Abstract
The specialists ‘activity in the field of sports (coaches, instructors, heads of the national teams and sport school directors) is connected with the high level of psycho-emotional stress which is determined by the raising of competition, extremely stressful atmosphere of the contests and intensive toll because of increasing the volume of training process of sportsmen. Based on this, it becomes relevant to study the role of those personal factors that can reduce mental capacity for work. The specialists of different age groups from 23 to 38 years, both the young specialists and professionals with experience of 8 -15 years, took part in the experiment. As a result, it was found that the young professionals had higher rates of reduced efficiency in comparison with more experienced ones, due to the higher indexes of their mental satiety, fatigue and feeling of stress. At the same time, the level of self-government is significantly higher among specialists with experience due to such indicators as self-assessment, self-knowledge, self-development, self-criticism, with equal indicators of self-realization scales. The studying of the relationship of mental states and indicators of self-government revealed an existing interrelation between the level of stress, satiety and the scales of self-assessment, self-criticism and self-development. The obtained data allow us to conclude that young professionals experience psycho-emotional overwork due to their unwillingness to make an objective assessment of their activity and its results, to assess their own capabilities adequately and focus on self-development.
Keywords: Mental stateself-governmentspecialists
Introduction
In recent decades, the rapid development of the sports industry has been observed in Russia. On the one hand, this is caused by the construction of sports facilities (stadiums, sports complexes, sports grounds, fitness clubs) and a large number of held sports events (from urban to international ones), but on the other hand, it is connected with the increasing need of the population in sports and health services (Vasjukova, Vorob'eva, Kovalenko, & Kushtova, 2016; Valiev, Isaeva, & Ponikarovskaya, 2018).
A key factor of the sports industry functioning success is qualified personnel. In this regard, the requirements not only to the level of specialists working in the field of physical culture and sports are increased, but also to preparation of young professionals (Kolodeznikova, 2012). At the same time, according to the opinion of scientists and employers, the system of higher education is not quite ready for the dynamic development of the labor market, and experiences some difficulties in the development of those students’ qualities that will promote their adaptation to future professional activities more (Volkov, 2017).
Therefore, it is justified to focus higher education on creating conditions for the development of personal and social potential of the younger generation. The solution of this problem can be facilitated by studies that not only identify psychological problems associated with the adaptation of young professionals to professional activities, but also provide recommendations for the development of those qualities that will contribute more to the adaptation and self-realization of young professionals in the field of sports.
Problem Statement
The problem of training of specialists in the field of sports (coaches, instructors, heads of national teams and Directors of sports school) is connected on the one hand with the high requirements for them as professionals, and on the other hand with the presence of objective and subjective difficulties of specialists’ activity in the field of sports. So the number of psychological challenges can include the high psycho-emotional stress associated with the increasing competitions in sports, a stressful competitive activity, like for athletes, and for coaches. An irregular working week and working day, connected with the increasing volume of training work of sportsmen, a busy competitions schedule and frequent sport travels should be also added to the list of psychological challenges (Taran, Kolomenskaya, & Anisimova, 2018).
Problem of the emotional burnout of young professionals in in the field of sport
A number of studies have shown that the specific conditions of work in the field of sports contribute to the development of emotional burnout not only of the coaches with experience, but also young professionals (Latypov & Usmanov, 2018). There are such signs of professional burnout of specialists in the field of sports as a high level of emotional exhaustion, a high level of depersonalization and a high level of reduction of personal achievements (Khramov, 2014; Voronova & Kovalchuk, 2016).
Ways to solve the problem
To solve the existing problem, new strategies for training specialists in the field of sports are proposed. These strategies take into account the factors that contribute to the successful adaptation of specialists (Lukin & Korzun, 2018; Zagidullin & Tokar, 2017; Maslikov & Shebeshtin, 2016). Among all the factors, the key factor is the psychological one associated with the formation of the professional position of a sports teacher (Biryukova & Volkov, 2016; Sagova & Kapturova, 2017; Ulyaeva & Strelnikova, 2017; Malkin & Osipova, 2018).
Research Questions
To reveal the influence of self-management on the mental state of specialists in the field of physical culture.
In the course of the study we considered the following questions.
To study the psychological state and the self-management
To study the peculiarities of the psychological states of specialists in the field of sports, we decided on the one hand to compare such states of "young professionals" (experience up to 5 years) and "experts with the experience" (over 10 years) and on the other hand to identify the level of development of self-management among specialists in the field of sports in accordance to the length of experience.
To determine the relationship between psychological state and the self-management
To determine the relationship between the psychological state of specialists in the field of sports and the level of development of self-government is very important to prove the role of psychological factors in the adaptation of young professionals.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study was to study the difficulties of professional adaptation of young specialists in the field of sports.
According to our hypothesis, the difficulties of professional adaptation of young professionals in the field of sports are associated with their insufficient development of self-government, which provides the ability to control and allocate their own resources in the process of professional activity.
The study was conducted according to the ethics committee of the university. In the course of the research, ethical standards were observed, the principles of voluntariness and confidentiality were respected.
Research Methods
The experiment involved 20 "young" specialists (experience from 1 to 3 years), the average age of 23 years, and 23 specialists "with experience" from 8 to 15 years, the average age of 31. The study was conducted at the Institute of physical culture of the Ural Federal University of Yekaterinburg.
At the first stage, a psychodiagnostic study was conducted using the method of A. B. Leonova and S. B. Velichkovskaya – differentiated assessment of reduced efficiency states (DARS) (as cited in Vodopyanova, 2009). The DARS questionnaire is designed for individual diagnosis of subjective representation of four reduced efficiency states: fatigue, monotony, satiety, stress. The questionnaire includes 40 statements describing the feelings and sensations that may arise in the process of work.
At the second stage, all respondents participated in the study on the methodology of Andreev (1995) "Questionnaire for determining the level and type of self-government". The questionnaire is aimed at studying a set of qualities that give an idea of the individual's abilities to self-government, in any activities, as well as communication. Nine levels of abilities to self-government are allocated in this technique.
Findings
The study was conducted in accordance with the primary tasks and in stages.
The study differentiated assessment of reduced efficiency states (DARS)
The study of the psychological states of efficiency of the specialists in the field of sports is presented in the figure
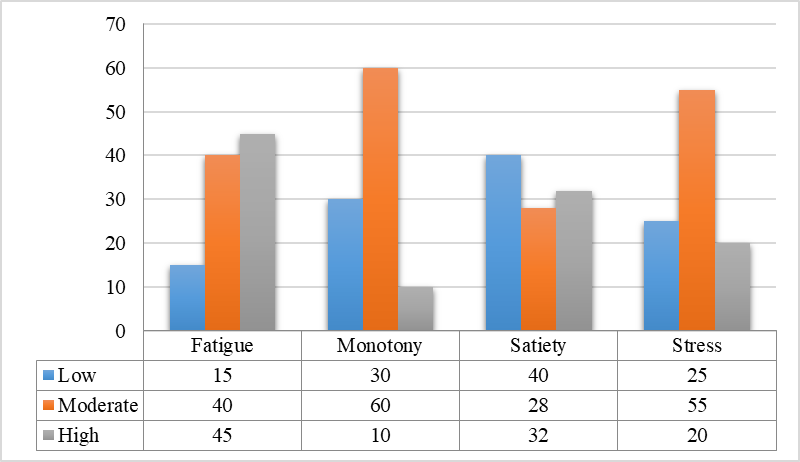
According to the data presented in Figure.
The state of fatigue occurs to young professionals as a result of prolonged and intense impact of workloads, with the dominant motivation for completion of work and rest. This fact confirms the study Kolodeznikova (2012), where it is noted that young professionals, who are focused on self-assertion and getting a higher salary, in the conditions of the sports services market, work beyond the norm of working time, that is more than 10-12 hours a day, that leads to their fatigue.
The state of monotony is moderately expressed in 60 % of young professionals, and 10 % of them have it at a high level, while the state of satiety at a moderate level is observed in 10 %, and at a high level - in 32 % of young professionals.
This may be caused by a lack of understanding among young professionals the goals of their activities and ways to achieve them, fixation not on the future, but the present, the lack of prospects, which creates a sense of monotony, leads to a loss of interest and a desire to change the type of activity.
The state of stress among young professionals is more moderate for 55 % and high for 20 % of them. This fact is consistent with the work Malkin, Rogaleva, and Bredikhina (2018), which indicates that one of the reasons for the stress of young professionals is the lack of experience and unwillingness to communicate.
The obtained data confirm the existence of the problem of reducing the efficiency of young professionals due to the experience of negative psychological states, the difficulty of adaptation to enter into professional activity.
At the same time, the data of the research on the DARS method obtained in the survey of experienced professionals have different meanings and are presented in Figure
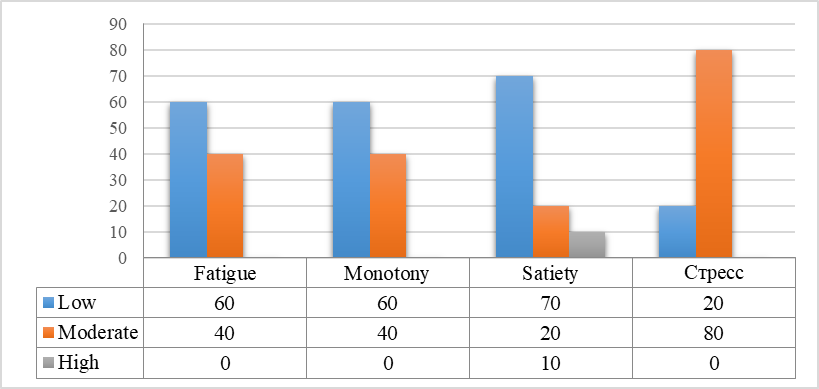
According to the Figure
On the stress scale, 80 % of experienced professionals have a moderate level, that indicates the need of mobilization and efforts to achieve their professional goals, but at the same time these efforts do not cause excessive stress as it happens with a number of young professionals.
This is confirmed by the data on the state of satiety, which is at a low level in 70 % of the specialists. It means that the majority of specialists "with experience" accept all kinds of activity and they are interested in it.
Thus, the study revealed that more experienced professionals feel less negative states of reduced efficiency compared to young professionals.
Therefore, it is important to identify those personal determinants that help them cope with their activity more successfully.
Study of the level of development of the ability to self-government
The following research was devoted to the study of the development of the ability to self-government by the method of Andreev (1995).
The data of the levels of self-government development of young professionals and experienced professionals are presented in the figure
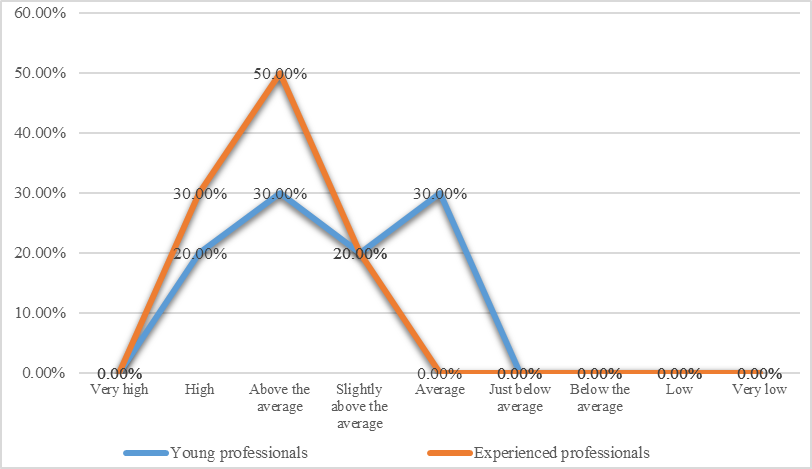
It is revealed that the experienced specialists possess higher level of self-government than young professionals have. 30 % of the experienced professionals have a high level of self – government and 50 % of them have the level which is above of average. While young professionals are characterized by such numbers: 30 % of them have an average level of self-government, 20 %t - slightly above average, 30 % - above average, and only 20 % have the high level.
The following results relate to the study of expressing the types of abilities to self-government in the study groups (figure
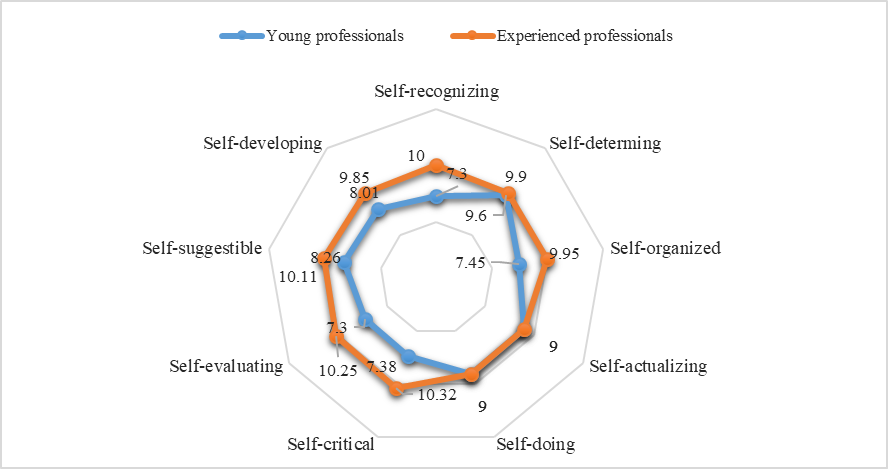
On the basis of the received data reflected in the figure
The use of the test t-Student showed the presence of significant differences in the seven selected indicators with confidence (p ≤ 0.01).
At the same time, it can be noted that there were no differences in the groups of specialists in terms of “self-actualizing” (9 points) and “self-doing” (9 points). These data, to our opinion, speak about the creative potential of young professionals, their readiness to show initiative, independence and the desire to realize their plans.
They were also identified as a dominant type of self – governing abilities - "self-determining" (9.6 points). This can be explained by the fact that the students are at the stage of self –determination at the moment of their lives. It is a long process of reflection, perhaps a revision of their life goals, guidelines.
Conclusion
The obtained data confirm the existence of the problem of reducing the efficiency of young professionals due to the experience of negative psychological states, the difficulty of adaptation to enter into professional activity.
It is revealed that young professionals experience psycho-emotional overload due to underdeveloped components of self-government, such as self-criticism, self-esteem, self-development and self-organization. This is reflected in the fact that they cannot assess their activities and their results objectively, assess their abilities adequately and focus on self-development.
The obtained results propose the necessity of further improvement of training programs and training of young professionals in the field of sports.
Improving the level of training for sports requires the study of those personal characteristics that provide better adaptation throughout a professional career.
The held research indicates the need in orientation of teaching programs and professional training for young specialists on the development of their capacity for self-government. Further direction of research should be aimed at the design of programs for the development of self-government in the students of physical education institutions.
References
- Andreev, V. I. (1995). Self-development manager. Moscow. Public education.
- Biryukova, G.M. & Volkov, I.P. (2016). Psychological aspects of the formation of the professional position of a sports coach. Actual problems of physical and special training of power structures, 4, 123-127.
- Khramov, R.V. (2014). Professional destructions in the work of the teacher sphera of physical Education and health. Bulletin of Medical Internet Conferences, 4(5), 573.
- Kolodeznikova, M.G. (2012). Problems of the modern system of professional coaching staff training. Modern studies of social problems, 2, 38-50.
- Latypov, I. K. & Usmanov, Z. T. (2018). Professional burnout of sports trainers. Physical education: education, training, 5, 62-64.
- Lukin, Yu. C. & Korzun, D. L. (2018). Problems of rapid adaptation to the initial professional activity of coaches in youth football. Collection of materials of the XI International Scientific, Practical and Educational Conference. Modern problems of physical culture and sports in the XXI century, 11, 199-202.
- Malkin, V. & Osipova, Ya. (2018). The Application of Questionnaire on Reflection in Sport. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Contemporary Education and Economic Development (CEED).
- Malkin, V. R., Rogaleva, L. N., & Bredikhina, Y. A. (2018). Emotional intelligence rating in physical education institute coach and students. Theory and Practice of Physical Culture, 11, 20-22.
- Maslikov, A. A. & Shebeshtin, O. E. (2016). Ways to improve the professionally important psychological qualities of the coach. All-Russian with international participation of an internal-correspondence scientific-practical conference. Physical culture, sport, health, 177-182.
- Sagova, Z. A. & Kapturova, V.M. (2017). Professional reflection as a factor in the success of a coach in sports. National Psychological Journal, 2(26), 26-34.
- Taran, I. I., Kolomenskaya, V.V. & Anisimova, E.V. (2018). Satisfaction of work as a factor of emotional burnout in sports teachers. Bulletin of the Kostroma State University. Series: Pedagogy. Psychology. Sociokinetics, 24(3), 212-215.
- Ulyaeva, L. G. & Strelnikova, I. V. (2017). Interrelation between psycho-pedagogical personality characteristics of a coach and his professional self-fulfillment. World of Science. Pedagogy and psychology, 5(1), 58-76.
- Valiev, Sh. Z., Isaeva, N. V., & Ponikarovskaya, A. A. (2018). Features of formation and development of the fitness services market. Vestnik USPTU. Science, education, economy. series: economics, 2(24), 7-14.
- Vasjukova, V. A., Vorob'eva, I.V., Kovalenko, N. P. & Kushtova, M.H. (2016). Innovative activity in the sphere of physical culture and sports as an integral part of the element of the national economy. ASR: Economics and Management, 3(16), 68-73.
- Vodopyanova, N. E. (2009). Psychodiagnostics of stress. St. Petersburg: Peter.
- Volkov, P. A. (2017). Analysis of necessity and availability of professional abilities and skills of employees in the field of physical education and sports. Society: politics, economics, law, 12, 74-79.
- Voronova, V. &, Kovalchuk, V. (2016). Specific manifestations of coach personality burnout in the course of professional activities. Science in the Olympic sport, 1, 46-50.
- Zagidullin, B. Kh., & Tokar, V. M. (2017). Improvement of personnel potential in the sphere of physical culture and sport: the case of republic of Tatarstan. Management of sustainable development, 6(13), 74-77.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
16 May 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-060-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
61
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-87
Subjects
Sports, sport science, physical education
Cite this article as:
Rogaleva, L., Martynova, T., Boyarskaya, L., & Shtokolok, V. (2019). The Relationship Of The Mental State Of Specialists And Their Level Development Of Self-Government. In E. Lupu, G. Niculescu, & E. Sabău (Eds.), Sport, Education and Psychology - icSEP 2019, vol 61. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 10-18). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.05.2

