Abstract
The need to provide methodological, psychological, pedagogical, diagnostic, informational support to parents of children of preschool age is associated primarily with the difficulties, that parents (legal representatives) have in raising a child. It’s also associated with the urgent need for the help of various levels of specialists in strengthening and preserving children's health and full-fledged residence of the childhood period. Particular attention should be paid to the provision of information support to parents of preschool children, including those who do not attend pre-school educational organizations. It will allow them to navigate in the choice of organizations and specialists, who are ready and able to provide the necessary qualified assistance, including aspects of social and communicative personality development of preschool children. The most relevant in this regard is the creation of conditions for the disclosure of talents and abilities of each child in various cultural practices. To do this, it is necessary to develop such practice-oriented educational technologies, that will be directed not only at increasing children's motivation to learn and become involved in the educational process. It also necessary for educating the younger generation in the spirit of tolerant communication, peace, respect for the basic life values of other nations, mutual understanding and solidarity.
Keywords: Pre-school educationparents supportsocial and communicative development
Introduction
Formation of civil identity of the person and to introduce children to the historical, cultural heritage of multinational Russia
Currently approved at the state level strategic documents: Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2018 "About the national goals and strategic tasks of development of the Russian Federation for the period till 2023", the Federal Government of the Russian Federation from 29.05.2015 N 996-p "Strategy the development of education in the Russian Federation for the period till 2025". They noted the need to educate socially responsible and harmoniously developed personality on the basis of moral and spiritual values of the peoples of the Russian Federation, the national cultural and historical traditions. Especially important is the solution of these problems at the stage of pre-school and primary levels of the educational system (Zaporozhets,1986), because at this age begin to form the foundations of civic identity of the person and to introduce children to the historical, cultural heritage of multinational Russia.
Scientific and methodological support of the organization of educational process on social and communicative development of children
The efficiency of this work depends on the scientific and methodological support of the organization of educational process in educational institutions and in the family, directed primarily at social and communicative development of children and to ensure continuity in this respect between the preschool and primary levels of general education.
Problem Statement
According to the results of foreign and domestic research concluded that the degree of influence of the family on development of children is significantly higher than the pre-school educational institution. In this connection special importance is the composition and structure of a family, education and social status of parents established a family tradition and the style of communication between family members (Feldstein,1998).
When a child starts attending pre-school educational organizations, mostly are those expectations that parents put in the definition of child development and education. Change parental views and requirements to the conditions, not only provides the child to physical, psychological and emotional comfort, but also the individual trajectory of development and socialization in a prosperous society of peers and adults.
Research Questions
Identify the most popular areas to provide targeted support to parents (legal representatives) of preschool children on issues relating to the upbringing, education and social and communicative development of preschool children based on the analysis of the needs of parents.
Purpose of the Study
To analyze the needs of parents (legal representatives) preschool children in helping them address support in issues, relating to the upbringing, education and social and communicative development of preschool children
Determine the conditions for the effective provision of targeted support for parents of preschool children on issues, relating to the upbringing, education and social and communicative development of preschool children based on the analysis.
Research Methods
In the course of work used methods of theoretical research, systematization and classification, processing the empirical data, comparative studies, statistical analysis and sociological data, comparative analysis.
Findings
The feature of the modern preschool education in Russia is a very large coverage of children's social forms of education. In this regard, particular attention should be paid to the needs of parents of children under school age, which are aimed at providing targeted support for the development, upbringing and education of children in various forms of public preschool education (Vandanova & Radionova, 2018).
In August-September 2018 the specialists of Federal Institute for Educational Development RANEPA conducted a sociological survey of parents of preschool children. The survey involved 384 parents of the 32 subjects of the Russian Federation of 8 federal districts.
In the course of the survey participants showed the highest activity of the Central (22.6% of all respondents) and Privolzhsky districts (31,7% of all respondents).
Were the most active parents of children 3-7 years: the total number of respondents are parents with children from 3 to 5 years - 114 people (29.68%); and from 5 to 7 years - 146 people (38%). 88 people (22.9%) - it is the parents of children from 0 to 3 years; others - 36 (9.42%) (fig. 1).
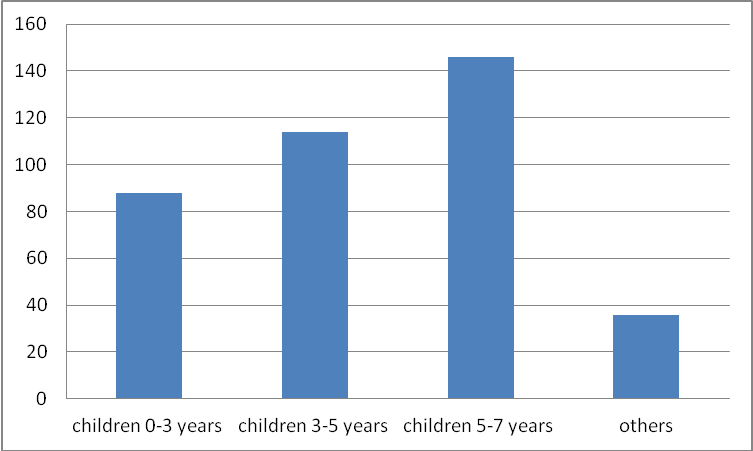
A special interest among the respondents are represents two groups of parents. It is the parents whose children attend pre-school organization at least one year (85 respondents), or do not attend at all (43 respondents).
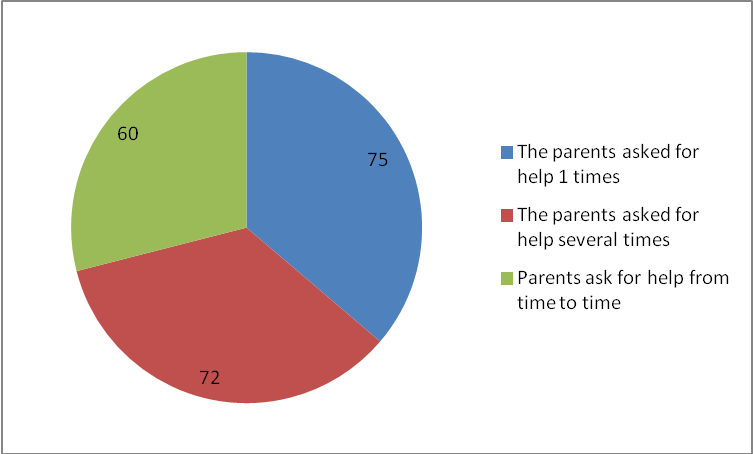
53.9% (207 people) of the total number of respondents - those parents who applied individually for expert help on pre-school education. Appeals frequency also varies: repeatedly sought help and support 72 people (34.8%); periodically turn - 60 people (29%); once asked for help 75 people (36.2%).
Among parents, seeking assistance to the skilled preschool, frequency references distributed substantially uniformly (Figure
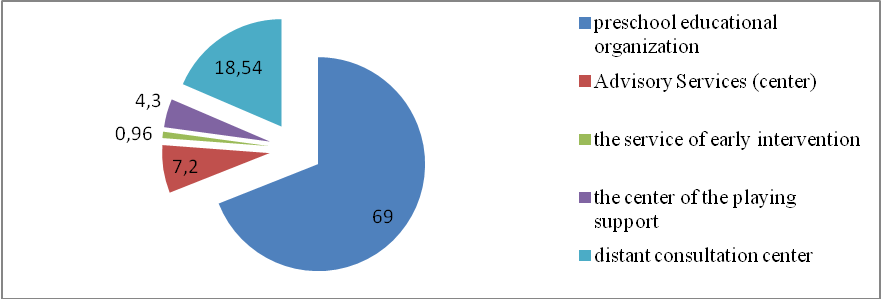
Most often, parents turn for help in pre-school organizations (69%), less often - in early support services (0.96% of the respondents) and Game Center support (4.3% of respondents). The reason for these parents is associated with lack of information about the presence of these forms of support, on the directions of the work (Figure
The analysis showed that in preschool educational organization for help turns the majority of parents - 143 people (69%); Advisory Services (center) - 15 people (7.2%); in the service of early intervention - 2 persons (0.96%); in the center of the playing support - 9 people (4.3%); in remote consultation center and more - 38 people (18.54%).
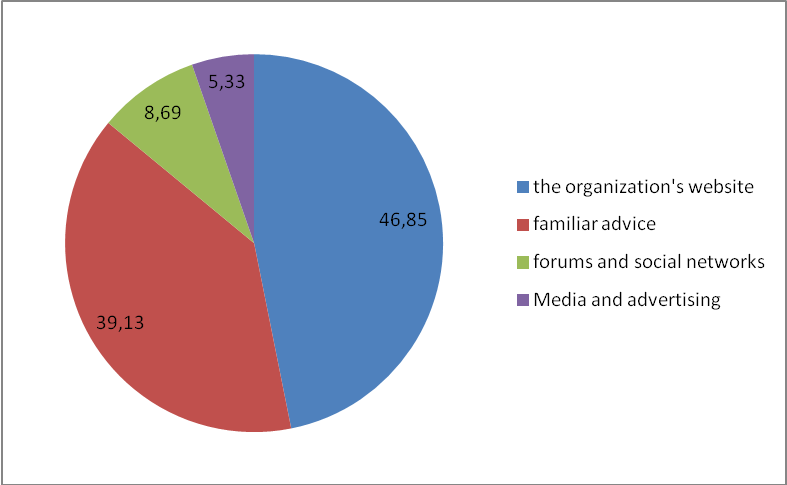
In a survey the largest number of parents noted that they receive information on training, development and education of children, especially on sites of educational institutions. But it happens, more often, by a random sample of organizations, or source of information on these organizations, they pointed to familiar people. Media and social networks, in this case are not named as a reliable and popular source of information with parents. Figure
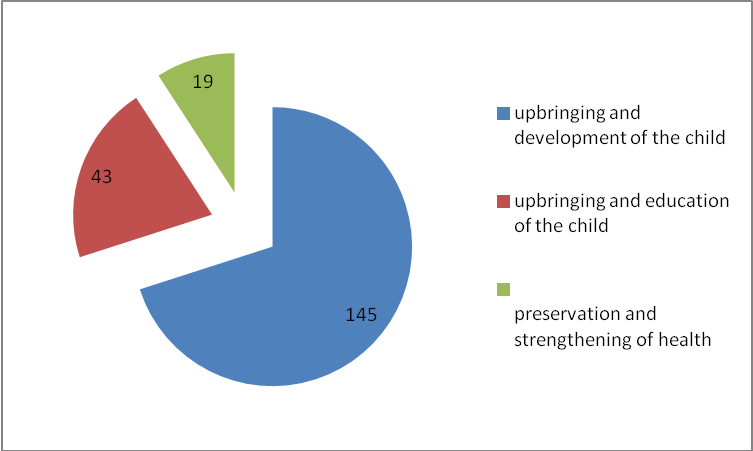
Based on parents' requests analysis of the results for support and help, we can say that with the upbringing and development of the child is due most of the questions (70%) (Figure
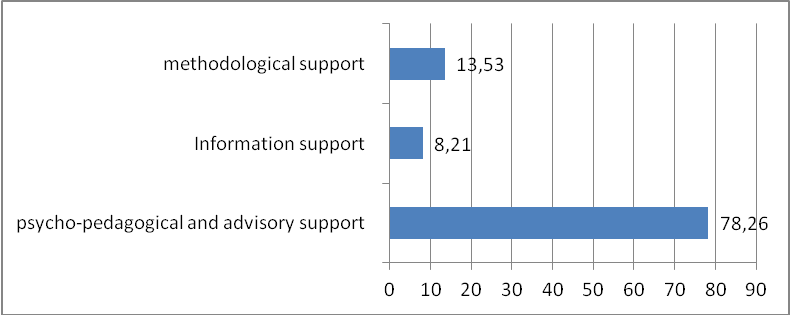
The analysis of complaints showed that the most popular among parents of children of preschool age (78.26% respondents) diagnostic, consulting, educational and psycho-pedagogical support. Only 13.53% of the requests for help related to the methodical support. The informational support is needed only 8.21% of the survey participants (Figure
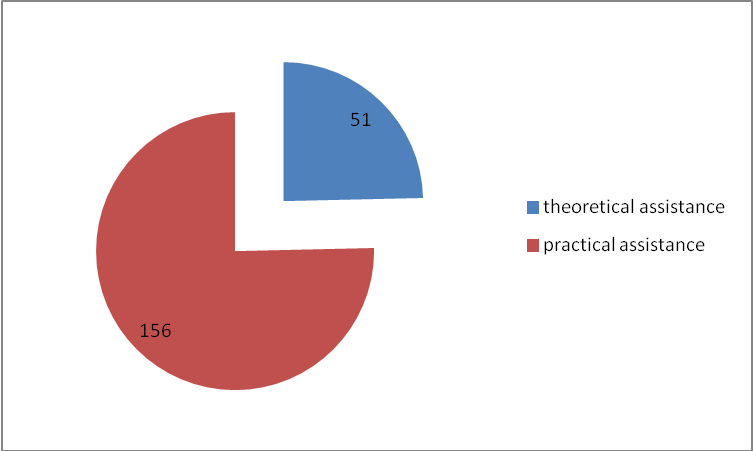
The most popular and effective for the respondents among the various types of assistance in a survey is a practical help. It takes the form of consultations at the request of parents, practical advice, joint activities with the child and others. It is worth noting that only 24.63% of the parents, to ask for help was necessary theoretical support in the form of instructions on how to interact with the child, a variety of lectures, providing a list of recommended study literature, etc (Figure
Survey respondents indicated that they had to provide expert assistance in handling. However, as noted by 54 respondents, at the moment they are still in need of professional assistance that can be given subject to a number of conditions. First of all, such conditions include the presence of experts corresponding to the request of qualification.
Identified in the survey the problems associated with education, development and education of children, which the parents (the number of those wishing denoted with) still plan to seek professional support, are shown in the list below. These include: the child's adaptation and adjustment to kindergarten - 3; education, child behavior and development - 13; the assistance of a speech pathologist - 1; speech therapy help - 11; preparing a child for school - 9; psychological and pedagogical support -3; behavior in public places - 2; consultations on the development of a child's speech-disabled person - 1; control results - 1; features Early Childhood Development - 1; on education and childhood psychology - 1; verbal and psychological development of the child - 1; behavioral modification - 1; selection of additional educational program - 1; getting the child to comply with requests adult - 1; age crisis and how to behave correctly with the child - 1; education of the child's upbringing - 1; the physical and artistic development - 1.
This list shows that over 80% of the wishes of the parents related to the problems of social and communicative nature (the socialization of children, adaptation to new conditions, the development of positive social skills with peers and adults, and others.).
With what may be due to such a serious concern of parents of preschool children on social and communicative development of children?
There can be several reasons. Firstly, it is the absence of the parents of certain knowledge and skills to enable them to prevent and correct deficiencies in the behavior of children and entering them into the society. This is largely due to excessive professional employment of modern parents, entailing the lack of time to communicate with their own child. The trend is shifting in child-rearing responsibilities to "third parties" - relatives, nurses, employees of preschool educational institutions, specialists of additional education system. Young families tend to live separately, independently of the older generations, their own conduct farming and raising children, based on their own are not so rich life experience. Broken family traditions and customs, their mechanism of transmission from one generation to another. The role of each member of the family in building family relationships is offset as a value. Pointless to explain to the children that the elderly or sick people need care and attention, based on the literature and other examples. Only in the case where children not only see, as it happens in the family, but also directly involved in the provision of such assistance and support to those in need such behavior come into their lives as the most important and reliable sample of building positive relationships with people.
Second, is the lack of necessary skills among specialists of pre-school education to provide targeted assistance to children regarding their education and training, social and communicative development.
Federal state educational standards of preschool education identified a number of targets in the field of social and communicative development of children (Oder of the Russian Ministry of Education and Science, dated October 17, 2013 № 1155 "On approval of the federal state educational standards of preschool education").
The standards say, that at the stage of completion of the pre-school child has a positive attitude to install the world, to different kinds of work, to others and to himself. Senior preschooler actively interacts with peers and adults, participated in the joint games; adequately express their feelings, including a sense of self-belief, trying to resolve conflicts. Senior preschooler is able to negotiate and to take into account the interests and feelings of others, empathy failures and rejoice in the successes of others; has a sense of self-esteem.
How to create such conditions when choosing a copyright or complex partial program when writing the basic educational program of preschool educational institution for pre-school child to develop and to demonstrate the above listed qualities?
Obviously, for this purpose it is necessary a deeper study of qualification deficits of teachers of preschool educational institutions (Efimova & Postalyuk, 2018).
The employees of the Federal Institute of Education Development RANEPA carried out a survey of pre-school education specialists on the analysis of personal resources specialist’s activity-based algorithm for identifying qualification shortfalls teaching staff of educational institutions (Golub, Kogan, Postalyuk, & Prudnikova, 2014) in 2019. Very relevant as an analysis of modern domestic and foreign programs and educational technologies, aimed at social and communicative development of children of preschool age, which will justify the necessary conditions of scientific-methodical and psychological approaches to the development of practice-oriented technology to implement federal standards in terms of social and communicative development of preschool children.
Conclusion
Special attention should be paid to the provision of information support to parents of preschool children, including those who do not attend pre-school educational institutions, which will allow them to find their way in the selection of organizations and professionals, willing and able to provide the necessary expert assistance in terms of social and communicative development of preschool personality. The most relevant in this regard is the creation of conditions for the disclosure of the talents and abilities of each child in different cultural practices. This requires the development of practice-oriented educational technologies, which will focus not only on increasing in motivating children to learn and involvement in the educational process, but also on the education of the younger generation in the spirit of tolerant dialogue, peace, respect for fundamental values in life of other peoples, mutual understanding and solidarity.
Acknowledgments
The survey is conducted as part of research work 18.4 "Analysis of the implementation of the federal state educational standards of preschool education in educational institutions, and suggestions for improvement", commissioned by the Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration on 2019.
References
- Efimova, S.A., & Postalyuk, N.U. (2018). Methodical service of the educational organization: content and tools activities: Tutorial. State budgetary educational institution of additional professional education (training) of experts Center for Vocational Education of the Samara region. Samara: ATEC.
- Feldstein, D. (1998). Childhood as a socio-psychological phenomenon and a special state of development. Voprosy Psychologii, 1, 3-19.
- Golub, G.B., Kogan, E.Y., Postalyuk, N.U., & Prudnikova, V.A. (2014). Staffing of the new technologies: the development of educational programs on request of the employer: Manual. Moscow: Federal Institute of Education Development.
- Order of the Russian Ministry of Education and Science on October 17, 2013 № 1155 "On approval of the federal state educational standards of preschool education." Retrieved from http://legalacts.ru/doc/prikaz-minobrnauki-rossii-ot-17102013-n-1155/.
- Vandanova, E.L., & Radionova, O.R. (2018). Support for families with infants and preschool children with special educational needs. In E.V. Trifonova & N.E. Vasukova (Eds.), The child - a researcher, activist, creator: the experience of "child-specific activities» organization: materials of the international scientific-practical conference (pp. 54-63). Moscow: Moscow State Pedagogical University.
- Zaporozhets, A. V. (1986). Selected psychological works. Moscow: Pedagogy.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
14 July 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-063-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
64
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-829
Subjects
Psychology, educational psychology, counseling psychology
Cite this article as:
Radionova*, O. R., Alekseeva, A. S., & Alieva, E. F. (2019). Supporting Parents In Issues Of Education And Development Of Children. In T. Martsinkovskaya, & V. R. Orestova (Eds.), Psychology of Subculture: Phenomenology and Contemporary Tendencies of Development, vol 64. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 538-547). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.07.70
