Abstract
Today, we need some system actions to develop efficient financial and economic standards of Russian commercial banks, and to ensure their innovative unity with the international banking system due to the growth of macroeconomical uncertainty, financial globalization followed by law liberalization and banking market deregulation, substantial increase of the risks for business dealing, development of information and communication technologies, and enlargement of global competitiveness both in some financial intermediaries’ groups and on the interbank market. These trends have a contradictory impact on banking business. On the one hand, they stimulate the development of new promising banking products, services and technologies, but on the other hand, they intensify the competition, and stipulate mobile and original solutions. Consequently, the policy of constant changes and the implementation of innovations have become the key factor for stability, sound and balanced long-term progress, and high competitiveness in modern economic circumstances. The implementation of innovations in all business agents` activities and economic change-over to innovative evolution become both one of the state priorities that influences economic growth and structural changes in the economy, and the most important tool to maintain competitiveness of the national economy, including the banking sector. That is why, quality improvement in the banking activity (an increasing number of banking products and services, perfecting the mode of provision, improving long-term efficiency and business continuity) must become a new evolutionary stage in the banking sector. Therefore, the development and implementation of financial innovations in the banking sector is becoming currently central.
Keywords: Banking innovationsinnovative activitiesrisksfinancial innovationsfinancial productsfinancial relations
Introduction
The last quarter of XX century became a new development stage for humanity to build a postindustrial society that is the result of todays` socio-economic revolution. Every socio-economic revolution includes specific technologies, engineering and manufacturing systems, and labor-management relations. Information and high production technologies, computer systems have this role in a postindustrial society. Building a new innovative form of an economic organization must result itself. According to the Russian and foreign researches, building the innovative economy is a strategic way to develop our country at the first half of XXI century (Schumpeter, 1942; Clark, 1988).
The innovative economy is the economy based on knowledge, innovations, positive perception of new ideas, systems and technologies, and readiness to apply them practically in different kinds of people`s activities. The innovative economy pays attention to the significant role of scientific knowledge. Influenced by scientific and technological knowledge, traditional forms of material production are transforming and changing their technological base in the innovative economy because producing without new knowledge and innovations becomes inviable. Innovative technologies implementation is the main criterion to strengthen market competition, and to increase industrial growth and the quality of goods and services. Generally, we should consider innovations in any sectors and activities. The subject of this study is banking innovations that are one of the financial innovations components. The term «financial» in the innovative sphere is commodity-money relationships to form and to apply funds in the circular movement. Thus, financial innovations are an instrument to develop public production. The important difference from other innovations is that financial innovations apply capital assets as a resource to set innovative funds. Financial innovations are a resource and a way to modernize and develop commodity-money relationships. They are an indispensable constituent of the development of modern production forces and productive relations in the society. The financial environment create itself financial instruments and technologies that are the independent spontaneously developing products, and their quality and quantity is constantly growing, according with increasing macroagents` and microagents` economic needs and with the microenvironmental circumstances. That is why, the sector of financial commodities production has been formed, and it is related to financial innovations. Financial innovations are both customers` tools and a way to make business in micro and macroeconomy. They can be determined as a commodity and investment goods (Kazi, Shahbaze, & Hammoudehfg, 2018). The financial innovation is a financial product with the goal to take advantage of applying financial resources, risks profitability, liquidity position, and information underestimated in such conditions (Wang, 2018).
Problem Statement
Banking system is a source and a key provider of financial resources with differential order of priority. This fact necessitates determining some specifics of financial innovations in the banking sector, elaborating financial innovations classification, implementing practically innovative products, services and solutions, and forming strategies for innovative developing of Russian commercial banks. These steps allow banks to allocate resources in an optimum way, cut costs, increase service quality, and find new delivery ways for banking products. All this results in bank competition growth on the financial market.
One of the specificities of banking innovative business is that backgrounds to introduce technological banking innovations with information technologies are produced in other sectors (electronic engineering, computing technique and communications). Due to this, they are considered as imported ones. It generates a need for the research on the adaptive capability and introduction of modern information technologies to create new financial products, and their further application in financial decision-making by the companies.
The innovations designed by the banks, are related to structure and infrastructure changes, and to new banking products that reveal a direct interconnection with the banking service market. Thus, cost value to conduct scientific researches in a region or a city plays a prominent part. Just stepping after the innovative banking leaders, banks have only costs to purchase technologies and licenses. This fact gives rise to elaborate a study on creating new financial products in the banking sector.
Research Questions
The innovative development of the banking sector is the priority in both banking modernization and the economy. The most important aspects to study are:
Theoretical and methodological aspects to implement financial innovations in the banking business, their classifications and application. Analysis of current and promising implementations of financial innovations in Russian and international bank practices.
Problems and risks to develop financial innovations in current economic circumstances. Problem analysis to implement financial innovations in Blockchain technology. Clarifications for further development of financial products market.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the paper is to study financial innovations in the banking business, to analyze current financial products, and to work out theoretical and practical recommendations and mechanisms for their further development and implementation.
Research Methods
To carry out the research, the following methods have been used: theoretical method (systematic, reproductive, historical, and institutionally evolutionary), empiric method (a sociological survey to calculate Net-Ready international index number), mathematical statistics, graphic representations and tabular pictures with results.
As an experimental base, the Russian Central Bank statistics, the World Bank scientific reports, international credit-rating companies’ reports, and expert evaluation of the leading international scholars have been used in this research.
Findings
Banking innovation is a result of the banking innovative business, and a financial innovation applied in the banking business, which is a completely new/improved banking service, product, process or processing operation in new/traditional market segment.
Firstly, the banking innovative business specifity is that backgrounds to introduce technological banking innovations with information technologies have been produced in other sectors (electronic engineering, computing technique, and communications). Due to this, they are considered as imported ones (Economidou, Grilli, Henrekson, & Sanders, 2018).
Secondly, division into leaders and losers/simulators in the banking sector is relative, because information technologies are imported. Leading banks succeed in technological innovations implementation from other economic sectors. The relationship with the banking service market is intermediated (Huang & Zhao, 2018).
Thirdly, the innovations designed by the banks, are related to structure and infrastructure changes and to new banking products that reveal a direct interconnection with the banking service market (Tamer & Keren, 2018).
Fourthly, cost value to conduct scientific researches in a region or a city plays a prominent part. Just stepping after the innovative banking leaders, banks have only costs to purchase technologies and licenses.
Rapid evolution of information technologies, in particular innovative development in the banking sector, has allowed globalization to extend beyond the limits of financial conglomerates formed earlier, and to enter retail markets (Giudici, 2018).
Banks holding themselves out as the world leaders, have proceeded to provide online services all over the world, and stopped developing expensive retail chains (Marszk & Lechman, 2018). Today, the repartition of the e-service and communication market through the conglomeration of large banks with telecommunication businesses is coming to end (Hoa, Hao, & Wub, 2018). Rapid emergence of online banking and electronic payments through the Internet has influenced the non-bank financial institution development with traditional transreflective operations for population (lending facilities/bank deposits). As a financial organization, online banking is an innovative organization. Investments in online banking is risky.
Innovations in the banking business turn focus toward the development and implementation of goods and services that is more profitable. Peter Rose distinguishes the following reasons for the development of innovative banking services:
Increased competition and financial market deregulation (as a result, it could be an initiating of the banking service development by managers), fierce competition both between the world banking sector and the national one, and bank and nonbank financial institutions.
Tightening of the international rules of banking business regulation and sourcing the recompense for diminishing return in banking services. Reallocation tendency to increase the capital base and to decrease the assets on the balance sheet (by the aid of loan granting decrease) (Pradhana, Arvinb, & Bahmanic, 2018). Due to this, banks have to develop new risk-free forms of chargeable services to accord with international bank capital needs. They increase revenue, stand against the risky assets on the balance sheet and against the scarce fund applications. Thus, underwriting, financial planning, insurance, and mutual funds selling have a lot of play.
The profit from diversification, described as a rapid cash liquidity turnover and earnings growth due to the current banking services, consists of:
- risk level reduction by means of the financial activity diversification,
-innovative approaches to the cash liquidity turnover and to expected profit from new services implementation,
-standard fluctuation caused by cash flow or profit from active banking services,
- correlation of cash flow in innovative and current banking services,
- forecasted and scalable moneyed resources volume to produce and provide services.
4. Bank equity dependence on a possible number of services, offered to a client.
5. Service activity risk consists of the banking service extension due to the bank size growth that invariably leads to structure organizational management weakening. It deteriorates the correction retraction between innovations and growing banking needs and decreases the efficient cost supervision. Earnings growth due to the bank size growth, an economic effect of driving down costs by means of an industrial scale (more efficient use of natural resources), and an economic benefit of the successful banking services extension might be reduced to nothing by the price increase (Wang, 2018). This translates to postmortem check weakening by the bank management, and to increasing costs of new banking services development.
Public demands, innovation`s life cycle, bank competition, growing financial market globalization, banking system oligopolization, statutory regulation, introduced restrictions and changes (capital adequacy according to Basel II and Basel III), information technologies development, and banking and insurance system integration are the banking innovations factors. Innovations, designed to satisfy a consumer demand and to stimulate increased competition for leadership on the banking services market, determine the follow-on development and implementation of innovative banking goods and services (Pradhana et al., 2018). Innovations are an urgent need in the current competition circumstances.
Two interpenetrating processes of the globalization and the rapid development of information and communication technologies have influenced the image and the prototype of the current banking business. In spite of contradictory influence on the banking business, these two trends define the current world banking system. On the one hand, they bring innovative technological capabilities, but on the other hand, they strengthen the traditional and new banking authorities` influence, and demand unusual and quick decisions that have an impact on a strategic development (Sorescu, Sorescu, Armstrong, & Devoldere, 2018).
According to the banking market survey in Russia in 2017 on new and modified banking products, current pilot reforms, implemented technologies and promising strategic development in Russian financial establishments, the majority of banking innovations is oriented to private banking customers (Bayonaa & Lópezbc, 2018).
Innovations and a product development for individuals are more popular. Products for business and business process amelioration in the banks follow them (fig. 01).
According to the ARG study on the banking innovation market, remote banking, Internet banking, mobile applications, websites and marketplaces were modified more often than any other innovative banking products in 2017 (49.3%). This is not surprising, taking into account a rapid development of digital services and the reduction of off-line bank attendance. Experts from the Central Bank of Russia notice that by the middle of the next decade, there will have been 40-50% banks less than there are now.
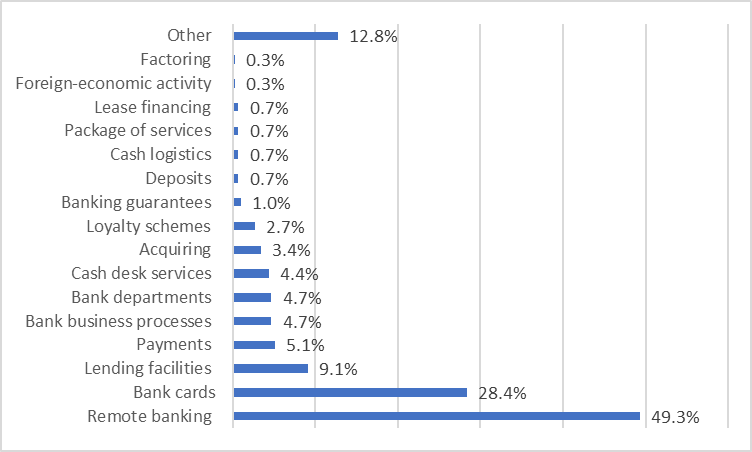
The sum of the proportions is more than 100% as some innovations are related to several products.
Bank cards are the second most popular bank products with 28.4%. They include contactless payments (Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, Android Pay and others), bracelets and rings with payment support production, and unusual kinds of bank cards. Lending products (9.1 %) are the third most popular bank products. They include SMS customer lending (Alfa-Bank), automatic cash dispenser lending (Promsvyaz bank), online registration and mortgage approval, and others.
Let us look more closely at first two items on the financial innovations market: remote banking (Internet banking) and bank cards.
Internet banking is a bank digital service that provides a customer an access to bank services from any computer, which has Internet connection with a web browser (fig. 02).
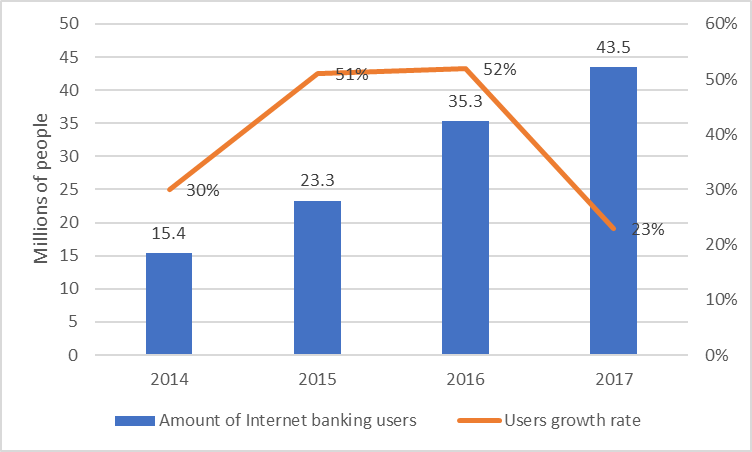
More than 43.5 million Russian people used Internet banking in 2017, a figure that is 24% higher than that one for the previous period. The number of Internet banking users has increased for more than 28 million people since 2014 (15.4 million people). The growth rate has been 183% for the period 2014-2017. More than 28 million Russian people (82%) use Sberbank Online. VTB24-Online (9%), Alfa-Click (7%) and Tinkoff Internet banking (6%) have the second, the third and the forth rate, respectively.
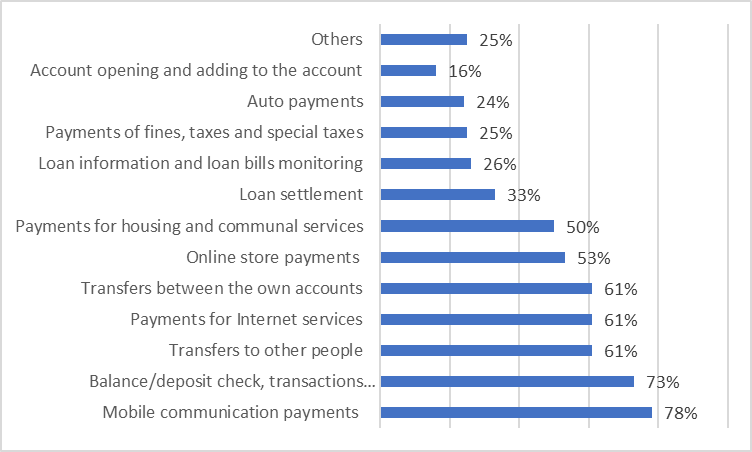
Mobile communication payments (78%) and card/deposit transactions monitoring (73%) became the highly desired features in the Internet banking in 2017. 61% people accomplished transfers to other people, payments for the Internet services, and transfers between their own accounts through the Internet banking. 53% effected online store payments. Only 2% people conducted investment products/services transactions (fig. 03).
We shall now examine the market analysis of the card banking products.
Plastic cards are one of the best examples of information technologies implementation in the banking business. An active development of this business segment proves that it is an efficient instrument for banking institutions, and it is very popular with the customers.
Pattern of the bank card utilization is considered as one of the most important indicators of the development level of the retail banking business. Plastic card is a re-usable payment product and a lending instrument of long-term use that has a high-grade security and contains the cardholder information to check the repayment ability. There has been an increase in bank cards amount for the period from 1 January 2008 till 1 January 2017. The amount of the bank cards, issued by banking institutions, had totaled 103,041,000 items by 1 January 2008, where 94,097,000 items were pay cards.
There were 147,872,000 pay cards at the beginning of 2012, 169,013,000 in 2013, 188,275,000 in 2014 and 224,617,000 in 2017.
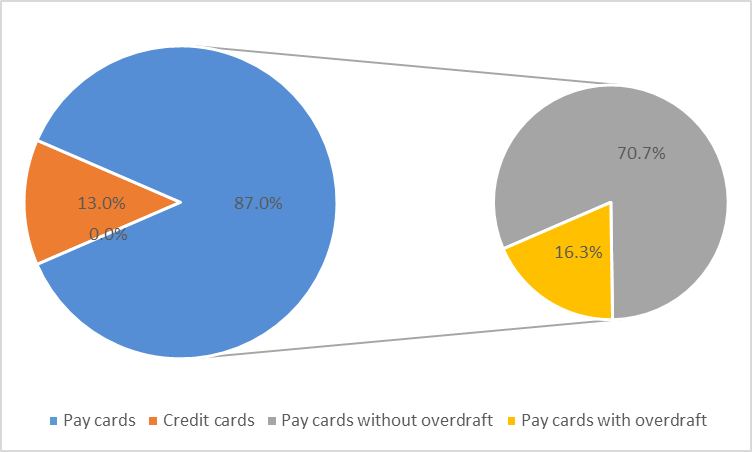
If we compare the statistical data on pay cards with overdraft from 2010 until 2017, we can make a conclusion that there has been an increase (21,268,000 items in 2010 and 34,230,000 items in 2017). According to the experts, the popularity of this bank product is due to the credit boom. The public need borrowed funds, and it is easier and more comfortable to obtain them with a card. Credit cards are bank cards that allow a customer to pay for goods services using bank assets. Classically, credit cards do not contain customer`s own funds.
We should mention the structure of pay cards and credit cards, issued by the banking institutions. Statistical data analysis has shown that, in percentage terms, pay cards without overdraft (87.0%) dominate pay cards with overdraft (16.3%) (fig.04).
Conclusion
Financial innovations have the following specifics: obligation to be practically implemented on the financial market, presence of the life cycle, involving scientific results of both financial sphere and related fields in the economic activity, market impact on the implementation and further development process, and non-applicability of the patent law that leads to the imitation in the financial innovations on the part of economic agents that have not taken part in their elaboration. Banking innovations are a separate component of the financial innovations in the banking sector.
That is because an innovative development of the commercial bank has become a shaping factor of competitiveness on the current market of banking services. Financial and banking innovations are interdependent in the context of an innovative development of the economic banking sector, and this fact standardizes the role of banking innovations in Russian innovative environment. The main motives to develop innovative banking goods and services and to implement them on both international and national financial market are the following: shaping a new paradigm of an economic innovative development, introduction of knowledge-based economy, banking innovations as a part of current economic innovations, banking business situated in the information technologies environment, bank account management through the Internet as one of the most popular banking service, use of the information concept as an integrant instrument of the economic activity.
References
- Bayonaa, A., & Lópezbc, A.L. (2018). Silent Financial Interests and Product Innovation. Economics Letters, 170, 109-112.
- Clark, J.B. (1988). The Limits of Competition. In J.B. Clark & F.H.Giddings (Eds.), The Modern Distributive Process. Boston, Massachusetts: Ginn & Co
- Economidou, C., Grilli, L., Henrekson, M., & Sanders, M. (2018). Financial and Institutional Reforms for an Entrepreneurial Society. Small Business Economics, 51(2), 279-291.
- Giudici, P. (2018). Financial Data. Science Statistics & Probability Letters, 136, 160-164.
- Hoa, C.Y., Hao, S.H., & Wub S.J. (2018). Financial Deepening and Innovation: The role of Political Institutions. World Development, 109, 1-13.
- Huang, L., & Zhao, X. (2018). Impact of Financial Development on Trade-Embodied Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from 30 Provinces in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 198, 721-736.
- Kazi, M., Shahbaze, S.M., & Hammoudehfg, S. (2018). Financial Markets, Innovations and Cleaner Energy Production in OECD CountriesMdAl. Energy Economics, 72, 236-254.
- Marszk, A., & Lechman, E. (2018). Tracing Financial Innovation Diffusion and Substitution Trajectories. Recent Evidence on Exchange-Traded Funds in Japan and South Korea. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 133, 51-71.
- Pradhana, R.P., Arvinb, M.B., & Bahmanic, S. (2018). Are Innovation and Financial Development Causative Factors in Economic Growth? Evidence from a Panel Granger Causality Test. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 132, 130-142.
- Pradhana, R.P., Arvinb, M.B., Nairc, M., Bennettd, S.E., Bahmanie, S., & Hal, J.H. (2018). Endogenous Dynamics between Innovation, Financial Markets, Venture Capital and Economic Growth: Evidence from Europe. Journal of Multinational Financial Management, 45, 15-34.
- Schumpeter, J. A. (1942). Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy. New York, NY: Harper and Brothers
- Sorescu, A., Sorescu, S.M., Armstrong, W.J., & Devoldere, B. (2018). Two Centuries of Innovations and Stock Market Bubbles. Marketing Science, 37 (4), 507-529.
- Tamer, К., & Keren, А. (2018). Can we Have a General Theory of Financial Innovation Processes? A Conceptual Review. Financial Innovation, 4 (1), 1-27.
- Wang, J. (2018). From Aperture Satellite to "Internet Finance": Institutionalization of ICTs in China's Financial Sector since 1991. Telecommunications Policy, 42 (7), 566-574.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-056-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
57
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1887
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Konovalova, M., Kuzmina, O., & Kapustina, L. (2019). Development Of Financial Innovations In The Banking Sector In Current Circumstances. In V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 57. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 869-877). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.86

