Abstract
Strategy planning is part of management’s activities which helps businesses setting priorities, strengthening its operations, ensuring that employees and other stakeholders are working toward common goals and adjusting business’s direction .Its implementation requires a process comprising seven steps as well as a suitable strategic tool that will simplify the whole procedure and will be selected by the executives of the enterprise. Over the years, many tools have been developed but given the fact that business’s environment is constantly changing, the scientific community searching for substitute tools which will guide the enterprise to an effective strategy. In this context, The Goals Grid tool was created recently as an alternative method. Its versatility and graspable structure can be one of the most suitable options for businesses to formulate their strategic plan. The purpose of this paper is twofold: firstly, the systematic presentation of the tool, as it is quite absent from the international literature due to the fact that it is an empirical and not an academic one. Secondly, the final objective is to highlight its deep connection with the strategy management process. The matrix of the tool is based on a grid which consists of four thematic target categories (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate). Its main motive is to direct the executives in proper decision making, by taking into account all the factors that are arisen from both the external and internal environment, in order to develop a targeted strategic plan.
Keywords: Businessesstrategic management processstrategic planstrategic toolthe Goals Grid
Introduction
Basically strategic planning is a strategic management tool that can help a business to make decisions and actions in order to determine its: a) vision, b) mission, and c) objectives. Its main purpose is to increase enterprises’ efficiency and effectiveness by improving their present and future operations and to provide an adequate framework for managing the future vision (Maleka, 2014, p.16-17).
The implementation is the second phase of the strategic planning process and requires the use of appropriate strategic tools that are able to present all the factors exercising influence from both its internal and external environment (Bagher & Milad, 2017). Given that the factors having influence on the enterprise’s functioning are numerous, the tool which finally will be selected and implemented, needs to filter out all the data that are presented in an appropriate way, for not confusing the senior executives that are called to take right decisions in a relatively short time (Cook, Inayatullah, Burgman, Sutherland, & Wintle, 2014). The Goals Grid can keep up with the above characteristics despite it counts only a few years in the field of strategy management. Its matrix is consisted of four thematic target groups (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate) and is supplemented by the executives in a climate of cooperation. The tool gives to the executives of the company, the possibility of guidance during the decision making process, which will contribute to the formulation of an effective strategic plan. Moreover, it is a practical and comprehensible instrument because it does not require obligatory preliminary training of the employees participating to the process, and this means saving time for those that have to define the goals of the company (Nickols, 2015).
The aim of the research is not only to present The Goals Grid and its properties but to focus on its connection with the strategic management process. Especially, each of the thematic target category that is included in the grid of the tool, can lead to the clarification of the goals of a business and not only to the recording of them. As a result, the tool contributes to the analysis of the current situation and therefore to the development of a strategic plan. The above-mentioned steps are some of the basic ones that strategic management necessitates for business’s long-term success.
The research questions that arise through this paper are: (i) which are those specifications that a tool should meet in order to be properly implemented by the companies? , (ii) to what extent does it contribute to the strategic management process? , (iii) does it facilitate the senior executives during the decision-making process? and (iv) does the tool being involved in the strategic formulation process?
Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
Strategic management is a continuous process which is consisted of four steps: the environment scanning, strategy formulation, strategy implementation and strategy evaluation. It defines the company’s strategy (Huff & Reger, 1987). Each of the component are carried out in chronological order focusing on the creation of a new strategic plan. Before the procedure, managers should select the appropriate strategic management tool as this step is very important for the formulation of the strategic plan (Qehaja, Kutllovci, & Pula, 2017).
Over the years, a variety of strategic tools with great importance has been developed and used by businesses. Initially, Porter's Five Forces Model (Porter, 2008) is one of the most popular as it is focusing on the structural analysis of the business sector and the achievement of its highest performance, through the use of operational efficiency and competitive strategy. Other well-known tools are the SWOT Analysis (Gurel & Tat, 2017) which is used for external and internal evaluations and the PEST Analysis (Sammut-Bonnici & Galea, 2014) which is limited only to the analysis of the external environment of the enterprise. As an alternative and more comprehensive solution to the above presented strategic tools is the Goals Grid which was created by Nickols Fred. Though, he is not an academic but a business consultant he has managed, with his many years of experience in the business sector, to devise a comprehensible and easy-to-use strategic planning tool (Ledgerwood & Nickols, 2005).
The structure of “The Goals Grid” tool
Nickols (2015) created a simple tool that categorized, organized and analysed the goals of a business. The Goals Grid tool is 2x2 matrix (see Figure
Do you want something?
Do you have it?
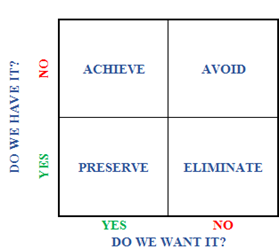
Even if the above questions seem to be very simple, in reality they are quite complex. It is not a priori obvious that managers can give a detailed response. Consequently, it is proposed, in a first step, to simplify the process, giving the possibility to respond only by “Yes” or “No” inducing four thematic categories of targets. (Ledgerwood & Nickols, 2005).
The resulting categories are as follows:
Achieve: This category includes all the goals that a company wants to achieve in order to develop and optimize its operation. Executives focus and invest more in this target group than others, believing that through them the business can be more competitive, enter new markets, increase profitability, and stand out with innovation. The executives in order to configure the targets of the business in which they work for, should take into account factors that arise from both enterprise's internal and external environment (Sassi, Pihlak, & Haldma, 2017). As for the internal environment, it is influenced by the leadership, human resource and the culture of the company, while in contrast the influences of the external environment arising from the political, social, economic and technological field (Voiculet, Belu, Parpandel, & Rizea, 2010).Preserve: The preserved goals are elements that have already had a company and contribute to the consolidation of the market, the development and creation of a positive image for business’s customers and do not want to achieve, avoid or eliminate any of them. All that wants an enterprise is to keep these goals and improve them as much as possible in order to continue its good progress in the area of its activity. Examples, which may be part of this group of goals, for a company, is to maintain the mood of creativity and enthusiasm of existing human resources or its flexibility to adapt to new circumstances when required by its environment.Avoid: The goals to be avoided are not part of businesses and they do not wish to obtain them. They strive in any way to keep them at a distance, leaving no margin for them to penetrate into and influence them definitely. At this stage, the managers should be very cautious and give emphasis to avoid elements which are able to produce various types of problems which may reduce the efficiency, productivity, growth and profitability. Some examples of negative influences may be the stagnation of businesses in terms of their technology level or their abstention from exhibitions in where they were advertised in order to their consolidation on the market. Generally, through the set of goals to avoid, the business can consider whether it is strong in keeping out factors that can adversely affect it, but even if it has some of these elements to be able to identify which of its sections are weak and which not substantially and to make improvements where it is necessary.Eliminate: After recording the goals that should be achieved, preserved and avoided, the last thematic category in order to complete the grid concern the elimination of inappropriate goals (Nickols, 2015). Firstly, the company in order to identify those goals (if any) collects all the necessary information that will help the executives to make the right decisions. The collection of that data is a process that can be carried out either by company’s internal procedures or by external consultants. Essentially, the administration wants to protect the environment of the business from internal weaknesses which in the case of non-improvement, may turn into threats. Moreover, the identification of business risks and their management results in an optimal attainment of its goals and contribute to its more efficient operation (Kenneth & Stein, 1998). Some examples of risks that enterprises faces are the labor accidents, IT threats, mechanical damage and technological change.
Like each proposed tool, the Goals Gridpresents some positive aspects as well as negative. Consequently, it is necessary to examine in more detail its intrinsic characteristics in order to evaluate its added value.
The positive and negative aspects of “The Goals Grid” tool
Nickols's tool develops a variety of applications to demonstrate not only its efficiency but also its versatility. It is accompanied by plenty of benefits that help businesses shape their strategy. Some of the most important are analyzed as follows:
A company is confronted on a daily basis with strategic issues that must be resolved in order not to disrupt its smooth operation (Abedin, Kordnaeij, Fard, & Hoseini, 2015). Therefore it is necessary to develop a set of actions with the contribution of an appropriate strategic tool. The tool can facilitate the above process, since it separates the goals into four thematic target categories (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate). As a result, this method contributes to the sound decision-making by the enterprise as to whether to proceed on the basis of its original plan or to intervene with amendments in some of its points.
The above procedure follows an organized and logical way of thinking aimed at reducing or even avoiding mistaken movements that have occurred through accidentally or because of omission of essential factors.
The sensible configuration of the targets and their organization by using the tool contributes to good communication between the staff members of the enterprise. The good communication in an enterprise means the exchange and/or transfer of ideas among individuals, sound decision-making and coordination of activities (Hargie, 2016). The Goals Grid has all the specifications for a more efficient implementation of the communication system, since it gives the opportunity to senior executives to express their point of view. In addition, teamwork and collaboration are enhanced by providing the business with a comparative advantage against the others and improving its performance and profitability (Nickols, 2011; Cardona & Wilkinson, 2006). The creation of composed teams requires both the right choice of their members and the selection of the appropriate leader who will guide and coordinate his time in the best way.
In addition, the tool redounds to the presentation and analysis of all the products and services that provided by the company. This is achieved through the development of the dialogue between the members of the company. The main purpose is to delete those factors that obstruct the course and development of the firm or to preserve those ones that enhance its profitability and competitiveness.
Time saving during decision-making is also one of the key benefits of the tool. Given that the decision-making process is quite complex and time-consuming, and that the daily program of the executives is particularly stressed (Gasser, Fischer, & Wafler, 2011), the Goals Grid tool helps by making the decisions optimal requiring as little time as possible from the executives.
The Goals Grid tool is distinguished by flexibility, a necessary feature for the operation of businesses. Generally, the concept of flexibility does not mean to be absent in any enterprise, as the conditions around it are constantly changing. In this case, the actions of the businesses must be fast and targeted so that they can be easily adjusted without counting potential losses. The ability of the tool to process the strengths and weaknesses of the company, as well as the opportunities and risks it can face along the way, makes it ready to face any new change.
Another positive feature of the tool is its function as a shield for the business. The analysis of all factors, primarily of the negative ones, gives the company the option to eliminate or avoid anything that can prevent its growth. Moreover, the administration can be almost certain that has covered most of the negative influences that can accept and that has discovered all possible gaps that may emerge in the future.
Above all, the Goals Grid tool is the basis for the development of an efficient, practical, collective, and effective strategic plan by the company's management. It is a simple and comprehensible way of collecting and recording the target, has flexibility and adaptability and characterized by broad applications.
The advantages of the Goals Grid enhance its image and highlight its simple and targeted implementation. However, the tool is also distinguished by negative features with the most important ones to be the following:
The basic function of The Goals Grid is to record and place the goals in the appropriate thematic group based on the estimation of the individual member of the administration. The filling of the grid can reveal two types of conflicts: (i) the conflict of the individual with himself and (ii) the conflict between two or more people or between groups. The confrontation refers to a competitive state where one part tries to prevent the other from achieving its goals (Slocum, Lei, & Buller, 2014). An example of the diversity of people's views, in relation to a business issue, is the suggestion of a member to delete one of the company's products as it believes it is loss- making. In contrast, another colleague supports that the product should be retained because it is particularly innovative for the market for which it is addressed and increases the competitiveness of the business. In general, conflicts bring both positive and negative impacts on the members of the administration with the second category to prevail. Positive aspects include greatest decision making, presentation of new and innovative ideas, and better understanding of the causes of the problems that can be caused (Phillips & Thomas-Hunt, 2001). On the other hand, in the negative elements of the conflicts are included the decrease of people's ethics, the blocking of co-operation, the creation of suspicion and mistrust among conflicting members, and the cause of irresponsible behavior by some individuals (Spaho, 2013).
The two basic questions that guides the executives to complete each quadrant of the grid are the following: (i) do we want something and (ii) do we have something? The answers to the above questions are given by using YES or NO. This way of completing the thematic categories (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate) can be short and not time-consuming for the executives, but is capable of providing a complete picture of the characteristics of each factor which is presented; Do managers should devote more time to justify their choices and not simply rely on answers such as YES or NO? The questions that have arisen have to be put immediately for investigation as they can be an obstruction for the decision-making and business strategy development.
Finally, completing the four thematic categories of the Goals Grid does not require executive training. This may have negative consequences for the business and its progression, as the grid presents the goals that are involved in the preparation of its strategic plan. Therefore, executives who participate in the process, should be well informed about the strategic issue which they have to face and the way that they have to approach it. Generally, the training of human resource is good to be seen as an investment by the company and not as a cost. The training of employee is not only a development for themselves but also for the enterprise as a whole, so each entrepreneur has to follow this logic (Rakwoska & Babnik, 2015).
Evaluating performance, reviewing changes in the surrounding environment and making adjustments, are normal and necessary parts of the strategic management process and for this reason is characterized as an ongoing process (Nickols, 2016). So, it is imperative the use of strategic tools that can easily adjust to all the proper modifications that have to be done in order the chosen strategy to work better. The presentation of the Goals Grid tool shows that can guide the executives to review the strategic plan if it is necessary.
Research Method
The methodological approach of the present research is composed of two parts: the literature review and the questionnaire survey. The purpose of the literature review was twofold. Firstly, the Goals Grid tool was developed by an expert not belonging to the academic environment, the international literature the systematic presentation of this tool is very limited. Consequently, in order to evaluate its basics characteristics and functionality as well its added value for firms, it was necessary to carry out a preliminary review of the existing tools, already frequently used in order to better understand the Goals Grid tool and to proceed to a comparative analysis.
Taking into account the main results of the literature review a survey was conducted on a target and focused group of ten small and medium food firms with the implementation of interviews while in a second time, the executive staff of the selected firms were asked to fulfill an extended questionnaire. The structure of the questionnaire is based on the main research questions and consists of five parts: (i) firm’s profile, (ii) marketing actions followed by the firm, (iii) human resource, (iv) strategy and finally (v) the implementation in itself of The Goals Grid tool. The questionnaire was submitted to different executives of each enterprise. Considering the limited availability, the majority of the questions were closed ended. So, the respondents had to choose from a distinct set of pre-defined responses, such as: absolutely agree, agree, disagree, mainly disagree and absolutely.
Findings
The idea of strategic management might at first seem quite straightforward but into action is a far more complex and difficult procedure. It should analyse cross-functional business decisions prior to implementing them and typically involves the analysis of the internal and external environment, the formulation and the execution of the actions that have to take place and finally to evaluate to what degree actions plans have been successful and to make changes when desired results are not being produced. A crucial element to the strategic management is the selection of an appropriate strategic tool that will lead to the facilitation of the process. This is further corroborated by the research results from this study. Firstly, the findings of the literature review showed that the matrix of the Goals Grid tool can help businesses clarifying their goals and formulate with more precision their strategic plans. In addition, questionnaires pointed out the importance of the tool in administration’s decision-making and policymaking.
The Goals Grid tool and its contribution to the strategic management process
The presentation of the Goals Grid tool highlighted its particular contribution to the strategic management process. Generally the respondents recognize that the proposed tool can contribute to better develop of the vision and mission of their firm in its external and internal environment and consequently to better formulate the future objectives of the firm. Thus the tool enables senior managers to conceive of and implement a strategy that can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage (Hanasini, 2016). Specifically, a senior executive who participated in the survey stated that: “the fact that the objectives are divided into four different thematic categories helped our company to redefine its vision and mission. The result was the creation of a more focused strategic plan which contributes to the acquisition of competitive advantage against to its competitors”. Before a company proceed with the formulation of its strategic plan, it is vital to determine its mission and vision. Both steps can be achieved easily with the use of the Goals Grid tool. The four thematic categories of targets, which are included into the grid of the tool, guide the executives not only to clarify the goals of the company but to place or review its destination and to develop how to succeed it Also, each one of the thematic target category take into account to satisfy customers’ needs and are designed to be clear and easily understood from the senior executives. The helpful questions that are lead before the implementation of the quadrants tend to make goals more specific, short, sharply focused and realistic. The combination of the above characteristics results the company to build a solid foundation and to have a written, clear, concise and consistent mission and vision. Last but not least, the executives, by following these steps, can handle with the day-to-day operations and simplify the procedure of decision-making (Papulova, 2014). Another senior executive stated that: “our firm has greatly improved the decision-making process. Now we can better manage our goals without spending many hours to achieve the desired results”. Businesses are confronted with strategic issues in a daily basis that arise from both extraneous and endogenous factors and call for an immediate solution. Managers are urged to deal directly with risks and threats in order to avoid any negative impact on the strategic goals of the company (Pillania, 2008). For example, strategic issues can arise in relation to the culture and business identity. In this case,the manager with the contribution of the tool invites all the executives to answer to key questions, which are related to the goals of the four thematic categories (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate). This happens in order to collect the required set of information to address the problems. Then the manager, in collaboration with the rest members of the team, is able to draw up an appropriate strategic plan which is one of the most important steps of the strategic management process. Moreover, the tool can address executives to formulate a more targeted strategic plan. In other words, the tool is connected except of the activities in management with the targeting in marketing too. Targeting in marketing breaks a large market into smaller segments in order to concentrate on a specific group of customers. This way helps enterprises to develop effective marketing communication strategies (Cahill, 1997). For example, the distinction of the goals into four different thematic categories leads to the recognition of both the needs and requirements of customers. So, before the executives proceed to place the goals in each of the quadrant they take into account all those factors that they need to focus on, in order to satisfy their customers’ needs. As a result, appropriate decisions are made to establish a strategic plan that will be guided by customers’ wishes.
Finally, the respondents of the questionnaires referred that the tool does not only record the goals of a business. During its implementation it guided them to decide which goals should be achieved, preserved, avoided or eliminated something that had not met in any other strategic management tool still now. Especially, an owner of one of the companies that participated in the survey stated the following: the Goals Grid tool is not listed the goals of a company but leads to the formulation of the strategic plan in order to be achieved in the long-term future. Also, the tool helped us to revise and improve our policymaking.” Consequently, the tool can operate as a “map” for the companies. It is necessary to underline the importance of the instructions provided by the tool through the four thematic targets: following them precisely, the respondents are really able to reach their final objective which is nothing else than the design and implementation of an active strategic plan.
Conclusion
Firms spend many human capital hours by setting or reorganizing their strategy goals as they want to avoid any mistaken in the policy making of their strategy. An appropriate strategic plan is the core for their smooth operation and by extension is the step which guides them to succeed their goals. Moreover, the fact that strategic planning is one of the basic steps of strategic management process requires special attention from companies’ side. The senior executives who are responsible for setting the strategic plan should select an appropriate tool that will match enterprise’s desires. The Goals Grid tool can be an alternative solution to all those that have been applied the last decades such as SWOT and PEST Analysis. Some of its key features are that it can be used easily by companies and it is particularly comprehensible. But the trait that distinguishes it from the rest is the four thematic categories of targets (achieve, preserve, avoid, eliminate). Especially, the logic of the different categories is to guide the senior executives regarding business’s goals and as a result to facilitate the decision-making process. As the economy can change rapidly companies should be more flexible and reorganize their power in order to compete. Otherwise, they will face different types of difficulties such as to disappear in the long –term. The Goals Grid tool can help businesses to handle with these types of problems and as a result to improve their career path. Also, the use of the tool by the executives can increase the awareness of businesses ‘environment, help them evaluate the opportunities and threats by reducing with that way future risks and motivate companies, especially the bigger, to prioritize their needs.
On the other hand, there are some characteristics of the tool that need to be thoroughly investigated in order to be improved and to avoid potential conflicts between the firm’s executives. Through the implementation of the tool, it also appears the necessity to develop training for the staff who are participated in the defining of the goals.
Finally, the Goals Grid tool can be a suitable strategic mechanism for firms. It can contribute to a great extent to the research community as its philosophy is identified with that one of strategic management process. Basically, it can determine to (i) the vision and mission of the enterprise, (ii) the internal and external factors which can affect the operation of it (positively or negatively) and (iii) clarify its goals. Last but not least, the tool is connected with the targeting market which is extremely important for the development of an appropriate strategy.
References
- Abedin, B., Kordnaeij, A., Fard, H., & Hoseini, S. (2015). Formation and identification of strategic issues in organizations: a review and classification of current studies. The International Technology Management Review, 1, 28-39.
- Bagher, N., & Milad, S. (2017). Analyzing the use of strategic management tools and techniques between Iranian firms. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 1, 1-18.
- Cahill, D. (1997).Target marketing and segmentation: valid and useful tools for marketing. Management decision, 10-13.
- Cardona, P., & Wilkinson, H. (2006). Team Work. IESE Business Scholl University of Navarra. Occasional Paper OP no 07/10 – E, 1-8.
- Cook, C., Inayatullah, S., Burgman, M., Sutherland, W., &Wintle, B. (2014). Strategic foresight:how planning for the unpredictable can improve environmental decision-making. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 531-541.
- Gasser, R., Fischer, K., & Wafler, T. (2011). Decision Making in Planning and Scheduling: A Field Study of Planning Behavior in Manufacturing. Verlag Berlin Heidelberg: Springer –11-29.
- Gurel, E., & Tat, M. (2017). Swot Analysis: a theoretical review. The Journal of International Social Research, 51, 994-1006.
- Hargie, O. (2016). The importance of Communication for Organizational Effectiveness. Braga, Portugal, 15-32.
- Hanasini, A. (2016). An overview of strategic management: an analysis of the concepts and the importance of strategic management. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 2,124-127.
- Huff, A., & Reger, R. K. (1987). A review strategic process research. Journal of Management, 2, 211-236.
- Kenneth, F., & Stein, J. (1998). Risk management capital budgeting and capital structure policy for financial institutions: an integrated approach. Journal of Financial Economics, 47, 55-82.
- Ledgerwood, R., & Nickols, F. (2005). The Goals Grid: A New Tool for Strategic Planning, 1-4.
- Maleka, S. (2014). Strategic management and strategic planning process. South African Perspective, 4-26.
- Nickols, F. (2011). The Goals Grid: A Versatile, Multi-Purpose Tool. Distance Consulting LLC, 1-7.
- Nickols, F. (2015). The Goals Grid: A tool for Clarifying Goals and Objectives. Distance Consulting LLC, 1-6.
- Nickols, F. (2016). Strategy, strategic management, strategic planning and strategic thinking, 1-9.
- Porter, M. (2008). The five competitive forces that shape strategy. Harvard Business Review, 25-40.
- Papulova, Z. (2014). The significance of vision and mission development for enterprises in Slovak Republic. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 1, 12-16.
- Phillips, K., & Thomas-Hunt, M. (2001). Conflict in Organizational Groups: New Directions in Theory and Practice. Kellogg School of Management, 38-55.
- Pillania, R. (2008). Strategic issues in knowledge management in small and medium enterprises. Knowledge Management Research & Practise, 334-338.
- Qehaja, A., Kutllovci, E., & Pula, J. (2017). Strategic management tools and techniques: A comparative analysis of empirical studies. Croatian Economic Survey, 1, 67-99.
- Rakowska, A., & Babnik, K. (2015). Human Resources Management Challenges: Learning and Development, 9-20.
- Sammut-Bonnici, T., & Galea, D. (2014). PEST Analysis. Wiley Encyclopedia of Management, 1-7.
- Sassi, M., Pihlak, U., & Haldma, T. (2017). Factors affecting strategic management attitudes and practices in creative industries organizations. Journal of Cultural Management and Policy, 1, 2224-2554.
- Slocum, J., Lei, D., & Buller, P. (2014). Executing business strategies through human resource management practices. Organizational Dymanics,43, 73-87.
- Spaho, K. (2013). Organizational communication and conflict management. Management, 1, 103-118.
- Voiculet, A., Belu, N., Parpandel, D., & Rizea, I., (2010). The impact of external environment on organizational development strategy. Munich Personal RePEc Archive, 26303, 1-4.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 October 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-070-9
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
71
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-460
Subjects
Business, innovation, Strategic management, Leadership, Technology, Sustainability
Cite this article as:
Ragazou*, K. (2019). The Goals Grid Tool: Evolves The Strategic Management Process?. In M. Özşahin (Ed.), Strategic Management in an International Environment: The New Challenges for International Business and Logistics in the Age of Industry 4.0, vol 71. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 169-178). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.10.02.15
