Abstract
Modern economic development and widespread digitalization are accompanied by globalization, increasing competitiveness of national economies and development of new state instruments, including tax ones. The taxation system is a powerful tool that organizes activities of taxpayers and influences the financial system. The tax administration system has to respond to all changes in the national economy to implement government measures and conduct tax policies. The development of modern tax management mechanisms and tools is carried out within the state adopted tax policy adjusted to modern requirements of economic development. The study of tax administration issues is required to improve efficiency of the tax system and its individual tools and enhance the level of tax collection. The relevance of the problem is that without a continuous flow of funds, it is impossible for the government to perform its functions. Taxes as a permanent source of monetary resources can ensure proper and timely financing of government needs. The study identified areas and measures aimed at improving tax administration and reducing administrative costs: expanding the list of grounds for granting tax deferrals, using the institute of advances, reducing workflow for taxpayers, etc. The purpose of the article is to explore modern taxation management mechanisms used for implementing the state tax policy based on the best world tax administration models. The research results are obtained using empirical and theoretical methods, conceptual, logical and operational components. Methods of in-depth knowledge of reality, comparison, quantitative and qualitative analysis, systematization, and graphical interpretation are used.
Keywords: Tax policytaxtax managementmechanisms
Introduction
In the modern economy, accumulation of budget revenues plays a crucial role for optimizing socio-economic processes, finding sources of economic growth, and developing effective programs for territorial development. Currently, there are a number of works devoted to the study of the conceptual apparatus, conceptual provisions and theories of taxation, tax policy, tax administration, and management.
World experience of state economic regulation shows that efficiency of socio-economic development is determined by tax policies, whose main elements are the budget, taxes and the state. The efficiency of these policies is determined by the optimal construction of the tax system, the budget balance and correct proportions of accumulation and expenditure of socialized funds.
The study of modern tax administration mechanisms is a crucial research task in the light of formation of modern innovative elements of economic development.

Problem Statement
In the tax environment of the modern polycentric world, it is quite difficult to draw a clear distinction between a policy, a system, a mechanism and a legislation regulating taxation, on the one hand, and tax administration, on the other one. Tax administration can be a mechanism for implementating tax policies or an institution for regulating budget tax revenues (Dedkova, 2013).
In this context, tax administration is substantive, being an internal factor in the development of the tax system. It is a complex set of economic relations aimed at achieving key parameters of the effectiveness of the state tax policy, including planning and forecasting processes and phenomena, regulating and controlling actions of tax subjects (Korostelkina, 2017).
Issues of tax management are studied by foreign researchers. In particular, Tjen and Evans (2017) analyze the relationship between taxes and corruption, causes and consequences of corruption at tax and administrative levels in Indonesia, and identify and evaluate strategies to eliminate a corruption component.
Keen and Slemrod (2017) study the issue of optimal tax administration. In particular, they reveal the relevance of optimal interventions and suggest a summary indicator of the impact of government regulation on tax policies - “elasticity of tax revenues”.
Tax policy issues are studied by Elmendorf (2017) The author emphasizes the need to conduct distributive tax policies and and implement compensatory measures. The researchers analyze features of tax policies. Palaiodimos (2017) analyzes the features of indirect taxation administration in Greece, tax reforms and financial implications. Ultsch and Behnisch (2017) study the issues of the German income tax distribution system.
The concept “state tax administration” is often applied to the taxation management system involved in coordinating and improving tax relations and the entire taxation process. In the Russian literature, issues related to development of the taxation management mechanism are studied by Arsenieva and Yanpolskaya (2014), Basnukayev (2017). Given the specificity of tax relations at the macro level, it is necessary to organize an effective system of state tax administration.
There is no consensus on the concepts “tax management”, “tax administration”, and “tax policy”. The central element is the managerial nature of tax management. Lapin (2010) believes that instead of the capacious concept “tax management”, it is necessary to use the more general one “public administration” because state tax administration is part of the overall management system. Porshneva, Chernik, and Zamyatin (2003) define state tax management as “a process of tax impact on the behavior of business entities and the population through tax administration and tax planning, tax regulation and tax control aimed at the optimal and effective economic and social development” (p. 283).
Mayburov (2015) believes that state tax management aims to ensure effective development of the economy and long-term implementation of the functions of the state tax system.
We believe that the terms "tax management" and "tax administration are identical for the purpose of tax policy implementation. State tax management is a system of state administration of the national tax system aimed at ensuring regular taxation of the national budget.
Research Questions
Tax management as a taxation management system involves tax planning and forecasting, regulation, tax administration, monitoring and control.
All tax management elements are interrelated with each other and perform specific functions. It is necessary to plan tax indicators, control the tax process and legality of activities of the participants of tax relations.
The effectiveness of the state tax policy depends on its type. Tax policy as a complex of administrative, organizational, economic and legal measures implemented by the government is required for an effective tax system (Basnukayev, 2017).
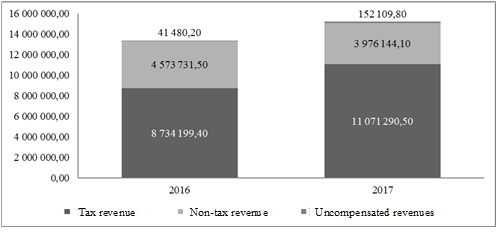
Tax policy measures determine efficiency of tax management. The Russian Federation cannot function without budget revenues. In 2017, there was an increase in the amount of tax revenues which increased the amount of federal budget revenues. The structure of revenues to the federal budget is presented in Figure
When considering the structure of tax revenues, it should be noted that in 201,7 the largest increase was characteristic of the corporate income tax (by 55.27%), excise taxes (by 43.88%)
The main regulator of socio-economic processes is the tax burden which is an assessment of the effect of government measures on the economy as a whole and categories of taxpayers. Analysis of the tax policies for 2017 and 2018-2019 shows that, as of 2014, the tax burden was 21.72%. The excessive threshold is observed in Denmark (50.88%), Belgium (44.66%), Italy (43.66%), Finland (43, 85%), and France (45.22%). The minimum tax burden is typical of Latin American countries (Mexico - 19.5%), Chile - 19.82%).
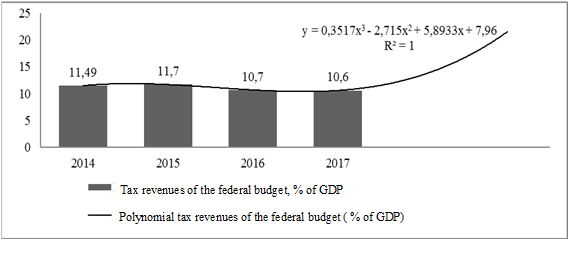
Indicators of the tax burden (% of GDP) of the Russian Federation for 2016-2017 are indicated in the tax passport. According to official statistics, in 2017, the tax burden on the federal budget was 10.6%, on the consolidated budget - 20.1%, which is 2.2% less than in 2016. In general, the tax burden on the consolidated budget is almost 2 times more than on the federal budget due to a smaller number of taxes.
For successful implementation of the tax policy, it is necessary to adopt rational tax laws and develop an effective tax management system. The tax system of Russia has been formed recently (Basnukayev, 2018). The problems of state tax administration are presented in Figure
These problems include the excessive fiscal nature of the management process, an increase in the basic VAT rate of up to 20% and an increase in excise rates (Basnukaev, 2018). These measures infringe interests of taxpayers in favor of the state. In order to obtain an additional source of income to cover the budget deficit, the state raises tax rates increases tax revenues; however, in the long-term, it forces businesses to evade taxes and transfer their activities to the shadow economy. An increase in tax burden reveals inequities in the tax system which leads to tax evasion and decreases the amount of budget revenues. To cover the resulting budget deficit, it is necessary to reduce costs or raise tax rates again.
Tax evasion causes the shadow economy and corruption schemes involving taxpayers, tax authorities or patrimonial structures. According to RBC, Russia ranks 4th with a shadow market volume of 39% of the national GDP.
It is important to develop an effective tax system. Annual changes in tax legislation, introduction of new taxes, qualitative implementation of the service function of the tax authorities generates unintentional tax evasion. The current changes in the tax system are of a pronounced fiscal nature and impair interests of taxpayers.
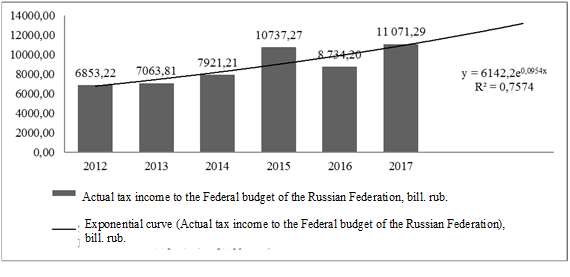
In 2018, an increase in tax revenues is expected to be 8.18% compared with 2017, and in 2019 - 10.01% compared with 2018. When predicting the size of the tax burden, a polynomial type of approximation with a maximum coefficient of 1 was used. The model allowed it to predict the 2018 increase of 13.51% which is 2.91% more than the 2017 figure. In 2019, the tax burden will increase by 8.33% compared to 2018. In general, an increase in the tax burden on the federal budget speaks for the insolvency of non-tax revenues; non-tax revenues are more susceptible to macroeconomic changes.
Purpose of the Study
In implementing tax administration measures, it is important to form an effective and relatively permanent tax system. Annual changes in tax legislation, introduction of new taxes cause fiscal evasion. Modern tax management mechanisms should ensure qualitative implementation of the state tax policy, including solution of systemic problems of legal, organizational, methodological and socio-motivational nature.
The existing system of tax administration is to be improved by encouraging participants of tax relations (citizens, small and medium businesses).
Research Methods
Using the least squares method, one can forecast performance indicators of the tax system, in particular, tax revenues (Figure
Findings
The study identified areas and measures aimed at improving tax administration and reducing administrative costs: expanding the list of grounds for granting tax deferrals, using the institute of advances, reducing workflow for taxpayers, supporting small businesses, creating favorable conditions for tax payments by implementing taxation principles, modernizing control activities, etc.
Conclusion
Implementation of these activities will ensure effective interaction of participants in tax relations, a qualitative organizational structure of tax authorities, and allow for the use of new test technologies, formation of analytical activities on a new technological platform, develop a code of behavior and professional standards for tax authorities.
Acknowledgments
The article is part of the research carried out within the project part of task No. 26.2758.2017 / 4.6 for 2017-2019. "The system of analysis of formation and distribution of the cost of innovative products based on the infrastructure concept".
References
- Arsenieva, V. A., & Yanpolskaya, E. A. (2014). Tax policy in the system of state regulation of the economy: analysis of approaches, estimates and methods of economic management. Science and education: economy and economics; entrepreneurship; law and administration, 4, 7–8.
- Basnukayev, M.S h. (2017). Contradictions and disadvantages of the tax system: Russian experience and practice. Bulletin of the North Ossetian State University n.a. Kosta Levanovich Khetagurov, 1, 110–113.
- Basnukaev, M. Sh. (2018). The tax system. Economic and Human Sciences, 9(320), 11–23.
- Dedkova, E. G. (2013). Building of the model of federal tax policy. Economic and Human Sciences, 3, 70–74.
- Elmendorf, D. W. (2017). Federal policy and economic growth. Business Economics, 52(3), 149–153.
- Keen, M., & Slemrod, J. (2017). Optimal tax administration. Journal of Public Economics, 152, 133–142.
- Korostelkina, I. A. (2017). Tax administration as a tool for implementation of the state tax policy. Fiscal policy: challenges and global perspectives. In Collection of materials of the All-Russian scientific-practical conference with international participation (pp. 133–136).
- Lapin, V. N. (2010). On the tax administration system. Bulletin of Saratov State Socio-Economic University, 4, 83–87. Retrieved from: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/k-voprosu-o-sisteme-nalogovogo-upravleniya
- Mayburov, I. A. (2015). Tax management. Advanced course: textbook for undergraduates. Moscow: LLC “Unity-Dana Publishing House”.
- Palaiodimos, G. (2017). Fiscal Implications of Fuel Taxation Adjustments. Recent Evidence from Greece. Public Finance Review, 45(5), 647–677.
- Porshneva, A. G., Chernik, D. G., & Zamyatin, D. I. (2003). Tax management. Moscow: INFRA-M.
- Russian Treasury (2019). Annual report on the execution of the Federal budget in 2018. Retrieved from: http://www.roskazna.ru/ispolnenie-byudzhetov/federalnyj-byudzhet/
- Tjen, C., & Evans, C. (2017). Causes and consequences of corruption in tax administration. An Indonesian case study. eJournal of Tax Research, 15(2), 243–261.
- Ultsch, A., & Behnisch, M. (2017). Effects of the payout system of income taxes to municipalities in Germany. Applied Geography, 81, 21–31.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Mambetova, A., Dzagoeva, M., Korostelkin, M., Vasilyeva, M., & Basnukaev*, M. (2019). Study Of Tax Administration Mechanisms Used For Implementing Government Tax Policies. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 252-258). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.35
