Abstract
Economic education nowadays is characterized by a growing trend to digitalization. The importance of e-learning in the educational system and the development of digital economy cannot be over-emphasized. A literature review results of some previous studies on e-learning from different parts of the world are presented. The paper is aimed at exploring the necessity and prospects of digital education and e-learning of foreign languages towards promoting best practices in higher education. It was discovered that effective communication between lecturers and students is enhanced through e-learning which has the potential to make learning more interesting, interactive and to be realized faster and more efficiently than existing learning methods. The study is focused on the role of digital technologies and educational platforms in teaching foreign languages at economic universities. The paper reflects real needs and priorities within foreign language teaching at the Saratov Socio-Economic Institute of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics. The aim of this article specifically is to focus on the role of digital technologies and educational platforms in teaching foreign languages at the economic universities. The main research methods are the analysis of scientific works concerning digital teaching. The investigation is carried on the basis of the educational platform Moodle. Results show that students are in general positively inclined towards e-learning and would be willing to take online courses. However, the majority of students do not want the full integration of Information Technology into the study process, meaning that the traditional learning methods combined with IT are preferred.
Keywords: Economic educatione-learningMoodleforeign language teachingprofessional developmentdigital teaching
Introduction
Current stage of economics education is characterized by active use of products related to technologic advance. Information technologies are broadly used for the development of such particular national infrastructure of state management that will meet the standards of present-day management. Digitalization of the economic system is the major stream of state development, economy and social relations. Digital economy encourages consistent development of society and social relations. A number of researchers have analyzed these problems (Bolgov & Dunaeva, 2016; Zinder & Yunatova, 2017).
According to the recent presidential thesis, which states "without digital economy we will not manage to move over to the next technological wave and without such move to the next technological economy in Russian economy, there is no future for our country", it may be affirmed that digitalization affects needs of modern economy, changes in labour characteristics and human's role in production chain, moreover it provides an opportunity to identify new professions in the context of educational and economy transformation. Digital technologies have a profound impact on the educational system, on buildup of competences (Kesici & Tunç, 2018). Moreover, people's motivation towards learning and education changes, labour organization transforms. But we quite agree that the education sector has invested heavily in digital technology; but this investment has not yet resulted in the radical improvements of learning experiences and educational attainment (Luckin et al., 2012).
But online education presents new opportunities not just for the mechanics of higher education, but for improving each student's experience and outcomes (Kelly, Coates, & Naylor, 2016).
The age of digitalization is characterized by the following features:
1. All types of information content are moving from analogue, material and static into digital and at the same time such content becomes mobile and personal.
2. Shift towards simple communication technologies (technology becomes just a tool for communication). A key characteristic of a tool and technology is controllability.
3. Communication becomes heterogeneous: vertical, hierarchical communication becomes irrelevant. A shift towards networked communication takes place.
Overviewed tendencies ensured the necessity to implement a Program "Digital economy of Russian Federation" (ratified 28 July 2017) nationwide. The Program identifies digital economy as “economic activity, where a key factor of production is data in digital form which encourages the development of information space with due account for society demands and human needs for the access to high quality and reliable data, development of information structure of Russian Federation, design and implementation of Russian information telecommunication technology and also formation of the new technological base for social and economic areas”.
Problem Statement
Successful functioning of national economy directly depends on the level of economics education of future financial experts, economists and accountants. Modern economics specialists should be able to come up with rational methods of implementation of managerial decisions in the area of economics and finance, to understand the scope of its efficient application.
New technologies should be implemented in the system of modern economics education because these information technologies enable for more active usage of scientific and educational potential in education, engage best professors in the development of e-learning courses and significantly broaden learning audience. According to society’s needs today we should learn what will be needed tomorrow. E-learning can be defined as “a set of practices that uses technology-aided interaction to create, provide and enhance learning” (Rice & Gregor, 2016, p. 83).
Digital economy, which is based on digital technologies, assumes a new method of technological production that requires new specialists and new development conditions. A modern expert is expected to meet several major requirements:
1. IT-proficiency. In the context of modern society specialists should develop digital competences and also there is a need to use information telecommunication technologies in professional activity.
2. Language flexibility. A specialist should be able to master different foreign languages as required by the professional aptitude.
Thus, there are two broader research objectives: first, finding out the possibilities of foreign language e-learning through Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment (Moodle); second, identifying students' knowledge and experience of e-learning.
Research Questions
The main research questions of this study addresses are:
1. The mismatch between the declared educational standards and its actual execution in the current education environment. In educational practice implementation of state educational standards of the Russian Federation comes across several problems that are related with organization of the educational process, contents of educational courses, lack of corresponding learning materials, etc.
2. Problem of digitization and its global consequences becomes urgent alongside modernization of educational processes. Digital culture creates the necessity of renewal of principles and working methods in higher education that are focused on future specialist of new age. We can characterize digital literacy as a technical competence, and a communicative practice. Digital literacy: offers alternative ways of representing, ideas and experiences, and this is attractive to educators when it allows for ways of capitalising on student learning within (and across) the curriculum can promote high levels of student engagement and enjoyment (Ibrahim, Shariman, & Woods, 2013). The theory of professional education problems of digital literacy and human culture are analyzed in works of Ruliene (2016) who states that digital literacy is the key functional literacy which enables to express information need, create new informational products with the utilization of digital devices, digital resources, digital technologies and readiness to take part in informational-educational cooperation. According to the researcher’s opinion, the educator should combine digital literacy with emotive influence and communication. But the educators and educational practices are not in complete harmony.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of this article specifically is to focus on the role of digital technologies and educational platforms in teaching foreign languages at the economic universities.
Certainly, one of the most important factors of developing modern educational model is the creation of worthy material and technical basis that can be characterized by the availability of high-speed computer with certain pack of software and applications which enables to work online, participate in online-conferences, take distance online tests. Key aspect of such educational process is the academic and methodological support of independent learning activity of students. An important criterion of high-quality preparation of academic and methodological support is the highly experienced developers of educational materials. It means not simply to send e-versions of printed educational editions to students, but to provide learners with multimedia audio and video, illustrations, graphics, animation, etc. to make courses more interesting, entertaining and interactive. All the above-mentioned aspects enable to meet the requirements of modern communication realities, which often move from “live” communication to online area.
As a consequence, e-learning is becoming more popular nowadays. It shifts a paradigm from teacher centeredness to learner centeredness.
A graduate should possess knowledge and skills that will allow him/her to compete in labour-market of the high-tech world; therefore, there is the necessity of self-thinking development, professional qualifications, social, personal and psychological skills of a worker (Turula, 2016).
The following tasks are formed in the education area for staff training in digital economy at the national level:
• development of key terms for staff training in digital economy;
• improvement of the educational system that should supply competent staff for digital economy;
• development of labour market that should be based on terms of digital economy;
• development of motivation system for mastering necessary competences and participation of staff in the development of digital economy in Russia.
E-learning, using the ICT, electronic media and learning platforms (Internet-Based Training, Web-Based Training, Computer Assisted Instruction, Multimedia learning, Technology Enhanced Learning, Virtual Learning Environment, Virtual Education and M-Learning), could help performing these tasks.
Research Methods
The main research methods are the analysis of scientific works concerning digital teaching in economic education, the pedagogical experience study.
E-learning may be synchronous learning (instructor led; there is collaboration and exchange of ideas and knowledge among participants at the same time) or asynchronous learning (self-paced; uses e-mail, blogs, wikis, discussion boards, web-supported textbooks, audio, video courses, web networks without necessarily involving all participants at the same time) (Damyanov & Tsankov, 2016).
The students now face rapidly changing demands, which require a new set of competences. The growing availability of online content and open educational resources provides new opportunities to students, but also to teaching professions.
It is necessary to study the actual problems of economic education in terms of digitalization of economy on the basis of teaching the “Foreign Language” course in Saratov Socio-Economic Institute of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics. The given course is a part of basic work program of all forms and educational program specializations in the field 38.03.01 “Economics”. The pedagogical documentation study method defines forming cultural competence (the ability to communicate orally and in writing in Russian and English for solving interpersonal and intercultural communication problems) as a qualifying aim of this pedagogical program. The study of innovative pedagogical experience has for several years been accomplished by the teachers of foreign languages department. Their personal observations, communication with students, different surveys in terms of digital economy development require not only “digitization” of several processes in the educational system but the introduction of a complex approach that brings new aims and changes the structure and contents of the educational process (Scrivner, Madwell, Buckley, & Perez, 2017).
An interesting experience of using modern technologies in the given direction will be the use of electronic textbooks. An electronic textbook is a specifically developed academic and methodological complex that has hyper-textual structure aimed at reproducing via different high-tech devices such as computers, mobile phones and tablets (Clark, Couldry, MacDonald, & Stephansen, 2015). Currently a textbook is not only an academic volume published online but also an information-driven education environment that is a system of instrumental means and sources providing realization of educational activities on the basis of information and communication technologies. An electronic textbook is an independent educational unit alongside its ability to supplement the original textbook used in the educational process. A major advantage of dealing with a high-quality electronic textbook is that it helps to find the necessary information promptly that saves time and gives almost immediate feedback. Such textbook also makes it possible to check the student’s knowledge of a particular section of the book in the tempo that best suits each individual. A digital textbook is one of the most promising informational and learning resources (Semenova & Svyatkina, 2016).
Electronic textbooks as well as distance learning courses are quite important in most of the higher education institutes in Russia. For example, on the basis of Saratov Socio-Economic Institute of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics an open-source learning platform “Moodle” in the form of distance learning tool is actively used nowadays. The given education platform was developed due to active implementation of distance learning and was firstly used to interact with part-time students at this institute. Currently educational content involved in this electronic shell is actively used for full-time students. The material of electronic education environment is an addition to the main course and can also be used in the self-study process by students of different grades. A virtual electronic shell contains work programs in various fields, references and methodological materials for practical classes, individual creative tasks, paper and essay topics, different questions and exercises for self-assessment and self-control, methodological recommendations for self-paced training and organization also necessary for midterm and final assessment (Osipova, Gnedkova, & Ushakov, 2017).
Findings
The current situation leads to introduction of new requirements and reconsideration of traditional education forms in higher institutions. For example, in higher professional education some modern informational library facilities of securing the educational process are actively and rapidly introduced. Recently in terms of digital communication in society the leading role in the pedagogic process has been given to electronic educational technologies. One of the most commonly used trends is the organization of massive open online courses for various systems of level and additional education.
So digital technology can support two kinds of interaction between a student and a teacher. Technology can even simulate the role of the teacher. Learners may need the support of teachers to interpret those ideas and to convert that information into knowledge. The increasing wealth of online resources offers great potential to both teachers and learners, but places great demands for both to evaluate and filter the information on offer.
It is important to state against the assumption that new technologies will smoothly and effortlessly improve learning. The evidence clearly suggests that digital media offer opportunities that are still to be realised; and that realising them is contingent on how we use them and the
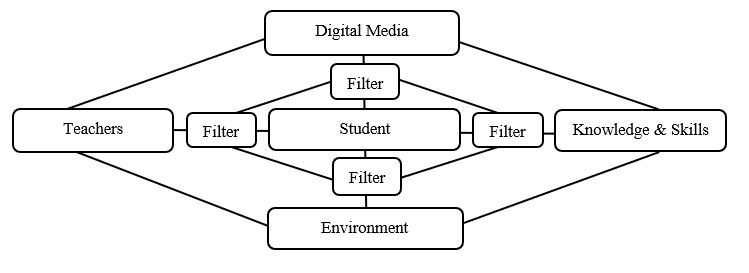
As digital tools become cheaper, more powerful and ubiquitous, learners of all ages have increasing access to learning resources outside of the classroom (Barber, 2016). It will be important to find ways to help them make the most of these – what works well in the classroom may not automatically work well in the home. Although several research examples of learning at home are considered. The key to success is the care and inclusiveness for which technologies have been designed and implemented.
Some studies show that till 2022 there will be a big segregation between online and offline studies. Learning won't be based on memorizing material anymore, people will put more effort in self-education, and e-learning has good prospects from this point of view (Alyaz & Genc, 2016; Beetham & Sharpe, 2013; Dong, 2017).
There is enormous potential for further innovation in digital education. Success will come from commercial developers, researchers, teachers and learners working together to develop, test and spread imaginative new technologies.
Much existing teaching practice may well not benefit greatly from new technologies. If we want to reach a success, we should develop our understanding of digital learning and teaching, potential and promise, we have an unprecedented opportunity to improve learning experiences of our students.
The findings of this study indicate that resources for learners are becoming increasingly complex. A teacher may be confident in making their own digital worksheet or interactive presentation and sharing these with his colleagues (Osipov, Volinsky, & Grishin, 2015). It suggests that the majority of teachers should adapt and change the way they approach teaching and learning. As a result, teachers have to filter and adapt digital tools in order to make them suitable for learning. It can be time-consuming.
Digital technologies offer opportunities for innovation in teaching, but to achieve success it is important to concentrate on the way technologies can be used by students – the learning activities. Linking learning activities and using a variety of technologies and approaches to achieve this gives a far richer experience. Focusing on individual learning activities using only technologies will not provide a maximum impact.
Conclusion
The study of pedagogic experience of teaching the “Foreign Language” course in higher education proves that digitalization of education can’t only be confined to creation of digital copies of original textbooks, digitalization of documents and providing fast-speed Internet facilities. Moodle was implemented to serve the on-going practices in Saratov Socio-Economic Institute of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics by providing a variety of supplemental tools to be used in English language learning. Regarding the students’ perceptions towards the Moodle system, the results of the present study showed that they were digitally literate and able to cope with newly implemented systems.
There is enormous potential for further innovation in digital economic education. Innovations in digital teaching are not just technical innovations but rather academic, curricular, organizational and structural. There is no doubt that the university’s strategy ultimately determines whether the digitalization process will succeed or fail. Getting into the digital environment is an inevitable reality for our time.
Therefore, today’s graduate must be competitive, mainly within the applicants for the same position and employees having the same specialization. Besides professional competence, workers should possess such characteristics as independence, leadership, communicativeness, sociability, psychological stability. Modern employers choose workers having multi-professional knowledge and skills – those speaking foreign languages fluently and able to use different software and understand the present market situation.
References
- Alyaz, Y., & Genc, Z.S. (2016). Digital game-based language learning in foreign language teacher education. Turkish Online Journal Of Distance Education, 17(4), 130–146.
- Barber, J. F. (2016). Digital storytelling: New opportunities for humanities scholarship and pedagogy. Cogent Arts & Humanities, 3(1), 1–14. DOI:
- Beetham, H., & Sharpe, R. (2013). Rethinking Pedagogy for a Digital Age: Designing for 21st Century Learning.
- Bolgov, R., & Dunaeva, Y. (2016). University in the global knowledge society: from digital idea to distance learning practice. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 674, 404–410. DOI:
- Clark, W., Couldry, N., MacDonald, R., & Stephansen, H. C. (2015). Digital platforms and narrative exchange: Hidden constraints, emerging agency. New Media & Society, 17(6), 919–938.
- Damyanov, I., & Tsankov, N. (2016). Variation degree in e-learning courses: Assessment through feature models. Chemistry, 26(2), 277–283.
- Dong, F. (2017). An optimization mode of college English multiple interactive teaching under the computer network and digital technology. Technical Bulletin, 55(10), 371–378.
- Ibrahim, N., Shariman, T. N. T., & Woods, P. (2013). The Concept of Digital Literacy from the Perspective of the Creative Multimedia Industry International Conference (pp. 259–264).
- Kelly, P., Coates, H., & Naylor, R. (2016). Leading Online Education: from Participation to Success, 3, 34–58. DOI: 10.17323/1814-9545-2016-3-34-58
- Kesici, A., & Tunç, N. F. (2018). Investigating the Digital Addiction Level of the University Students According to Their Purposes for Using Digital Tools. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 6(2), 235–241. DOI:
- Luckin, R., Bligh, B., Manches, A., Ainsworth, S., Crook, C., & Noss, R. (2012). Decoding Learning: The Proof, Promise and Potential of Digital Education, pp. 1–89.
- Osipov, I. V., Volinsky, A. A., & Grishin, V. V. (2015). Gamification, virality and retention in educational online platform. Measurable indicators and market entry strategy. Int. J. Advanced Comput. Sci. Appl, 6(4), 11–18
- Osipova, N., Gnedkova, O., & Ushakov, D. (2017). Mobile learning technologies in English learning. Communications in computer and information science, 783, 169–183. DOI:
- Putin, V.V. (2017). Vystuplenie Putina V.V. na Peterburgskom mezhdunarodnom ehkonomicheskom forume, Retrieved from: kremlin.ru/events/president/news/54667
- Rice, S., & Gregor, M. N. (2016). E-Learning and the Academic Library: Essays on Innovative Initiatives, 192 p.
- Ruliene, L. N. (2016) Digital literacy and humanitarian culture of the teacher in innovative educational practice. Otkrytoe i distancionnoe obrazovanie, 4(64), 53–58.
- Scrivner, O., Madwell, J., Buckley, C., & Perez, N. (2017). Augmented reality digital technologies (ARDT) for foreign language teaching and learning. In FTC 2016 – Proceedings of Future Technologies Conference (pp. 395–398). DOI:
- Semenova, N. V., & Svyatkina, E. A. (2016). Digital textbook for vocationally-oriented informative reading in the research university. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 674, 363–369. DOI:
- Turula, A. (2016). What the good (digital) language learner can teach us? Teaching English with Technology, 16(3), 52–73.
- Zinder, E., & Yunatova, I. (2017). Digital Economy and knowledge barriers; their origin and dealing with them. Communications in computer and information science, 745, 445–463. DOI:
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-075-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
76
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3763
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Dolgova, S., Ismailova*, O., Kozlovsky, D., & Kudryashova, A. (2019). The Use Of Digital Media As An Instrument Of Higher Economic Education. In D. Karim-Sultanovich Bataev, S. Aidievich Gapurov, A. Dogievich Osmaev, V. Khumaidovich Akaev, L. Musaevna Idigova, M. Rukmanovich Ovhadov, A. Ruslanovich Salgiriev, & M. Muslamovna Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 76. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1365-1372). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.04.184
