Abstract
Within the conditions of the Housing and Utilities Sector reform, the developing of new approaches in the management system happens. The Housing and Utilities Sector is transferred from the social to the commercial sphere through the mandatory creation of management companies to provide housing services in the moderate continental climate of the region. At the same time, the housing stock is in a critical condition, the main part of it is dilapidated and is not modernized, it requires high repair expenses and maintenance costs by a private trader. Even Individual Metering Devices (IMDs) are installed at the expense of the owners, giving the effect to save resources for the resource supply companies and the management company while the tariffs increase. There is a disproportion between the subjects of the market-sellers and customers, and this requires creating a new mechanism of the housing and utilities sector, to determine the optimal housing policy and strategy at the regional level. Practically, in all countries with market economies, the management in the housing and utilities sector is a separate type of business. Management companies ensure their liability against the harm to property owners in almost all European countries and in the United States. Thus, managerial decisions are made by associations on the recommendations from the management company. This experience can be applied also in our country – by increasing the role of the community of the owners of residential houses and its Chairman.
Keywords: Housing sectorhousing stocktariffsreformstrategyprediction
Introduction
The significance and relevance of the topic are determined by the need to improve the mechanisms of the reform implementation in the housing sector at the regional level.
It can be noted that modern housing sector of the region is one of the most important sectors of the regional economy. This industry provides people with a wide range of the housing and utilities services. One of the main directions of reforming the development of the housing sector is the demonopolization and development of competition in the housing and utilities sector.
The main component of effective activity of the housing sector enterprises is the balanced tariff policy relating to the housing services and profitability of activity of the management companies providing housing services and the imposed tariffs for utilities. Under these conditions, it is necessary to create a new housing policy and strategy at the regional and local levels, ensuring the functioning and maintenance of a high level of housing conditions for citizens.
The degree of scientific development of the topic. The issues relating to the development of organizational and economic management mechanism of the housing and utilities services were considered in the works of Kozhevnikov (2016), Melnikov (2017), Rutkautas (2017), etc. Kozlyuk (2018) considers the financial and economic aspects of tariff policy in the markets of natural monopolies. The validity and practicability of the tariff policy are reflected in the works of Akimkin (2018), Bobrovskaya (2013), Buryak (2015), Voskolovich (2015), Lopatkin (2017)
Problem Statement
Some problems of organization, management and financing of the housing and utilities sector as an element of the state management system in the structure of the urban economy were considered in the works of Akimkin (2018), Bobrovskaya (2013) and others.
In the works of foreign economists, such as Kauppila (2001), Natelson (2015) and others, the main attention is paid to the peculiarities of the housing management, the formation of homeowners associations in the market.
Despite a large number of publications, the issues of improving the functioning mechanism of the housing sector in the context of reform at the regional level are not fully considered.
Research Questions
The subject of the study is the formation of the functioning mechanism of the housing and utilities sector within the reforming conditions.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to analyse the functioning mechanism of the housing sector implementing and to suggest ways to improve it.
The purpose of the study involves the following tasks:
1) to determine the economic essence of the concepts of "housing", "housing stock", "operation of housing stock" and their role in the socio-economic development of the region;
2) to analyse the methodological aspects of the functioning of the mechanism of the housing sector implementing at the regional level;
3) to analyse the housing stock of the Russian Federation, including the Smolensk Region, and to expose the features of the functioning and management of the housing and utilities sector at the regional level;
4) to analyse the specifics of the formation of the functioning mechanism of the housing and utilities sector;
5) to develop a strategy for the development of the housing and utilities sector at the regional level and measures to improve the functioning and management of the housing and utilities sector at the regional level;
6) to propose measures to improve the functioning mechanism of the housing and utilities sector for implementation at the regional level.
Research Methods
The methodological basis of the work comprises the personal-social-activity approach, competence approach, systematic approach, terminological approach, universal communication and development, analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction.
Findings
The scientific novelty of the work lies in the theoretical and practical justification of improving the functioning mechanism of the housing and utilities sector at the regional level.
The degree of scientific novelty is characterized by the following research results:
- the concepts of "housing stock" and "operation of housing stock" have been clarified;
- the main methods of the regional management implementing and the formation of tariff policy have been specified;
- the housing stock in the Smolensk Region has been analysed, and the prediction of the volume of housing services has been produced;
- measures to improve the mechanism of functioning of the housing sector for implementation at the regional level have been developed.
In modern economic science such concept as housing is often considered evaluating the level of socio-economic condition of the region.
In our opinion, the housing stock is an important factor of the socio-economic development of the region or country, which is a criterion of well-being of the population living in the territory, reflecting the total amount of housing which are used to provide a person with minimum living needs and are located in buildings suitable for his residence.
It should be noted that in economic science as independent objects to study the housing stock it is customary to allocate such structures as "housing and utilities services (HUS)", "housing and utilities complex (HUC)" and "housing sector (HS)", which were considered in the works of Lopatkin (2017), Chernyak (2017) and other authors.
In our opinion, the housing and utilities sector is a special complex multi-profile part of the economy, which is closely related to the housing construction and the real estate market, provides maintenance and restoration of the housing stock, and the housing and utilities sector is a set of measures to manage the housing stocks taking into account its condition and state policy in the housing and utilities sector.
At present, there has been appeared the following system of the housing and utilities sector functioning, including the private-public partnership, where the state controls and regulates the functioning of management companies (granting them licences), tariffs, and the rest subjects of the market interact on a contractual basis.
At present, in the Russian Federation in the housing and utilities sector, there are more than 52 thousand enterprises, which involve about 4.2 million people, covering 1,092 cities and 1,872 villages. The housing and utilities sector plays an important role in the national economy, the share of utilities in the GDP of the Russian Federation is growing from 1.6% to 1.7% in 2017.
In the works of Kozlyuk (2018), Lopatkin (2017), Melnikov (2017) and other authors the following classification of the branches of the housing and utilities sector is presented: 1) housing services; 2) hotel industry; 3) resource supporting of housing stock and other buildings and premises (water, heat, gas, electricity); 4) cleaning and landscaping of settlements.
According to the Federal State Statistics Service (RosStat, 2017), the share of fixed assets in the housing and utilities sector is about 24% (3rd place), which is lower than only the level of this indicator in the transport sector (29.5%) and the industrial complex (27.4%). At the same time, the housing supply in Russia is quite high in comparison with other countries (figure
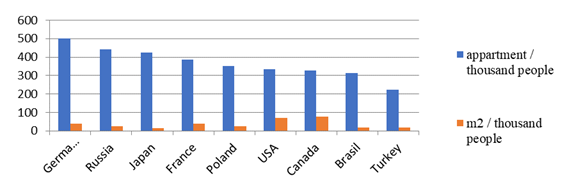
According to the Russian Statistical Service, the housing stock in Russia, including the Smolensk Region, is growing significantly, and in 2016 in comparison with 2005, it was 23.6% and 12.5%, respectively. At the same time, the increasing rate in urban housing is higher than in rural housing, which is 6.3 and 12.5%, respectively (table
Considering the structure of houses by number of storeys, it can be noted that the total share of low-rise housing (1-3 floors), including the built houses, is reduced to 46% (in 2015 – 49%), 1-storey – up to 16.7% (22.1%), 2-3 storey – 1.1 and 1%, respectively.
In addition to the above, in the Smolensk Region, the share of Private Fund is lower than in the country as a whole by 1.2%, but it is higher than the average for the Central Federal District – by 1.7%.
Depending on the form of ownership Article 19 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation allocates the types of housing stock: "private, state, municipal and collective property". The law of the Russian Federation "On the bases of Federal housing policy" clarifies: private, state, municipal and public funds.
At present, the share of the municipal housing stock is high – 8.8%. Today, the majority of domestic scientists and economists, construe the housing sector by the now invalid law of the Russian Federation of December 24, 1992, № 4218-1.
Adopted in 2004, the Housing Code provides: the separation of powers to regulate relations in the housing and utilities sector, the allocation of housing stock classification by the separate criteria, the establishment of a special procedure to transfer housing and other category, the rights and obligations of the parties in the sphere of housing relations, including the choice of control method in the MDU. In 2011 the Housing and Utilities Sector was amended, which eliminated the housing management office and demanded to create the management companies and partnerships operating on a commercial basis, to transfer the payment system of housing services on the market rules.
In these conditions Filimonov (2015) explains the modern concept of management system of multiple dwelling unit: “the activity of management organizations aimed at ensuring favourable and safe living conditions for citizens, including the processes to organize proper maintenance and repair of common property, to organize providing public services, as well as other processes aimed at achieving the goals of management of multiple dwelling unit” (p. 21).
In our opinion, the market management of MDU is the activity of specialized organizations in accordance with contracts concluded with the owners and tenants of residential premises, that is carried out by their own or specialized third parties.
The system of management of the Housing stock (according to Section
Akimkin (2018) notes that the operation of the housing stock is "the process of implementing activities related to the using, maintaining and repairing by owners, proprietors, managers, tenants, tenants of residential and non-residential premises of the housing stock of the city and service organizations" (p. 11).
In our opinion, the operation of the housing stock is a set of measures to ensure the normal functioning of the current housing stock, taking into account the completion of the established minimum list of works and the frequency of their implementation.
The minimum list of works to maintain a MDU is included into the Rules for the operation of the housing stock (Resolution of the State Construction Committee of 27.09. 2003 No. 170, Appendix No. 2 of The Rules to carry out by the local government of open competitions for selection of MC to manage MDU approved by the Order of the Government of 06.02.2006 No. 75).
According to the Fundamentals of the housing legislation of the USSR and the Union republics of 08.06.1984 (ed. 22.05.1990) Art. 7 "nobody can be evicted or limited in the right of use of premises".
From 2018 the eviction of residents is possible. According to Art.153 of the Housing Code of the RF the utilities are the duty of a citizen. Art. 155 of the Housing Code of the RF establishes the term of payment. Benefits are offered to soldiers, veterans and other citizens. The maximum delay is 31 days, followed by penalties. Delay is a serious illness, loss of job or a single breadwinner. FL No. 307 defines the procedure for charging interest (up to 91 days is 1/300 of the refinancing rate, from 91 days is 1/130).
Mortgage flats are not the exception, even in the case of a single home and registration of dependent children. They are disposed, the amount goes to cover the debt on utilities services, legal costs and payment to the Bank, and the balance goes to the owner. The eviction for the debts of utilities services in the case of municipal flat is provided by Art. 90 of the Housing Code of the RF by decision of the court.
According to Sate Information System of the Housing and Utilities Sector in 2018 the wear of the housing stock in the Smolensk Region according to the branches of management is characterized by the following data: on average, the region – 18.61%, and in terms of management methods: 16.67% in management companies, 19.47% in condominiums, 36% in the HСС, 34.86% – direct management, 49.1% in the MDU which have not selected a method of management and for 21.84% the information is not available.
According to the SIS of the HUS for the analysed period there is a reduction in the share of dilapidated and emergency housing in Russia from 3.2% in 2005 up to 2.4% in 2016., including the old one from 2.8% to 1.8%. However, since 1994 according to Art. 210 of the Civil code of the Russian Federation it was stated that the owner begins to bear burden of the maintenance not only the property, but also finances carrying out the capital repairs.
Subsequently, in the HUS of the Russian Federation it was introduced a provision in Article 158 according to which the owners of premises in MDU is charged with meeting the costs of the maintenance of not only their dwelling, but the common property, proportionate to the share.
According to the monitoring of the infrastructure of the Smolensk Region, it can be noted that the share of the average life of boilers which is more than 10 years is about 60.5%. The heat networks are dilapidated or 33.7% of the total length, and that fact leads to 80% of all damage to the heat supply system. In the Smolensk Region in 2018 there have been 1,227 units of water supply systems and individual water supply networks, also 1,564 units of pumping stations of the first lifting capacity of 728,93 thousand m3 per day and water length of 5,264.4 km, and in those 1,988.23 km or 38% requires replacement.
During the analysed period, there was a fairly good situation with regard to the provision of the housing stock improvement, although the equipment is almost worn out by 25-50% (table
In the Smolensk Region for the period from 2012 to 2017 it was put into the operation 2.7 million m2 of housing. According to the Russian State Statistics Service, in 2017 6,315 of new flats with the total area 483.7 thousand m2 were built, which is below the level of 2016 by 23.2%. Individual developers commissioned 219.2 thousand m2, which is below the level of 2016 by 28.7%. The share of the individual housing construction in the total area of completed housing was 45.3%. At the same time, the growth rate of housing built by the population is 3.5 times higher than the growth rate of built MDU – 1.5 times, which is due to the active construction of country houses with an increase in the welfare of the population in 2010-2016. However, the structure of the housing stock is dominated by houses built between 1971 and 1995.
The difficult situation in the situation of the housing stock, which was shifted to private business in the housing and utilities sector leads to the unprofitability of many management companies. The housing and utilities services occupy a high level in the total amount of consumer needs and in the cost of services payment. And this share is growing in the whole country, including the region. And in the Smolensk Region, although the situation is better than in the CFD, but is worse than in Russia, as a whole (table
The ongoing reform in the housing and utilities sector has led to a sharp increase in incoming payments from the provision of housing and utilities services in the Smolensk region with a decrease in the population (Figure
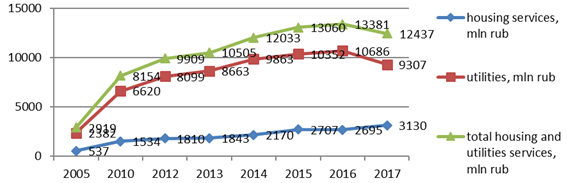
Hence the need to develop regional housing policies and strategies aimed at saving costs and resources in the provision of utility services and the formation of tariffs.
Regulation of the housing sector can be presented in following forms: administrative regulation to protect competition and property rights and economic regulation. In our opinion, the state regional housing policy should act in the following directions - stimulating the supply of housing and stimulating demand.
Based on these activities, it is possible to make a forecast for the development of housing and utilities in the region (Figure
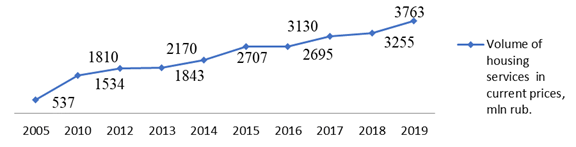
Conclusion
It is necessary to carry out the following measures to improve the functioning mechanism of the housing and utilities sector in the region:
1. determining the characteristics of companies operating in the housing sector, the housing stock, to create an efficient model of housing and utilities, drawing on the experience of housing cooperatives in Western countries and introducing modern technologies;
2. determining of large powers of local and regional authorities in the determination of tariffs. In financing the housing and utilities sector, both budget financing for a separate project and pooling can be used — attracting other management companies to jointly solve a particularly significant problem in MDU with tax breaks.
3. creating new pricing mechanisms in the housing sector, the introduction of innovations in the operation of the housing stock and resource conservation.
4. management, accounting and planning
These measures will allow settling the unequal conditions of relations between all subjects of the housing market, both suppliers and buyers.
References
- Akimkin, A. I. (2018). Problems of management of residential buildings after the adoption of the new Housing Code. Management, 6, 11-13.
- Bobrovskaya, N. I. (2013). Russian State policy in the field of housing and communal services: theoretical aspects and problems. State and municipal government. Scientific notes of NCAPA, 3, 31-40.
- Buryak, A. S. (2015). Management company as a subject of the Russian real estate market. In Management problems materials of the 21st All-Russian Student Conference: Issue 1 (pp 17-19). Moscow: State University of Management.
- Chernyak, V. Z. (2017). Housing and utilities: development, management, economy: study guide, KNORUS, 392.
- Filimonov, S. L. (2015). On management in the housing sector. Housing and Utilities: magazine of the head and chief accountant, 1, 21.
- Kauppila, V. (2001). Experience of Finland in management and modernization of housing stock. Journal of the head and chief accountant of housing and utilities, 10, 98-107.
- Kozhevnikov, S. A. (2016). Public-private partnership in the housing and communal services of the region: problems and prospects of development. Vologda: ISEDT RAS.
- Kozlyuk, A. G. (2018) How utilities go to self-sufficiency. Housing and utilities, 3, 10.
- Lopatkin, N. T. (2017). On the transition to a new system of payment for housing and utilities. Housing and utilities, 11, 245-255.
- Melnikov, P. S. (2017). Features of the housing reform. TerraEconomicus, 3, 123-129.
- Natelson, R. (2015). Comments on the Historiography of Condominium. The Myth of Roman OriginCity of Oklahoma Law Review, 1, 12.
- RosStat (2017). RUSSIA IN FIGURES. Retrieved from: https://www.gks.ru/free_doc/doc_2017/rusfig/rus17e.pdf
- Rutkautas, T. K. (2017). Formation of the housing market: trends and prospects (regional aspect). NSUEM, 23.
- Voskolovich, N.A. (2015). The specifics of the formation of the availability of paid consumer services. Bulletin of Moscow University Series 6. ECONOMY, 3, 3-11.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Sapozhnikova*, S., Kramlikh, O., Chudakova, S., Kuptsova, V., & Lavrova, E. (2019). Formation Of Functioning Mechanism Of Housing And Utilities Sector Of Region. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2774-2782). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.373
