increased competitiveness among all corporations around the world. New companies from industrialized and developing countries have already entered the world markets for cars, computers and electronics to gain significant competitive advantages.
Purpose of the Study
The main objective of the study is to assess the prospects of the globalization impact on the digital economy development in the regions of the Russian Federation.
The main problem relevant to most regions of Russian Federation is the lack of qualified staff to work with digital software and operational processes. The problem refers to the lack of "human capital" in modern Russia. According to this there comes a complex of globalization tools: the technology impact on people through the prism of digital economy and the subsequent competition of regions within the country and abroad. Education and cultural background form the qualitative characteristics, define values and competencies of human capital. The development of these characteristics are considered to be crucial for economic growth of the country. The government is concerned about it and taking reasonable steps forward. The project “Chief Digital Transformation Officer” (Kostyleva, 2018) is a great example for it. The project started in 2019 at the Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration and was supported by the President of the Russian Federation. Obviously there comes a problem of displacement of employees by technology as a result of technical and informational changes. The digital economy causes the inconvenience mostly to older employee. On the other hand, according to the previous experiences, while getting into the new digital system, people acquire the necessary technical skills for working in new conditions. The project should contribute to the qualitative improvement of the professional competencies of civil servants. A group of 40 federal employees and 30 regional ministers took part in the project. As a result of training, the members of the projects gained skills in strategic planning of digital transformation, working with data, developing draft documents, and managing teams.
On the other hand, there are positive aspects of the globalization influence on the population of our country. According to the Center for Strategic Research, the level of education and the mass standard of consumption in Russia were developed and the quality of human resources has been increased significantly during last 20 years. Nowadays there is an immense global competitiveness among the economically literate people with professional competencies. Obviously, the level of proficiency will grow further and by 2035 the human capital development will show incredible evolution.
At the same time, the question of financing regionally digitalization in the country is still being discussed. It affects the shortage of funding, as well as the economic instability of the regions which is caused by the problem of introducing new technology. From a more rational point of view, the methodology of globalization is influencing the creation of a positive political environment in the regions, both by improving management decisions of the state apparatus and by focusing on increasing the level of digitalization in the regions. So in 2019, subsidies will be increased for 49 subjects of Russia, but they will decrease for 23. In general, the number of regions that do not require subsidies remains minimal. The main part of the subsidized subjects is depicted in Figure
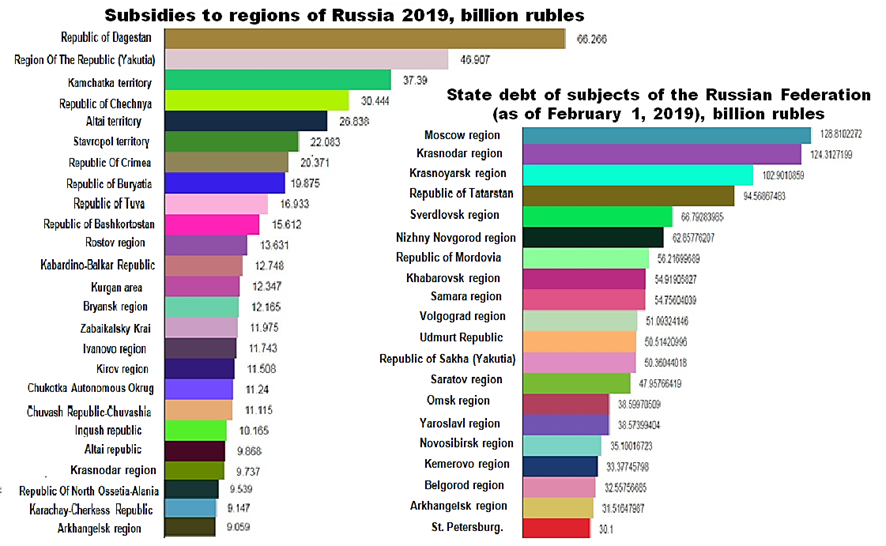
As an example, the Krasnodar Territory having debt in about 1,243 million rubles is still on the 22 place in the rating and stays one of the regions in Russian Federation which receives a fixed amount of subsidies in 2019. The government continues trying to maintain the financial stability of the territorial entities of the Russian Federation. Although, there is a need for more efforts.
Research Methods
The modern financial system and regional infrastructure of Russia mostly supports large projects with high stability. Although the standards of traditional financial institutions are not well adapted to the new economics and digital globalization as most innovative and technology intensive projects are often referred to high-risk. It makes the government to seek alternative funding such as new money sources. This is a set of alternative mechanisms for involving the projects into the new private equity technology which had not been used or was partially involved in the economy. These types of investments compared to classical financial instruments have a number of advantages:
1) financial transactions can be completed electronically having less counterparty risks;
2) alternative investment tools attract wide range of non-professional investors in the most dynamic economy sector;
3) transaction costs are reduced according to process simplification of transactions and conducting them through automated platforms;
4) investor gets an additional flexibility based on varying amount of investment and a portfolio corresponding to his personal profile.
Also, the idea of a State-like-Platform was discussed in 2017 in the Russian regions. This is an idea of modernization of public administration using the new technology opportunities. The project was focused on the citizens’ well-being and economic development based on the introduction of digital technologies. The main purpose of the platform is a citizen in a new reality. According to this idea the government should aim to create a convenient and safe environment for a person to live and reveal their abilities which will lead to the creation and implementation of innovative technologies. Thus, the introduction of this technology will lead to the development of regions: it will reduce the quality gap between them and the center, will eliminate the digital inequality and provide the same opportunities to use modern business tools. This will require regions cooperation on the decisions leading to wide digitalization. However, many regions with less opportunity to make significant investments in digital transformation using centralized solutions will be profitable.
Despite the negative aspects, the government has a certain amount of funding for development of digitalization in its territorial entities, and the amount of funding is increasing annually. Large-scale informatization and digitalization programs as “Smart City” in Moscow, “Informatization Program” in the Republic of Tatarstan are great example of digitalization development in the Russian Federation. Developing regions of Russian Federation need to establish special group of leaders dealing with the development of digitalization, creating of incubator centers, reducing the disadvantages in the provision of digital services to the population, including government services in electronic form.
Findings
The main tools of the Russian regions globalization are knowledge-intensive production and information networks. According to the study, the digitalization of society should be focused on three major aspects:
1. Firstly, most efforts should be focused on "person";
2. Maintaining stability and sustainability;
3. Comprehending all aspects of society.
The main problem is digital changes of the entire country and its territorial entity. Hence people should have long-term opportunities and the inequality created by globalization 3.0 will be minimized.
Conclusion
Within the minimizing risks of regional economic system disruptions and maximizing the benefits of Russian territories, we must adapt digital data and international integration policies, labor policies, as well as education and competition within new realities. With a competent policy and readiness for world cooperation, there is a need to use these fundamental technologies to improve the well-being of our regions, while not slowing down the energy and enthusiasm of the digital age.
References
- Betelin, V.B. (2018). Problems and prospects of the formation of the digital economy in Russia. Herald of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 88(1), 3.
- Bin, Zh., & Shuhua, W. (2017). Tax law reform in China, 3(3), 158.
- Brown, B. (2019). Global state of digital in 2019. Retrieved from: https://hootsuite.com/platform/ analytics#
- Dagayev, A. A. (2018). Knowledge Economy and Information Society: Ten Years Later. Information Society, 1, 11.
- Danchikov, E. A., Gureva, M. A., Polozhentseva, Y. S., Chernenko, E. M., & Varavenko, V. E. (2017). Problems of economics and economics. Serials Publications, 15(23), 83.
- Dyatlov, S. A., Lobanov, O. S., & Zhou, V. (2018). Management of regional information space in a digital economy. Economy of the region, 14(4), 1194.
- Khizbullin, F. F., Sologub, T. G., Bulganina, S. V., Lebedeva, T. E., Novikov, V. S., & Prokhorova, V. V. (2017). The Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences, 25, 45.
- Kostyleva, T. (2018). Rating of regions by the level of digitalization development “Digital Russia”. Retrieved from: http://d-russia.ru/.html
- Kuzmina, A. S. (2018). Priority directions for the introduction of smart city technologies in Russian cities. Expert-analytical report. Retrieved from: https://www.csr.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Report-Smart-Cities-WEB.pdf
- Nosova, S. S., Semenova, A. N., Redin, D. V., Tarakanova, N. V., & Makarenko, A. V. (2018). Digital economy in ESPACIOS. Sociacion de Profesionales y Tecnicos del CONICIT. 39(31), 254.
- Pankov, V. S. (2011). Economic globalization: qualis es et quo vadis? World economy and international relations, 1, 16.
- Popova, A. V. (2018). New subjects of the information society and the knowledge society: on the issue of normative legal regulation. Journal of Russian law, 11(263), 14.
- Sadovaya, E. S. (2018). Digital economy and the new paradigm of the labor market. World economy and international relations, 62(12), 35.
- Tsvetkov, V. A., Shutkov, A. A., Dudin, M. N., & Lyasnikov, N. V. (2018). Digital economy and digital technologies as a vector of strategic development of the national agro-industrial sector. Moscow University Bulletin, ser. 6: Economy, 1, 45.
- Vasilyeva, E. V. (2018). Development of creative abilities and competencies of digital future professionals. Scientific and technical information, ser. 2: Information processes and systems, 10(1).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Zelinskaya*, M., & Adamyan, Z. (2019). Digital Economy: Regional And Global Aspects. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 3447-3453). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.463
