Abstract
The system of strategic management of municipal social and economic development is being adopted in Russia. In the context of digital economy, the methodology and the relevant range of tools grounding strategic decisions considering key factors of local development seem to be urgent. Russian municipal strategies usually rely on traditional factors. However, new creative factors becoming of special importance in the context of new economy are often disregarded while managing municipal development. The paper is aimed at developing methodological framework of image studies concerning municipal (local) territorial systems including the development of the relevant range of tools to identify key image forming factors of strategic development of municipal areas. The study is based upon empirical data collected by the authors in 2016–2018 while providing scientific background and developing municipal strategies. The authors worked out and successfully approved the new model of municipal development strategic planning in the context of digital economy reflecting the role of innovative creative factors of local development. The study has solved two main tasks: 1) The authors worked out the range of tools allowing to identify the key image forming factors of perspective municipal development. 2) The authors laid down recommendations for the use of the identified factors in the strategic management of municipal development. The results of the study are aimed at local self-government authorities, all key players of strategic planning in Russian municipal areas.
Keywords: Model of strategic planningplace imagestrategic managementmunicipal strategymunicipal arealocal development
Introduction
The current stage of social and economic development is considered as digital economy, with innovative sector playing an important role in it (Timofeev, Bayandin, & Kulikova, 2018). One aim of the sector is to create ‘impressions’ and attract customers’ attention as the most limited resource. This context increases the role of creative cognitive technologies and non-material assets such as image, brand, brand identity, design, etc.
Today, economic growth and competitiveness of aa territory increasingly depend upon its ability to harness the transformative opportunities of the Internet, computers, and data, to create its digital images.
Hence, place image becomes a new resource specifying economic, political and social prospects for any territory, and image technologies are increasingly used in territorial management as new instruments to impact targeting audiences. Therefore, the scope of marketing involves a broadened view of marketing (including goods, services, and places) (Kotler and Keller, 2016). The key role of marketing becomes ever more obvious in competitive success and sustainable development of territories.
Problem Statement
Marketing instruments and technologies have been broadly penetrating territorial management due to new mainstreaming line of strategic territorial management (Frolov, 2013), the use of market regulating methods along with administrative ones. Strategic management of municipal areas is the development and realization of the system of strategic decisions considering the interests of most subjects of a municipal social and economic system about its future changes in the process of interaction with a dynamic, volatile and competitive environment (Koroleva & Kurnikova, 2018).
The Samara Region traditionally spends much time and effort on strategic development: regional municipal areas started to develop their strategies in 2001. By the end of 2018, all 27 municipal raions and 10 urban okrugs will have finished their strategic planning and officially published their strategies on their sites. The researchers of the Samara State University of Economics are providing the scientific and methodological basis for most of these strategies being prepared to publish.
The monograph by Koroleva (2006) has a detailed discussion of the peculiarities of the methodological approach that was used in strategic planning. The author offers a conceptual foundation for a municipal area which is invariant to its type. In this framework it is presented as the holder of its own interests and the subject of socioeconomic relations, as a comprehensive and herewith multifunctional and multiple-aspect system (see Figure
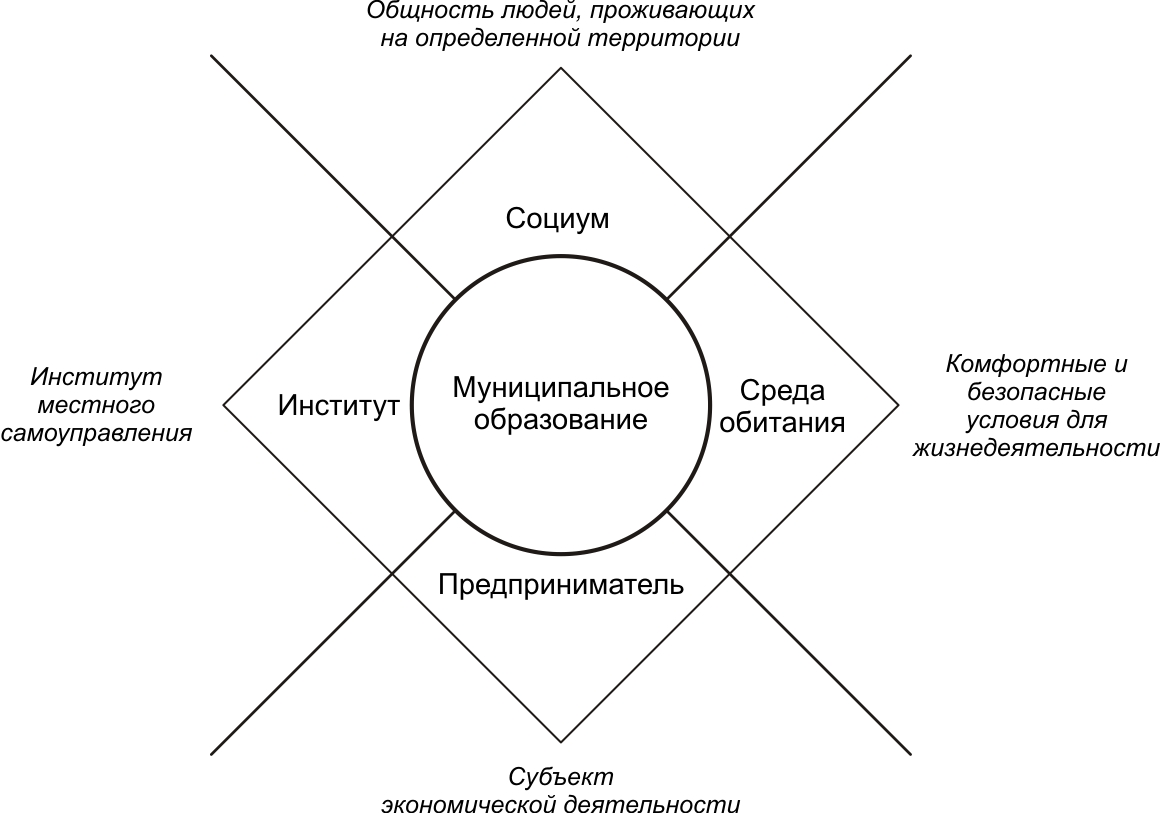
According to the first aspect, a municipal area is a community of people inhabiting a territory (a municipal area – community). This supposes the study of replacement of the population, sex-age, national and social structure; living standards of the population across social groups; educational, medical, social and psychological life aspects of urban and rural community and the formation of the appropriate strategy of social development and social policy.
The second aspect is connected with an approach to a municipal area as a living environment providing comfortable and safe living (a municipal area – living environment). This approach supposes the study of climatic and natural conditions; the issues of territorial usage; displacement of population; social infrastructure; city transport and communications; utility equipment and providing of public amenities; ecological situation; town-planning activities. These involves the development of an appropriate spatial strategy, town-planning, utility and ecological policy.
The third aspect reflects the vision of a municipal area as a subject of economic activity (a municipal area – entrepreneur), which supposes the study of its geo-economic, transport location, its place in a territorial division of labour; the system of its productive and economic potential; productive and market infrastructure; sectoral makeup of its economy; transformation of ownership; competitive ability of business, entrepreneurial, innovative and investment climate; agglomerative, inter-regional and foreign economic relations and the development of an appropriate strategy of economic development, innovative and investment policy.
According to the fourth aspect, a municipal area is considered as an institute of municipal management (a municipal area – institute), which supposes the evaluation of the regulatory and legal framework of its administration; institutional structure and the system of its management; budget potential; the study of the interrelations between municipal governing bodies and local businesses, federal bodies within a region where it is located, other regional municipalities; the study of the municipal area as a subject of globalized economy, the system of intermunicipal interaction; the finding of the interest system of local community and the formation of the system of common goals, the strategies of their achievement, including competitive strategies.
This conceptual foundation is mainly based on material (natural resources, productive funds and infrastructure) and non-material factors (labour resources and intellectual potential, cultural and historic heritage, financial potential. However, new (creative) factors such as place image, brand and place reputation – are disregarded. It is obvious that new context of digital economy sufficiently changes traditional economic principles and laws impacting local development (Lebedinskaya, Timofeev, Abyzova, & Berger, 2018). Thus, in the new economy, the development of world electronic networks, computers and software, digital technologies, electronic products and services cardinally changes the content, balance and importance of material and non-material, geography and distance, space and time, value proposition and cost, quality and quantity, competitive ability and customer preference, intermediary and logistics, human capital and business ethics, transactions and efficiency, the behavior of salesmen and purchasers, new relationship between producers and customers, marketing and sales technologies, etc.
With most socio-economic relations being transferred into virtual space, municipal areas as subjects of digital economy assume one more aspect of their development together with the four above mentioned (see Figure
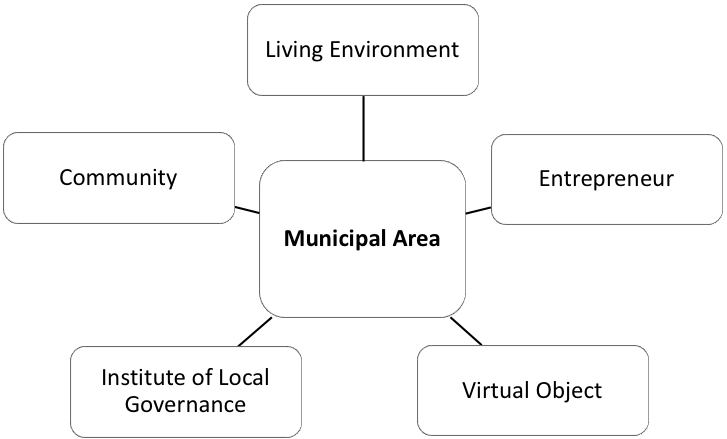
The additional aspect reflects the conceptual framework of a municipal area as an object of virtual reality and a subject of digital economy. This involves the study of the complex of non-material (image) insights, value of the territory, value of the resources, municipal positioning, comfort and uniqueness of the territory, attractiveness of the territory, value and charisma of its leaders, cognitive control of the area, participative management, communication and information transparency and availability, satisfaction level of the population.
The reason to include the new aspect into a traditional municipal model mainly is determined by real-life issues.
The problems of image constructing by nations (Anholt, 2007, 2010), countries (Dinnie, 2015), macroregions (Zenker, Braun, & Petersen, 2017), cities (Prilenska, 2012; Antirroiko, 2005), local places (Hankinson, 2009), tourist destinations (Almeyda-Ibáñez & George, 2017; Blain, Levy, & Ritchie, 2005; George, Henthorne, & Williams, 2017; Gartner, 2014) have become an object of scientific interest and practical developments in foreign studies since 1990s. They focus on image technologies and branding as a factor of economic growth (Prilenska, 2012), socioeconomic development and improved life quality of people (Kavaratzis, 2005). The strategic approach to developing place image was primarily understood at national level and successfully used by Australia, Hong Kong and Spain and later adopted by European and North American megapolises – Barcelona, Paris, New-York, Toronto, later by other cities – Ahmadabad, Montevideo, Accra, Chongqing, etc. Overall, all these studies are based on methodological framework for commercial branding, adjusted to multifaceted and complex nature of places and communities consisting of independent and competing businesses, products and developments.
In recent years, due to the necessity to implement the Federal Law No 172 on the development of municipal socioeconomic strategies, a number of publications appeared that reflected the practical image positioning of municipal areas in the Republic of Tatarstan (Galeeva, 2009), the Republic of Mordovia (Neretina & Tcharaeva, 2012; Kudrina, Yudina, & Mukhamedieva, 2015), the Kemerovskaya Oblast (Karavaeva & Gutova, 2012), the Belgorod Oblast, etc. Likewise, we can highlight the papers presenting positive image as a factor of certain municipal spheres development: tourism (Shcherbakova, 2013), culture (Startseva, 2015), investment attractivity (Firsov, 2013).
However, the role of image is often disregarded while developing municipal areas that degrades the results of strategic planning. This primarily concerns the stage of diagnostic and competitive analysis aimed at discovering factors and potentials of local prospective development. Usually, the analytical stage is supplied by most detailed guidelines. We should acknowledge that there are no official generally accepted guidelines on developing municipal strategies in Russia, which are addressed to any municipal area. Each Russian region solves the problems of methodological support of municipal strategic planning of municipal areas situated on its territory in its own way. According to our estimates, image is not mentioned in any regional official methodical document among local factors of prospective development which should be analyzed.
The same conclusion refers to scientific publications researching best practices of strategic development of towns and rural areas (Zhiharevich, Lebedeva, Ruseckaya, & Pribyshin, 2017).
Thus, the issues of place image and new factors of local development are studied piecewise. There are no studies containing methodical tools to identify image factors for localities, that is why image cannot be used in strategic planning. These sidelines and degrades the quality of grounding strategic decisions for most Russian municipal areas and restrict the opportunity to use image as a necessary tool of strategic management on the stages of goal-setting and strategies for achieving goals within the new model of municipal strategic planning imposed by digital economy.
Research Questions
The research is aimed at three main tasks:
1) Working out the new model of municipal strategic planning imposed by digital economy and reflecting a municipal area as a virtual object possessing a certain image.
2) The development and approbation of the range of tools to identify key image factors of municipal prospective development within the aspect ‘Municipal area – Virtual Object’.
3) The substantiation of guidelines to use the identified factors in strategic management of municipal development.
Purpose of the Study
The study is aimed at developing methodological basis for researching local (municipal) image, including the working out of the range of tools to identify key image factors of municipal strategic development and to use them while setting goals of local strategic development (mission, general goal, strategic goals).
Research Methods
The research is based on empirical data collected by the authors in 2016-2018 while providing scientific support for working out the strategies of socioeconomic development of municipal raions of the Samara region.
The research uses sociological methods (questioning, interviewing, polling) due to the following reasons:
Local image as a whole of representations (stereotypes) about a certain area has a limited number of components, whose precise identification may be achieved by sufficient representativeness of the sampling.
The phenomenon of image has no standard and units of measurement that restricts the use of quantitative and qualitive researches.
The sociological survey was conducted in two rural municipal raions of the Samara region. Their brief description is presented in Table
The main method of sociological survey was unrestricted random sample enabling high level of representativeness.
The sociological survey in the Alekseevskiy municipal raion was conducted in May, 2016 by sampled questioning of 270 respondents, the Bezenchukskij municipal raion held this stage of strategic planning in February 2018, with 493 respondents participating in the questioning.
To carry out the questioning, we developed the questionnaire whose questions were divided into three sets. The sets (combining similar questions) with the number and type of questions are given in Table
The first set questions enabled to obtain the portrait of respondents: sex, age, social status and the period of living in the municipal area. The second set questions were investigative and involved the estimation of socioeconomic situation in the municipal area influencing local image. This set consisted of 4 questions whose answers allow to sound out respondents’ view of local socioeconomic situation and perspectives of its development; 2 questions aimed at investigating respondents’ attitude to their home area. The third set contains mostly open-ended questions enabling to research the main resources that are necessary to use while designing a positive image as a factor of municipal strategic development. Moreover, here the method of semantic differentials was used, with each end of the scale marked is with opposing statements. It enabled to define deep-seated, unconscious characteristics of the rations.
We used simple and complex grouping while processing the results. The method enabled to carry out an in-depth study of the main image-forming features of the municipal raions which can be used as a resource of local development.
Findings
Social and demographic portrait of respondents speaks for the balanced sampling. The respondents in the Alekseevskiy raion were 50 men and 220 women (18,5 и 81,5 per cent respectively); 159 men and 309 women took part in the questioning in the Bezenchukskiy raion (32,3 и 62,7 per cent respectively), with 25 people (5.1 per cent) omitting this question.
According to their social status, the group of respondents in the Alekseevskiy raion consisted of 198 working people, 40 pensioners, 20 self-employed entrepreneurs, 12 local government employers. In the Bezenchukskiy raion, 23 students, 390 workers (including employed pensioners), 49 pensioners, 8 unemployed, 6 self-employed entrepreneurs, 6 housewives participated in the survey. In both raions, most respondents are long-term residents: 81.5 and 71.8 per cent of respondents have been living for more than 25 years in the Alekseevskiy and Bezenchukskiy raions respectively.
Study methodology of image-forming factors within the aspects ‘Municipal Area – Virtual Object’
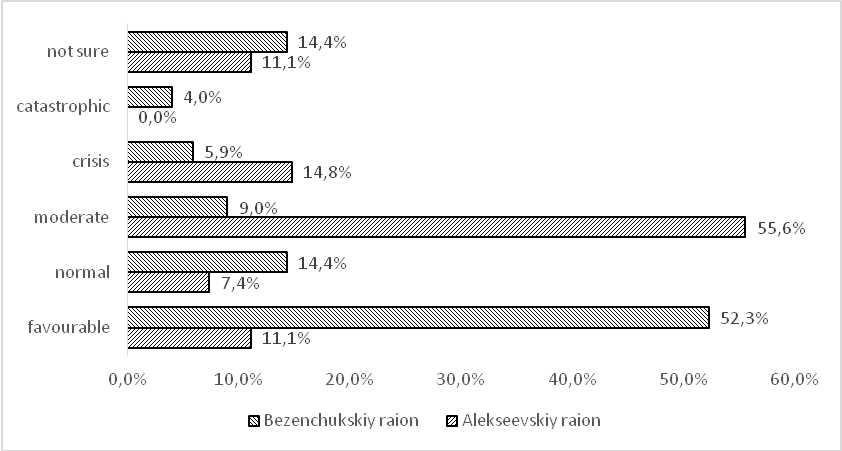
A separate set of the questionnaire consisted of the questions aimed at the estimation of the municipal socioeconomic situation by respondents. The survey showed that the position of the raions is mostly positive (estimates ‘favourable’, ‘normal’, ‘moderate’ were given by 88.9 per cent of respondents in the Alekseevskiy raion, 75.7 per cent of respondents in the Bezenchukskiy raion (see Figure
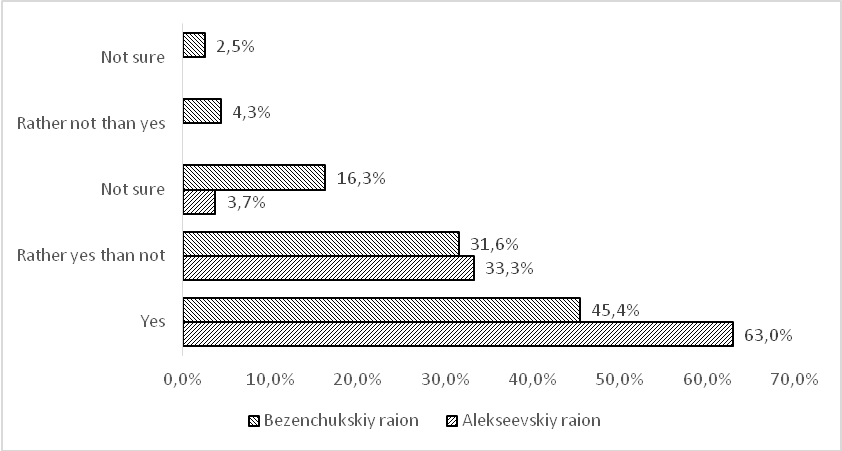
One of the sets consisting of two questions was aimed at identifying patriotism of local residents and their readiness to contribute to local prosperity. Within these questions, we asked respondents if they were patriots and what kind of contribution to local development they were ready to make. The replies sorted in the following way (see Figure
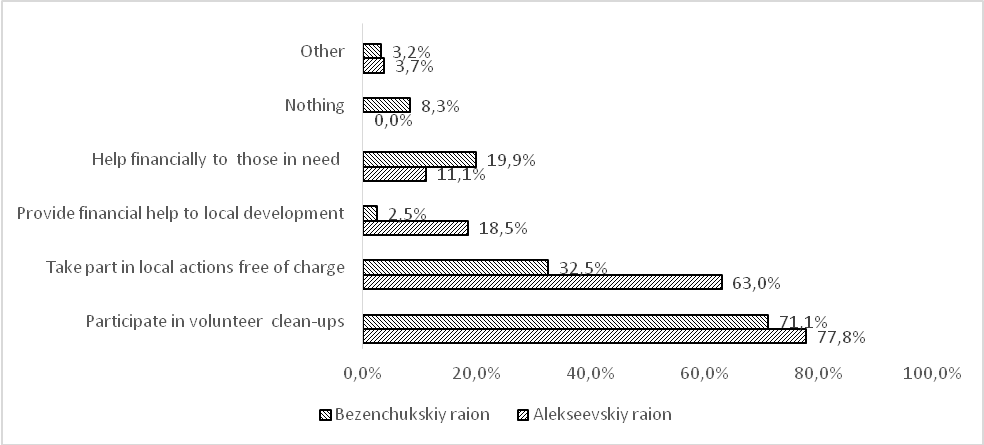
Further on, we asked respondents to express their readiness to contribute to local development asking about certain options of such contribution. The distribution of respondents answering this question is presented in Figure
Thus, 77.8 per cent of respondents in the Alekseevskiy raion are ready to take part in volunteer clean-ups; 63.0 per cent expressed their willingness to exercise initiative and take part in local actions free of charge. Less than 20.0 per cent of residents are ready to provide financial help. The situation is the same in the Bezenchukskiy raion: 73,6 per cent of respondents are ready to take part in volunteer clean-ups contributing to local redevelopment. 34.3 per cent of respondents expressed their willingness to exercise initiative and take part in local actions free of charge. Less than 3 per cent of residents are ready to provide financial help.
Within the survey, we asked respondents to design a desirable image of the raion in future, answering the question ‘How do you picture the future of the raion in 10-15 years?’ The answer to this question supposed the vision of the desirable future in a few words. Adequate replies to these questions were given in 82.1 and 72.2 per cent of respondents in the Alekseevskiy and Bezenchukskiy raions respectively. Adjusted and grouped valid replies to this question are presented in Figures
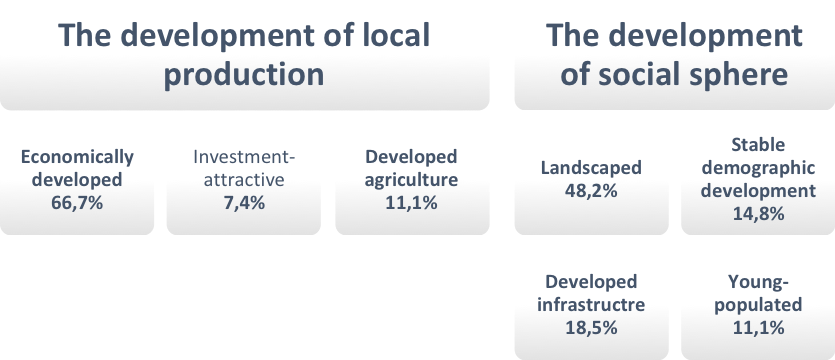
Among main advantages of the Alekseevskiy raion, the respondents named rich land resources – 22.2 percent, human resources (‘people’) – 14.8 per cent, local ecological situation – 14.8 per cent, resources to develop agriculture – 11.1 per cent, the availability of necessary infrastructure (gas, water and heat supply systems) – 7.4 per cent, cultural and historic heritage (the church and Russian author Leo Tolstoy’s country seat) – by 7.4 per cent each. Besides, among undoubted advantages the residents pointed out such positive characteristics of local people as diligence and patriotism, the readiness to do their life better – by 7.4 per cent each.
Among ‘visiting cards’ the respondents in the Bezenchukskiy raion point out the Vozrozhdeniye fish factory in Ekaterinovka (12.2 per cent) and Holy Trinity Cathedral (6.4 per cent), the Yubileyny cinema theatre (18.2 per cent), the Vasilyevsky hotel (16.3 per cent), and the famous boxing school ‘Ring’ (7.1 per cent).
The associative array of words and word combinations associated with the raions includes 19 items in the Alekseevskiy raion and 15 items in the Bezenchukskiy raion. In the Alekseevskiy raion, most respondents (37 per cent) associate it with the steppe. Two popular items yet are L. Tolstoy (14.8 per cent) and the adjective ‘native’ (11.1 per cent). Other words such as ‘sunny’, ‘field-wide’, ‘hospitable’ were pointed out by 7.4 percent of respondents each. Moreover, there were such associations as ‘horseraces’, ‘dugouts’, ‘school’, ‘oil’, ‘area of risk farming’, ‘peace’, ‘remoteness’.
Most respondents associate the Bezenchukskiy raion with such words as ‘native’, ‘favourite’ (18.5 per cent), many respondents pointed out the Volga as the main natural landmark (9.2 per cent), agriculture (9.2 per cent). There are negative images among associations – bad roads in Ekaterinovka (2.5 per cent), ‘uncertainty’ (4.8 per cent), unemployment (3.5 per cent). Other variants include the reconstruction of old buildings, white-tailed see eagle, oil production, labour, etc.
The conducted sociological survey enabled to formulate the main conclusions on the conceptual content of positive image elements providing the realization of the strategies of socioeconomic development for the Alekseevskiy and Bezenchukskiy municipal raions of the Samara Region. The results of the survey enabled to formulate the generalized perception of the raions by their residents – a complexity of emotionally coloured rational representations, convictions and feelings of inhabitants developed through their own experience of living on these territories and certain impressions. The whole of the replies got through the survey enabled to make out a symbolically expressed representation of place diversity, particularity and uniqueness, its reputation.
Such internal image of municipal raions determines the formation, maintenance and success of social identification of people with their territory. In our case, place identity developed as individual’s self-reference to a certain territorial community (municipal raion) characterizing by territorial, historic and cultural, political and legal and lingual entirety, being an interlink between a man and its place of living, a region, a country.
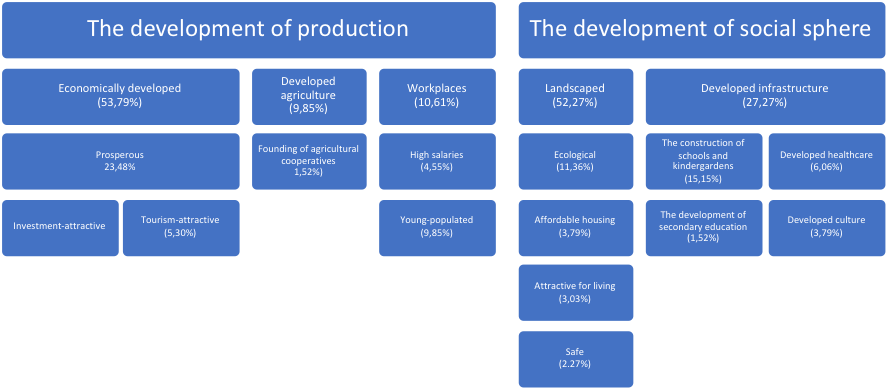
Image Factors in the New Model of Municipal Development Strategic Planning
The whole of the replies to the answer on the future vision of the municipal raions for 10-15 years (see fig.
adequate standard of living and residents’ welfare;
ecological environment and clean streets;
high level of social infrastructure, education and healthcare,
favourable conditions for work and business;
active leisure;
landscaped territory
conditions for tourism development.
With the specific character of the municipal raions under analysis, the starting points and the concepts for designing a favourable local image may become:
the peculiarities of natural potential, unique natural objects situated on the territory;
cultural and historic heritage;
traditional industries, type of production, unique opportunities for business;
population distribution principles;
everyday peculiarities of local life (including legends, anecdotes and stereotypes);
outstanding personalities, famous people.
The above-mentioned items have a potential to be promoted and positioned in municipal strategic management.
In the developed new model of municipal strategic planning image-forming features found out within the sociological survey should be used while working out the main strategic ‘triplicity’: mission – a general goal – strategic goals for five aspects of municipal perspective representation.
Let us consider the ‘triplicity’ based on the adopted Strategy of the socio-economic development of the Alekseevskiy municipal raion of the Samara Region until 2025 (see Figure
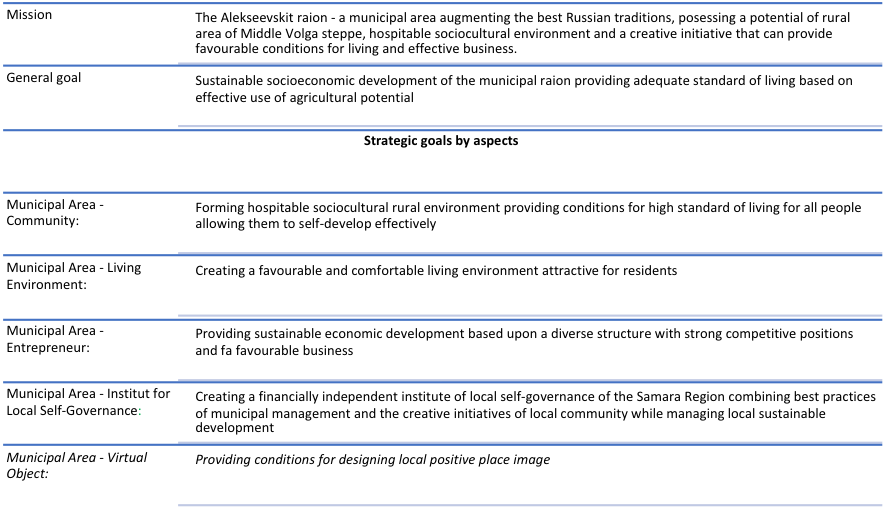

The realization of the strategic goal at providing conditions for designing a positive municipal image will be based on informational and communicative mechanisms and opportunities created by digital technologies.
The Bezenchukskiy raion has not finished yet working out the Strategy of socioeconomic development. However, the identified image-forming features will be included as conceptual components into a strategic ‘trinity’ of the municipal raion that is aimed at considering the prospective development of the area within the region, the country, the world.
Conclusion
The suggested methodological instrument tools of identifying key image-forming factors of the municipal raions as well as the practice of using image as a factor of municipal strategic development will further be embraced while conducting researches within this subject. With limited information on the practice of using image as a resource of strategic planning of municipal development, this paper is supposedly of interest for key-players of municipal strategic planning in Russia and abroad who are actively involved in strategic planning on the local level of territorial administration.
Acknowledgments
The authors of the paper express their gratitude to the Administrations of the Alekseevskiy and Bezenchukskiy raions of the Samara region for the facilitation in the organisation and conducting researches across their territory.
References
- Almeyda-Ibáñez, M., & George, B.P. (2017). “The evolution of destination branding: A review of branding literature in tourism”, Journal of Tourism, Heritage & Services Marketing, 3(1), 9-17.
- Anholt, S. (2007). Competitive Identity: The New Brand Management for Nations, Cities and Regions, London: Palgrave Macmillan
- Anholt, S. (2010). Places: Identity, Image and Reputation, London: Palgrave Macmillan
- Antirroiko, A.V. (2005). Cybercity. Encyclopedia of the City, London, UK: Routledge
- Blain, C., Levy, S.E., & Ritchie, J.R.B. (2005). “Destination branding: insights and practices from destination management organizations”, Journal of Travel Research. 43, 328-338.
- Dinnie, K. (2015). Nation Branding – Concepts, Issues, Practice. 2nd edition. London, UK: Routledge
- Firsov, Yu.I. (2013). Formirovanie imidzha territorii dlya obespecheniya ee investicionnoj privlekatel'nosti. Moscow, Russia: Financial University Under the Government of RF [in Rus].
- Frolov, D.P. (2013). Marketingovaya paradigma regional'nogo razvitiya, Volgograd, Russia: VolSU
- Galeeva, E.I. (2009). “Image Estimates of the Nizhnekamsky Municipal Area Using a Synergetic Model”, Actual Problems of Economics and Law, 2, 46-51.
- Gartner, W.C. (2014). “Brand equity in a tourism destination”, Place Branding and Public Diplomacy, 10(2), 108-116.
- George, B.P., Henthorne, T.L., & Williams, A.J. (2017). “Attraction diversity index: the concept, measure, and its relation with tourism destination competitiveness”, Revista Turismo: estudos e práticas, 5(2), 27-38.
- Hankinson, G. (2009). “Managing destination brands: establishing a theoretical foundation”, Journal of Marketing Management, 25(1-2), 97-115.
- Karavaeva, I.V., & Gutova S.V. (2012). “The Estimate of Place Image Perception”, Sociogumanitarnyj vestnik, 2(9), 28-33.
- Kavaratzis, M. (2005). “Branding the City through Culture and Entertainment”, Vienna: AESOP 05.
- Koroleva, E. N., & Kurnikova, M. V. (2018). “Place Image Factors in the Strategic Management of Rural Municipal Areas Development”, Ars Administrandi, 10(2), 294–318. https://dx.doi.org/10.17072/2218-9173-2018-2- 294-318.
- Koroleva, E.N. (2006). Strategicheskoe upravlenie razvitiem municipal'nyh social'no-ehkonomicheskih sistem v usloviyah globalizacii: teoretiko-metodologicheskie aspekty. Moscow, Russia: Tax Academy of the Russian Federation [in Rus].
- Kotler, Ph.T., & Keller, K.L. (2016). Marketing. Management. UK: Pearson
- Kudrina, E.L., Yudina, A.I., & Mukhamedieva, S.A. (2015). “Social and Cultural Technologies of Tourist Activity: a Project Approach”, Vestnik KemGUKI, 31, 207-215.
- Lebedinskaya, O.G., Timofeev, A.G., Abyzova, E.V., & Berger, E.G. (2018). GDP as the Most Important Indicator of the Global Tendencies of Economic Development in View of Production Account. In: Popkova E., Ostrovskaya V. (eds) Perspectives on the Use of New Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Modern Economy. ISC 2017. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, (97-107). Cham: Springer.
- Neretina, E.A., & Tcharaeva, A.A. (2012). “Marketing Study of Municipal Image”, Regional Economy: Theory and Practice, 45(276), 50-57.
- Prilenska, V. (2012). “City Branding as a Tool for Urban Regeneration: Towards a Theoretical Framework”, Architecture and Urban Planning, 6, 12-16.
- Shcherbakova, S.A. (2013). “The Image Formation of the Smolenskaya Region at the Tourist Market of Russia”, Regional Studies, 4, 109-113.
- Startseva, A.S. (2015). Kul'turnyj brending imidzha rossijskih regionov: tradicii i novacii, , Moscow, Russia: Moscow State Institute of Culture [in Rus].
- Timofeev, A.G., Bayandin, N.I., & Kulikova, S.V. (2018). Russia’s Problems and Potential in Accelerating the Rate of Economic Growth in the Conditions of Information Economy. In Endovitsky D., Popkova E. (Eds.), Management of Changes in Socio-Economic Systems. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (pp. 163-169). Cham: Springer.
- Zenker, S., Braun, E., & Petersen, S. (2017). “Branding the destination versus the place: The effects of brand complexity and identification for residents and visitors”, Tourism Management, 58, 15-27.
- Zhiharevich, B.S., Lebedeva, N.A., Ruseckaya, O.V., & Pribyshin, T.K. (2017). Strategii malyh gorodov: territoriya tvorchestva. St.Petersburg, Russia: Mezhdunarodnyj centr social'no-ehkonomicheskih issledovanij «Leont'evskij centr» [in Rus].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-056-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
57
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1887
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Kurnikova, M., Koroleva, E., & Timofeev, A. (2019). The Model Of Municipal Strategic Planning In The Context Of Digital Economy. In V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 57. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1469-1482). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.149

