Abstract
The paper considers modern problems, trends and prospects of agriculture in Russia. Through methods of economics and statistics analysis, methods of analysis and synthesis of economic information the paper addresses and analyzes problems of agriculture. The study considers current trends of agricultural development under conditions of economic crisis in the country following the results of 2017 and reveals significant changes in the industry. According to statistics it was defined that the actual volumes of livestock and crop production have increased. The results of the study, analysis and assessment of theoretical and legal base of agricultural taxation, analysis of current tax burdens of agro-industrial complex made it possible to define the need to improve the operating taxation procedure for the industry. The paper makes the conclusion that the existing system of privileges and preferences for agricultural producers does not fully foster and motivate the production in this industry. It is defined that the establishment of the tax impact center is caused by the need for the system approach to stimulate agriculture and ensure fair and efficient tax burden at the industry-specific level, increase of the rational use of land resources, optimization of tax burden. The results of the study make it possible to conclude that timely and relevant analysis of efficiency of the state support of agricultural producers is necessary for mutual coordination and satisfaction of the needs of the state budget and agricultural producers. The creation of a competitive branch of agriculture will guarantee food security in the country.
Keywords: Agriculturestate supportperformance indicators
Introduction
Over the past 4 years Russia has been facing a lot of tension from the international community represented by the introduction of political and economic restrictive measures caused, according to some states, by the Russia’s involvement in destabilizing events in Ukraine.
Let us also remind that since August, 2015 the Russian Federation imposed sanctions implying a ban on import of the general type of goods and food from countries that applied sanctions against Russia. These sanctions cover some meat and dairy products, vegetables, fruit, fish products imported from the countries of the European Union, the USA and other countries.
The current restrictive measures against Russia affect many significant spheres of the country, but mostly they impact agriculture serving a guarantor of food security and independence of Russia in terms of the needs for food provided by the domestic agrarian sector.
The imposed sanctions against Russia pushed the state into urgent decisions considering the current scenario. Some scientists and economists believe that the restrictive ban on imported agricultural products will stimulate the domestic agrarian sector to expand its production, the others talk about current inability to satisfy the food demand of the population.
Insufficient study of a current trend in agriculture in the conditions of bilateral sanctions, relevance of existing tasks and problems of agricultural industry defined the issues addressed in the given paper.
The analysis of the current state of the industry, the direction of efficient state support, and the introduction of tax incentives for agricultural producers were not sufficiently reflected in domestic literature.
Domestic scientists-economists made a substantial contribution to the study of modern problems of agricultural development. The analysis of problems and their solution in agricultural industry were reflected in works by R.A. Alborov, A.A. Anfinogentova, O.I. Botkin, A. Gladilin, R.S. Gaysin, N.D. Kondratyev, Yu.V. Glukhov, T.N. Medvedeva, F.Z. Michurina, V.G. Panskov, M.V. Romanovsky, L.I. Horuzhy, etc. At the same time there is a need to provide a relevant analysis of the current situation in agriculture, to generalize the key problems of the industry, to improve theoretical and methodological aspects of state support measures aimed at agro-industrial complex, to develop more efficient mechanisms of taxation.
Problem Statement
The scientific novelty of this study is to justify the current problems preventing the development of agriculture, to identify ways of their solution, to analyze and assess the current situation in the agrarian sector, to develop efficient tax measures for the industry.
According to economists, currently agriculture is facing the following problems:
One of the main problems in agriculture is climatic features of production. Out of the entire agricultural territory only 30% of lands have favorable farming climate with a possibility of more accurate forecasting of weather conditions. The rest is subject to droughts, dry hot winds, rushing mighty winds, which are adversely affecting the yield.
The second problem in the field of agrarian sector is insufficient state support of agricultural producers. In general, the level of support of the agrarian sector is much lower than the Central European indicators.
One of the aspects of this problem is inefficient and irrational use of budgetary funds, lack of continuous monitoring of expenditure efficiency.
The third problem is high level of operation and wear of the field fleet park in agriculture and shortage of specialized agricultural machinery in farms. This problem results from the previous one related to low funding of the industry.
The fourth problem is poor qualification of staff and inefficient management of enterprises within the industry. This is confirmed by different productivity of enterprises having similar climatic, technical and other conditions. It was defined that the domestic agrarian sector lacks the required number of competent experts. Considering multiple open vacancies in the industry, the applicants do not have qualification and knowledge satisfying the management of agricultural enterprises. In the conditions of the economic crisis in the country followed by collective redundancies in other industries the agricultural sector distinguished itself in optimization of regular staff and a small share of redundancies.
These problems require urgent solutions to improve competitiveness and profitability of agriculture within the current perspective.
Research Questions
The paper addresses the problems of agriculture, including insufficient state support of agricultural producers, irrational use of budgetary funds, lack of expenditure efficiency monitoring. It studies the current development trends of crop and livestock production, the direction of state support. The creation of favorable conditions to increase the investment attractiveness of the agricultural industry implies active state support of the industry.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to analyze and asses the current trends in the agrarian sector, to identify problems preventing the development of the industry, to form directions of state support via tax incentives.
The study sets the following tasks satisfying its purpose:
- to analyze current problems in the field of agriculture;
- to reveal current development trends of agriculture under the conditions of the economic crisis in the country;
- to define the directions of state support, to reveal conditions thus increasing the investment attractiveness of the industry;
- to create the areas for modernization of the operating taxation system of subjects within the studied industry.
Research Methods
Through the methods of economics and statistics analysis, methods of analysis and synthesis of economic information the paper addresses and analyzes the problems of agriculture. The method of comparative analysis based on official statistics and the author’s estimates, as well as statistical methods made it possible to define the dynamics of indicators characterizing the current trends in agriculture in the Russian Federation.
Findings
Today agriculture in Russia seeks not only to satisfy the needs of domestic market, but also to improve its positions in the international markets of agricultural products. Thus, following the results of 2017-2018 agricultural years Russia is among the top three countries on grain export (exclusively of grain legume crops and grain processing products).
An important factor ensuring the development of agriculture are retaliatory sanctions of Russia against the USA, the European Union and some other countries. The imposed sanctions limited the import some agricultural products, which reduced the competition and increased the demand for domestic agricultural goods.
The recent years are marked by the transition towards the import substitution policy in agriculture.
In 2017 subsidies amounting to 143.9 billion rubles were allocated from the federal budget for the development of agriculture, including:
decoupled support – 11.34 billion rubles;
increase of dairy cattle breeding efficiency – 8.08 billion rubles;
subsidized investment loans – 58.7 billion rubles;
subsidized part of direct incurred costs for creation and modernization of agro-industrial complex – 15.5 billion rubles.
Besides, the mechanism of preferential loans was introduced, which allows the organizations within the agro-industrial complex to keep their current assets to pay part of an interest rate without expecting their further return as subsidies as it happened earlier. In total, 9.1 billion rubles were allocated for this initiative (Nikolaeva, 2018). Since last year the new mechanism of state support – a single subsidy uniting a number of earlier existing directions of subsidizing is used (Amirova et al., 2018).
Following the 2017 results of financial and economic activity of agricultural producers getting state support from the federal budget, the profitability of agricultural organizations taking into account subsidies made 14.3%, without subsidies – 8.5%. The earned profit (before tax) accounts for more than 300 billion rubles. The share of profitable agricultural organizations increased by 2.2 percentage points and reached 87.1% of the total number of agricultural organizations (Khudyakova & Shmidt, 2018).
The growth of domestic production increased the specific weight of domestic agricultural products and food in the total amount of domestic market resources, which according to the Doctrine of Food Safety of the Russian Federation (further to be referred to as the Doctrine) serves the criterion of food safety.
In 2017 Russia demonstrated the following indicators of its food sovereignty:
grain – 99.3% (threshold value according to the Doctrine – at least 95%, 2016 – 99.2%);
sugar – 94.3% (according to the Doctrine – at least 80%, in 2016 – 88.5%);
vegetable oil – 84% (according to the Doctrine – at least 80%, in 2016 – 83.6%);
potatoes – 97.6% (according to the Doctrine – at least 95%, in 2016 – 97.5%);
meat and meat products – 90.3% (according to the Doctrine – at least 85%, in 2016 – 88.7%).
Despite adverse weather conditions (drought, hail, flood, excessive moistening during harvesting, emergency mode in 21 territorial subjects of the Russian Federation), the harvest rates of some crops reached their record (Naliukhin, Glinushkin, Khamitova, & Avdeev, 2018).
The agricultural output was increased in the 2010-2017 timeframe (Figure
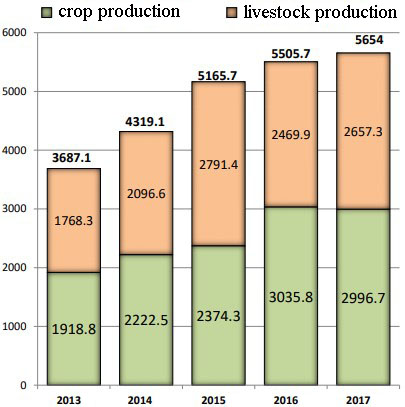
Throughout the entire studied period the crop production increases, the volume of livestock production is also growing except for 2016 (Figure
The record volume of grain and leguminous crops was achieved – 135.4 million tons (in weight after processing), which is 11.2% more than in 2016, and 35.3% more than the average annual production in 2012-2016 (Generalov, Kuchin, Suslov, Ryabova, & Kurilova, 2019).
The positive aspect is the increase of sugar beet production in 2017 up to 48.2 million tons, barley – up to 20.6 tons. The wheat yield made 85.8 million tons (in weight after processing), which is the main export culture or 17.1% more than in 2016, and 50.4% more than the average annual production in 2012-2016 (Kozlov et al., 2018).
The livestock production maintains a positive dynamics of meat production, which growth is ensured by pig-breeding and poultry farming. In 2017 the total of 14.6 million tons of cattle and poultry for slaughter (in body weight) or 104.7% by 2016 are produced. In comparison with 2012 the production of cattle and poultry increased by 25.8% (3 million tons).
Stabilization of milk production is also noted. In 2017 the farms produced 31.1 million tons of milk. The growth compared to the previous year made 1.2%, including agricultural organizations – 3.8%, farmers – 7.5%. The potential of subsectors of livestock production is substantially defined by the condition of livestock breeding. At present the state breeding register includes 2.5 thousand herds of breeding farm animals (Rosstat, 2018).
Meat and dairy production were mostly affected by imposed sanctions since currently they are not able to fully satisfy the consumption of the food market thus forcing to attract import products. At the same time, the introduced food embargo allows improving the competitiveness of domestic producers by monopolizing this segment of the food market having sufficient state support.
The dairy food market is mostly dependent on import products. This situation is followed by the fact that Russia is facing the growth of dairy consumption by 9% annually. This predetermines the need for full import substitution and increase of domestic dairy production.
The Federal Scientific and Technical Program of Agricultural Development for 2017-2025 will make it possible:
to reduce the level of import dependency through the introduction and use of domestic production technologies of primary seeds (original and elite), breeding products (material) within crop and livestock production;
to introduce production technologies of high-quality forages, feed additives for animals and medicines for veterinary use;
to introduce modern diagnostic tools for pathogens of crops, production technologies for pesticides and biological agrochemicals in agriculture;
to introduce modern technologies of production, processing and storage of agricultural products, raw materials and food, as well as modern methods of their quality control and inspection of genetic material;
to increase the number of highly qualified staff in new and perspective training fields and specialties and the number of enterprises within agro-industrial complex having a new technological level (Griewald, 2018).
Conclusion
The results of the study, analysis and assessment of theoretical and legal base of agricultural taxation, analysis of current tax burdens of agro-industrial complex made it possible to define the need to improve the operating taxation procedure for the industry. The existing system of benefits and preferences for agricultural producers does not fully foster and motivate the production in this industry. Fiscal functions of taxation dominate over the regulating functions within the procedure for calculation and collection of taxes in this sphere.
In this regard there is a need not only to develop the tax system for agricultural producers by reducing the tax burden, but also to provide preferential terms of taxation for organizations investing into this industry.
To define the influence of taxation tools on production factors there is a need to create the tax impact center in different subjects of agriculture focused on the most efficient and rational application due to the generalizing criterion for tax beneficiary: recognition of an enterprise as an agricultural producer.
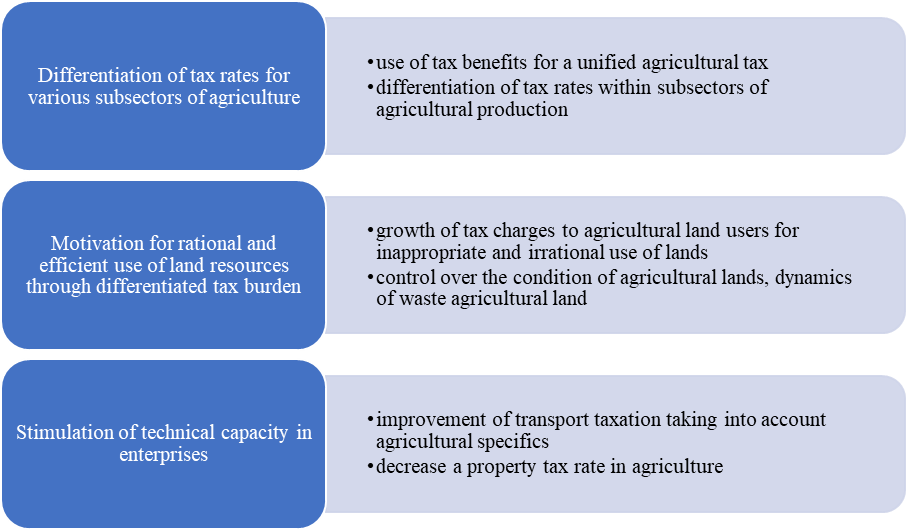
The establishment of the tax impact centers is caused by the need for the system approach to stimulate agriculture and ensure fair and efficient tax burden at the industry-specific level, increase of the rational use of land resources, optimization of tax burden on insurance, property tax, transport tax, personal income tax and corporate tax.
One of the areas for improvement of agriculture in Russia through tax incentives is the introduction of tax monitoring. Tax monitoring includes the system of observations over financial and economic activity of agricultural taxpayers in order to determine the efficiency of interaction between the state and producers, assessment of counter financial flows: volumes of state support of certain enterprises and tax payments to various level budgets (Zhahov, Krivoshlykov, & Shatokhin, 2017).
The selection of enterprises for tax monitoring is made against the best financial performance registered by the regional Ministry of Agriculture, statistical summary and accounting reports. Based on the received data the tax conditions of each enterprise are assessed, the list of organizations to be included into the plan of the field tax audit is developed.
The results of the study make it possible to conclude that timely and relevant analysis of efficiency of the state support of agricultural producers is necessary for mutual coordination and satisfaction of the state and agricultural needs. A restrictive ban on imported agricultural goods is required to serve as a driver for the domestic agrarian sector in order to expand its production, to strive towards full-fledged satisfaction of food demand. The creation of a competitive branch of agriculture will guarantee the reduction of import dependence almost in all segments of the food market and, respectively, will ensure food security in the country.
References
- Amirova, E. F., Voronkova, O. Y., Pyurveeva, K. A., Shatalov, M. A., Panteleeva, T. A., & Sorokina, O. A. (2018). Functioning of agroindustrial complex in the conditions of digital economy. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 9(12), 586–594.
- Department of plant growing, mechanization, chemicalization and plant protection of the Ministry of agriculture of Russia (2018). The results of the crop production industry in 2017 and tasks for 2018. Retrieved from: http://barley-malt.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/agronomycheskoe-soveschanye-ytogy-2017.pdf.
- Generalov, I. G., Kuchin, N. N., Suslov, S. A., Ryabova, I. V., & Kurilova, A. A. (2019). Assessment of regional grain farming development for sustainability. International Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Research, 10(1), 223–231.
- Griewald, Yu. (2018). The Art of the State to Intervene: Insights into Agricultural Land Management in Russia. Ecological Economics, 151, 1–9.
- Khudyakova, T., & Shmidt, A. (2018). The impact of crisis on the performance indicator of Russian enterprises. In International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conferences on Social Sciences and Arts. (pp. 741–748).
- Kozlov, A. V., Uromova, I. P., Koposova, N.N., Novik, I.R., Vershinina, I.V., Avdeev, … & Mokretsov, Y. V. (2018). Optimization of the Productivity of Agricultural Crops at Application of Natural Minerals as Ameliorants and Mineral Fertilizers on Sod-Podzolic Soils. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 10(3), 667–680.
- Naliukhin, A. N., Glinushkin, A. P., Khamitova, S. M., & Avdeev, Yu. M. (2018). The influence of biomodified fertilizers on the productivity of crops and biological properties of soddy-podzolic soils. Entomology and Applied Science Letters, 5(3), 1–7.
- Nikolaeva, E. (2018). Efficiency Analysis of Agricultural Cooperation in Russia. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 238, 364–373.
- Rosstat. (2018). Tsentralnaya baza statisticheskih dannyih. Central statistical database. Retrieved from: http://www.gks.ru/dbscripts/cbsd/DBInet.cgi?pl=9400001#Bottom.
- Zhahov, N. V., Krivoshlykov, V. S., & Shatokhin, M. V. (2017). Ways of modern agriculture in: specifics and state support. In 30th International business information management association conference – Vision 2020: sustainable economic development, innovation management, and global growth, IBIMA (pp. 3646–3652).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Khulkhachieva*, G., Boldyreva, E., Sarunova, M., Allyaeva, T., & Mandzhieva, D. (2019). Analytical Review Of Current Trends In Agriculture In Russia Under Bilateral Sanctions. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1652-1659). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.224
