Abstract
The paper uses the results of the systematic study of the role of local government bodies in the system of financial and legal functioning of municipal entities in the Russian Federation and the issues related to regulation of their activities to assert that the main function of local government bodies is the financial and legal function, which is reduced to municipal property management, municipal taxes and charges, and the local budget. The study states that second-order functions, which include the socio-legal function and the administrative-legal function, cannot be fulfilled without effective execution of the main function, since it accumulates all the financial resources of local government bodies in the form of a consolidated local budget. Most of these resources in modern practice face significant difficulties in terms of pumping up the budget revenues, which negatively affects the solution of local problems and execution of powers regulated by the Federal law On the General Principles of the Organization of Local Government in the Russian Federation. The study results show that under the present conditions, the municipal entities in the Russian Federation are not able to ensure progressive socio-economic development based on allowances, subsidies and subventions from higher-level budgets. The activities of local government bodies should be based on their own incomes. In accordance with budget legislation, allowances and subsidies are attributed to own incomes, though this is not entirely correct since they are not assigned to local budgets on an ongoing basis, but are financial support.
Keywords: Local government bodieslocal budgettax revenuesnon-tax revenues
Introduction
The study of current applied problems related to regulation of the activities of local government bodies that determine their place in the socio-economic processes of Russian regions is becoming increasingly relevant due to pronounced differentiation of municipal entities in the Russian Federation in terms of both their socio-economic development and, as a result, effectiveness of management of various processes and territories. Therefore, it is important to understand the place and role of local government bodies in the financial and legal system and the problems related to regulation of their activity, which is relevant for sustainable and progressive development of not only individual municipal entities, but regional economic systems as well.
Problem Statement
Issues of the effectiveness of financial and legal activities of local government bodies are priorities for the economy of any state and its regions since they affect the dynamics of socio-economic development at both macro and micro levels. The above determines the feasibility of studying the role of local government bodies and the problems of regulation of their activities in the system of financial and legal functioning of municipal entities in the Russian Federation.
Research Questions
The research subject is current problems of effective regulation of the activities of local government bodies, increasing their financial independence in the performance of local government functions.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to analyze the place and role of local government bodies in the system of financial and legal relations in order to develop an author's approach to defining the functions of local government bodies and their functional dependence, to identifying the most important financial and legal components of local government regulation in the modern economy in the Russian Federation and problems related to their activities.
Research Methods
The research methodology is based on application of general scientific research methods in the framework of the analytical and system-logical method and deductive and inductive methods.
Findings
Regulation of the activities of local government bodies to increase the efficiency of their activities should be primarily aimed at solving financial and legal problems, which we understand as a set of organizational, economic and organizational relations between the state and various economic subjects to stimulate the socio-economic development of local government bodies and to ensure the functions of local government by an appropriate resource potential. Therefore, it becomes important to study theoretical approaches and views on the definition of "local government functions" since the functionality of local government bodies reveals the entire financial and legal aspect of their activities, and partly reveals the problematic aspect of regulation of local government.
In modern literature and scientific research by various authors, interpretation of the definitions of "local government" and "functions of local government bodies" are diverse.
Thus, local government and its functions are considered by sociologists as an institution of civil society with priority powers of the population of municipalities exercised to solve the problems of local government to meet the common interests of both the population and interests of state bodies and local government.
Political scientists consider local government in terms of the institute of public authority and highlight the main areas of the activity of local government bodies, and the processes of development and execution of power of the municipal authority.
Legal science proceeds from the fact that the functions of local government in the Russian Federation are defined by law (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018), while there are both a representative body and the local government administration, which can be a legal entity. It should be noted that this concept has its drawbacks. It weakens the oversight of executive bodies and causes legal problems when it comes to allocation of certain rights, including the right of municipal ownership of the property of the local authority.
Economists consider local government a subject of economic authority to manage municipal property and local budgets, which focuses on the need to ensure a certain socio-economic effect from activities of local government bodies as an institution of public authority.
Vinnikov and Parkhomenko (2014) note, “In the Russian Federation, the focus is on the independence and autonomy of local government, on exclusive powers of the population to address local issues. This is the feature of the modern Russian model of local government, which is legally consolidated at the constitutional level” (p. 139).
Kojevnikov (2012) considers the functions of local government bodies in terms of the legislative regulation depending on the type of the municipal entity, and allocates the control function of public authorities of the municipal entity as the key function of local government bodies to reach the goals and objectives of local government bodies defined in various legislative acts.
Davydenko (2005) also adheres to a similar position, however, in his study he clarifies that the functions of local government executed by local government bodies should be carried out with direct involvement of the population of the municipal entity.
Bondar (2008) considers the meaning and functionality of local government bodies from a constitutional point of view. He argues that the relations of municipal property as an integral system are predetermined by subordinated structures, i.e. subjects, their holders and municipal property rights. The initial (basic) subjects holders of municipal property rights in an urban or rural settlement are the population itself (the local community) represented by a representative body and administration. The remaining components, though differ in the scope of their rights, are referred to the derived formations. Synchronization of their functions and powers should be performed in strict accordance with the constitutional provisions on the powers of the population to own, use and dispose municipal property (Part 1, Article 130), on the one hand, and on independent management of the municipal property by local government bodies (part 1 132) on the other. These norms must be perceived in systemic unity. Article 130 (Part 1) secures the powers of the population (local community) as a subject of municipal property law, whereas Article 132 (Part 1) reflects the process of subsequent execution of the relevant powers by local government bodies which act in this case on behalf of the municipal entity (Bondar, 2008).
A number of other authors also substantiate their position in terms of the constitution (Novoselov, Shtapova, Kovalenko, Medyanik, & Ram, 2016; Taran, Durdyeva, Aslanov, Bindasova, & Borlakova, 2016).
These positions are also consistent with the interpretation of local government in the Federal law No. 131-FZ of October 06, 2003 (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018). “Local government in the Russian Federation is a form of exercise of power by the population that ensures an independent and on their responsibility solution of local issues by the population directly and (or) through local governments based on the interests of the population with the consideration of the historical and other local traditions within the limits established by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, Federal laws, and in cases established by Federal laws, the laws of the subjects of the Russian Federation” (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018).
Thus, it is possible to assert that the function of local government bodies in the Russian Federation as an institution of public authority is reduced to resolving issues of local significance within the framework of the constitutionally-stated goal of local government bodies and their respective functions.
Quite a lot of attention is paid in the scientific literature to the issues of criterial systematization and classification of functions of local government bodies. Most of the classifications cited are based on legislative identification of issues of local importance in the framework of Federal law No. 131-FZ of October 06, 2003 On General Principles of the Organization of Local Government in the Russian Federation, which can be considered completely legitimate.
However, it should be noted that classification of functions of local government in the scientific literature does not fully reflect functional interrelationships (mutual impact) of functions of local government, which served as the basis for voicing the author’s position.
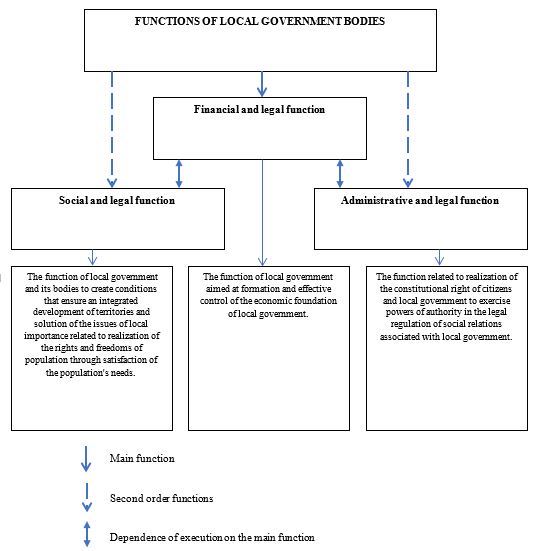
The author's position proceeds from the fact that there is the main function of local government, without which all other functions defined by local issues cannot be performed. Therefore, it is the key function of local government that has a direct impact on regulation of the activities of local government bodies in the Russian Federation.
The author highlights the financial and legal function as the main function that involves management of the municipal property, municipal taxes and fees, and the local budget.
In our opinion, second-order functions, which include the social and legal function, and the administrative and legal function, cannot be fulfilled without effective execution of the main function, since it accumulates financial resources of local government bodies (Figure
The financial and legal function is a function of effective control of the economic foundation of local government. Due to this, the main function cannot be replaced by components of other functions. In addition, the relevance of the financial and legal function is confirmed by Article 9 "Financial Resources of Local Government Bodies of the European Charter of Local Government (1985).
Based on the above and the structure of our study, we consider it necessary to investigate the main financial and legal issues on the control of the activities of the local government bodies to ensure the economic foundation of local government in Russia.
According to Article 49 Economic Foundation of Local Government of Federal Law No. 131-FZ of October 6, 2003, the economic foundation of local government includes the municipal property, funds of local budgets, and the property rights of municipal entities (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018).
These elements are also regulated by the Budget Code, the Civil Code, the Tax Code, and by other (over two hundred) regulatory acts, which confirms the relevance of the economic foundation for regulation of the activities of local government bodies (Taran & Sauvov, 2018). In addition, it should be noted that Article 132 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation states that the local budget is an integral part of local government as part of the economic foundation of local government.
Thus, it can be argued that the most important financial and legal part in the regulation of local government is the local budget.
The study of the regulatory framework of regulation of the municipal budget showed that the Budget Code of the Russian Federation is a basic document. The Budget Code of the Russian Federation ensures the budget independence at the municipal level, however, in some cases, the provisions of the Budget Code allow for restrictions on the independence of local government bodies.
This is also due to the fact that Federal Law No. 131-FZ contains 26 references to the provisions of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation and references to other legal acts in terms of regulation of the economic foundation of local government. In our opinion, this complicates the activities of all participants involved in the municipal budget process, although it is not a violation. In general, there is a certain conflict in the legal regulation of the activities of local government bodies. Thus, Article 9 of the Budget Code is called Budgetary Powers of Municipal Entities, although it would be correct, due to the established structure of the municipal level, to address it to local government, since Federal Law No. 131-FZ defines a municipal entity as an "urban or rural settlement, municipal district, urban district, urban district with intracity division, intracity district or intracity territory of the city of federal importance" (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018), and local government bodies are vested powers in the budgetary sector.
The provisions on the independence of local budgets exhibit some contradictions, since local government bodies receive allowances, subsidies and subventions from higher-levels budgets and are essentially dependent on them. However, it is necessary to understand that the current situation with extremely high differentiation of municipal entities in terms of the social and economic development causes a lack of financial resources in individual municipal entities, thus depriving local authorities of the opportunity to comply with the principle of self-financing in accordance with the powers conferred. In our opinion, this violates the provisions of the European Charter of Local Government (1985), which have been in force in the Russian Federation since September 1, 1998, in terms of the right to financial resources in accordance with the powers conferred.
It is also important to note that Article 9 of the European Charter of Local Government defines the right of local government bodies to "sufficiency of own financial resources". Nevertheless, despite the ratification of the European Charter of Local Government (1985) both in the Budget Code of the Russian Federation and in Federal Law No. 131-FZ, no other regulatory act contains a definition of "sufficiency of own financial resources", although this term indicates the ability of "self-financing" of local government bodies.
In our opinion, municipal entities are not able to ensure the ongoing social and economic development based on allowances, subsidies and subventions from higher-level budgets. In our opinion, the expenditures of local government bodies should be covered by their own revenues. It should be noted that, in accordance with budget legislation, allowances and subsidies are attributed to own revenues. In our opinion, this is not correct since they are not assigned to local budgets on ongoing basis and are a kind of financial support. Thus, local government bodies within their powers should rely on stable sources of income (tax and non-tax revenues) granted to them on an ongoing basis.
At the same time, it is very important to understand that the majority of municipal entities that have been formed by now are subsidized. Therefore, it is necessary to more actively transform (merge) and eliminate municipal entities in order to reduce administrative and management expenditures of local government bodies.
The provisions of Article 9 of the European Charter of Local Government cannot be fully executed due to the relatively low fiscal potential of both local taxes and municipal entities.
Conclusion
Thus, based on the study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. It seems appropriate to express the position of the author, which states that the function of local government bodies in the Russian Federation as an institution of public authority is reduced to solving the issues of local significance within the framework of the constitutionally-stated goal of local government bodies and to performing appropriate functions.
2. The classification of functions of local government available in the scientific literature does not fully reflect the functional interrelations (mutual influence) of functions of local government, which was the basis for the author’s position. The position is based on the fact that performance of the main function of local government is crucial to control all other functions defined by local issues that fall within the scope of Federal Law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003 On General Principles of the Organization of Local Government in the Russian Federation (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018).
3. The main function of local government has a direct impact on regulation of the activities of local government bodies in the Russian Federation. The author highlights the financial and legal function as the main function, which involves the control of the municipal property, municipal taxes and fees, and the local budget. In our opinion, second-order functions, which include the social and legal function, and the administrative and legal function, cannot be fulfilled without effective execution of the main function, since it accumulates the financial resources of local government bodies.
4. To date, the most important financial and legal element of the regulation of local government is the local budget. The study of the regulatory framework in the field of the municipal budget showed that the Budget Code of the Russian Federation is a basic document. Nevertheless, there is a groundless duplication of the norms of the Budget Code in Federal Law No. 131-FZ of October 6, 2003 (Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003, 2018).
5. High differentiation of municipal entities in terms of social and economic development causes a lack of financial resources in individual municipal entities, thus depriving local authorities of the opportunity to comply with the principle of self-financing in accordance with the powers conferred. In our opinion, this violates the provisions of the European Charter of Local Government (1985), which have been in force in the Russian Federation since September 1, 1998, in terms of the right to financial resources in accordance with the powers conferred.
6. The expenditures of local government bodies should be covered by their own revenues. It should be noted that, in accordance with budget legislation, allowances and subsidies are attributed to own revenues. In our opinion, this is not correct since they are not assigned to local budgets on ongoing basis and are a kind of financial support.
7. Most of the currently formed municipal entities are subsidized, and therefore it is necessary to more actively transform (merge) and eliminate municipal entities in order to reduce administrative and management expenditures of local government bodies.
References
- Bondar, N. S. (2008). Local government and constitutional justice: constitutionalization of municipal democracy in Russia. Moscow: NORMA. Retrieved from: http://library.khpg.org/files/docs/ 1331896802.pdf (20 Received February, 2019).
- Davydenko, O. A. (2005). Local government in the Russian Federation: constitutional and legal aspects of municipal power relations. Retrieved from: https://dlib.rsl.ru/viewer/01002943147#?page=5 (Received 20 February, 2019).
- European Charter of local government (1985). Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_20361/
- Federal law No. 131-FZ of 06.10.2003 (2018). On General principles of the organization of local government in the Russian Federation. Retrieved from: http://www.consultant.ru/cons/cgi/online.cgi?req=doc&base=LAW&n=317662&fld=134&dst=1000000001,0&rnd=0.3324010705826346#0604962536614259 (Received 20 February, 2019).
- Kojevnikov, O. A. (2012). Disputable Questions of the Legal Status Municipal Checking-Counting Organ in Russia. Russian laws: experience, analysis, practice, 9, 83–85. Retrieved from: https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_18078635_16275613.pdf (Received 20 February, 2019).
- Novoselov, S. N., Shtapova, I. S., Kovalenko, A. A., Medyanik, N. V., & Ram, O. L. (2016). Research of Specifics of Management of Regional Development for the Purpose of Observance of Reproduction Proportions. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(S1), 1–6. Retrieved from: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/irmm/article/view/1857/pdf (Received 20 February, 2019).
- Taran, O. L., & Sauvov, I. K. (2018). Assessment of the impact of regional policy on the effectiveness of counteraction to the expansion of the shadow sector of the economy in the Republic of Dagestan. In Experience and results of economic activity of socio-economic systems, countries, regions, industries and sectors of the economy materials III all-Russian scientific-practical conference (pp. 149–154). Pyatigorsk: Institute of service, tourism and design (branch) NCFU in Pyatigorsk.
- Taran, O. L., Durdyeva, D. A., Aslanov, D. I., Bindasova, N. A., & Borlakova, M. I. (2016). Assessment and Analysis of Resource Approach to Formation of Strategic Potential of Economy of the Region. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(S1), 84–89. Retrieved from: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/irmm/article/view/1881/pdf (Received February 20, 2019).
- Vinnikov, A. A., & Parkhomenko, A. G. (2014). Constitutional principles and guarantees local government in the Russian Federation. New law journal, 4, 137–147. Retrieved from: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=22829822 (Received 20 February, 2019).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Taran*, O., Laskovyy, A., Melnikov, V., Kutovoy, S., & Manar, A. (2019). Local Government Bodies In The System Of Financial And Legal Relations. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 3043-3051). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.410
