Behavioral Strategies Skill-Building In Terms Of Socio-Professional Adaptation Of Educational Psychologists
Abstract
People today are exposed to information and emotional risks, so the importance of educational psychologist profession has increased. Nevertheless, educational psychologist profession itself is a source of stress to a person of this profession, as he must operate in a situation of constant uncertainty, connected with the problems and demands of clients, seeking psychologist’s assistance. The young educational psychologist often feels frustration from the revealed substantial differences between his expectations from the profession and the real demands of the profession on how it should be implemented. The article observes the description of skilled-experimental work on education psychological condition and methodically ensuring of socio-professional adaptation of young educational psychologists. Skilled-experimental work constituted test the efficacy of specially developed educational course “Educational psychologists chose the behavioral strategy to address difficult life situations in terms of socio-professional adaptation”, which suggests efficient ways, means, methods, technics and technologies to ensure the psychologists profession, contains all possible behavioral strategies to adapt to professional psychologists activity. The research reveals, the proposed by this article authors elective course acts as sufficient psycho-pedagogical conditions and scientific and methodological support for socio-professional adaptation of educational psychologists, as a factor of behavioral strategies skill-building through various educational forms (additional knowledges) and interactive technologies (technics and technologies). The structure of the skill of behavioral strategies selection in terms of socio-professional adaptation, the methods of diagnostics of the main structural components of the skill establishments, and mode to verify the effectiveness elective course are described in this article.
Keywords: Behavioral strategiesselection skillstructural components of the skillsocio-professional adaptationeducational psychologist
Introduction
The difficulties of adaptation to the educational psychologist profession of young specialist related to the fact that the profession itself defines the work with people and assistance to them in difficult living or non-standard situations. Stress, experienced by the young specialist during the adaptation to the educational psychologist profession period, in its intensity go beyond the ordinary people experience, which leads to decrease in motivation and interest to professional activity, to disrupt of socio-professional adaptation in general. These factors necessitate a comprehensive work on search of conditions and technologies to form among young specialists the skill of behavioral strategies selection in terms of difficult living situation, minimisation of stress negative impact on young specialists psyche. Given that behavioral strategies considers as arbitrary and deliberate acts (Lazarus, 2006), the structural components of their selection skill-building should become a psychological education, diagnostics, prevention. However, the work on search of efficient professional readiness among young psychologists for the professional hardships isn’t new. This problem was addressed by both domestic and foreign scientists.
F.E. Vasilyk considers the distinguishing feature of critical situation as the impossibility to realize one’s personal aspiration, motivation, values – everything that could be called the inner living needs. (Vasilyk, 1981).
E.F. Zeer claims that the core reason of hard situation or crisis arrives in professional adaptation of young specialist is “divergence between the real professional life and formed own perceptions and expectations about psychiatrist profession of a graduate”(Zeer, 2003). Namely the discrepancy of professional activity of a psychiatrist to own expectations and fantasies often causes difficult living situation and crisis of professional aspirations.
M. Karver and M. Sheier on the base of conducted researches argue that optimism, as the positive guidance on future, increases the intense and efficiency of one’s activity, thereby contributing to overcome the hardships in socio-professional adaptation of young specialist (Carver & Scheier, 2002). E. Ericson pointed to the possibility of positive impact of crisis situation on life of a person (Ericson, 1996). He believed that crisis situations stimulate the revision and own behavioral mode change, and contribute to self-development (Shkuratova & Annenkova, 2007).
A new specialist, adapting to a new team, to increase the efficiency of professional adaptation uses different behavioral strategies to cope with difficult living situation. The efficiency of chosen behavioral strategies, as E.F. Serdyukova believe, depends on peculiarity of professional situation and on the existence and determination of personal resources system (Serdyukova, 2018), while using them young educational psychologist tries to develop his own strategies and ways to overcome the hardships, thus formulating the skill of proper and adequate behavioral strategy selection while solving the appeared socio-professional problems.
Problem Statement
Despite significant range of researches on the theme of human behavior in difficult living situations, available studies on the problems of overcoming behavior, the problem of establishment of behavioral strategies in difficult living situations selection skill among young specialists-psychologists during the adaptation to the profession is still one of the less developed area of pedagogical and psychological theory and practice. These assertions are proved by the following revealed by the authors contradictions:
On socio-pedagogical level: contradiction between the State contractual award and employers requirements for psychologists practicing, having the skill of behavioral selection under the socio-professional adaptation and lack of adaptive training in Universities conditions;
On psychological- didactic level: contradiction between didactic possibilities of elective courses, providing the higher degree of mastering the specialized educational curricula, professional adaptation of future educational psychologists and lack of courses, providing knowledges, skills and manners in the behavioral strategy selection under the socio-professional adaptation conditions while mastering the profession;
On organizational and methodological level: contradiction between the necessity to form among the future educational psychologists the skill of behavioral strategy selection under the socio-professional adaptation conditions and zero of specially organized psychological-pedagogical conditions for qualitative improvement of the process under study.
Revealed contradictions contributed to the research question: what kind of the psychological-pedagogical conditions, that promotes formation among the future educational psychologists of the skill of behavioral strategy selection in terms of socio-professional adaptation do we have?
Research Questions
The formation among the future educational psychologists of the skill of behavioral strategy selection in terms of socio-professional adaptation is under study in this article.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to analyze the psychological-pedagogical conditions and scientific and methodological support for providing the professional adaptation of educational psychologist as the factor of the skill of behavioral strategy selection establishment.
Research Methods
In order to reach the outlined purpose these methods were used in this study: theoretical (analysis, synthesis, specification, comparison, method of analogies, abstractions); applied (questionnaire, survey, monitoring, interview, and content analysis, analysis of documentation and results of the work). For the purpose of reliable processing of the results methods of mathematical statistics, in particular Adolpf Ketle theorem, were implemented.
Findings
In a challenging modern world, full of upheaval, changes and crisis, the state of uncertainty became an inherent characteristic of a human life, consequently, the demand for understanding human behavior, the peculiarities of his choice of behavioral strategy while solving problems the state of uncertainty, has been mainstreamed. So it is crucial to get the bottom of what is the behavioral strategy in overcoming a difficult living situation.
The relevance of the problem of personal behavior under difficult living situation exploration has always been and remains at the height of interest and the prospective of its following study. The term “behavior” itself defines as “an intrinsic to living creatures interaction with the environment, through their external (motor) and inner (psychic) activity”(Karelin, 2005).
S.L. Rubinshtein defines the behavior as “external activity expression of living beings, characterized by external manifestation of physiological processes, connected to the condition, communication between people, pose, facial expressions, intonation” (Abulkhanova-Slavskaya & Brushlinskiy, 1989). Human behavior is the way of life, actions, and his attitude towards society, family, other people, and surrounding objective world. In other words, human behavior – is his narration to other people about his feelings, what is going on inside, his reaction to the environment. “Human behavior – is the subject of research of modern psychology, including the ability of human to set the goals, reach these goals in material, intellectual or social area of life” (Verzunova & Serikh, 2007). But if person faces the obstacles, preventing him from implementing these goals, setting targets do not coincide with his abilities, he is placed in a position, which psychologists called difficult living situation.
Admittedly, today there is no generally accepted definition of “difficult living situation”, but it is commonly used in scientific researches. The situation is characterized from the position of two approaches. The point of the first approach is that situation defines as “external conditions of person's active lifetime”, meanwhile, the second approach defines “situation” as the result of intense human-environment interaction. “Situation, as the objective combination of environment elements, has external, stimulating, corrective impact on the subject, being influenced by the intense impact from the subject, on its turn” (Antcypov & Shipilov, 2016). In this article we defined the difficult living situation as those life circumstances, which are beyond the settled life reality, and which couldn’t be overcame through using ways and models of behavior, formed in previous years of life (Serdyukova, 2010).
Difficult living situations has often appeared from the contradictions of external and inner world of people, and the specify of people’s psychology, who operates in a difficult living situation – is the choice of certain life behavior strategies, overcoming this contradictions, being in a constant state of search for different approaches and methods of overcame.
The theory of coping of the person with a difficult living situation or the theory “Coping” appears due to Abraham Masloy, who defined the term “Coping”, as “constantly changing cognitive and behavioral attempts to surmount the specific external of inner demands, which considers as overexertion or exceeding the capacity of a person to handle them”(in cited in Istomina, 2014).
Organized and conducted by this article authors pilot study constituted the evaluation efficiency of the elective course “Educational psychologists chose the behavioral strategy to address difficult life situations in terms of socio-professional adaptation”, which suggests efficient ways, means, methods, technics and technologies to ensure the psychologists profession, contains all possible behavioral strategies to adapt to professional psychologists activity, formulating the skill of proper and adequate behavioral strategy selection while solving the appeared socio-professional problems.
On the resulting and final phases of this pilot study young specialists-psychologists from two North Caucuses republics – the Chechen Republic and the Republic of Dagestan – participated. They were the psychologists from general education schools and pre-school institutions, who, inter alia, provided information about their own difficulties during their professional adaptation. Survey covers 90 people. There were formed two groups– experimental and control – of 45 people each. The initial level of establishment of the skill of behavioral strategy selection while adapting the psychologist profession was defined through the exploration of its structure components: cognitive-evaluative, positive-thinking, communicative-empathic, coping-behavioral.
During the study of cognitive- evaluative component the author’s tasks on their understanding of the component were used. It gave the following result. 33% of students have a high level of cognitive- evaluative component, medium and low levels – 18% and 49% of participants respectively.
26 % of students from the control group have a high level of cognitive- evaluative component, medium and low levels – 15% and 59% of participants respectively.
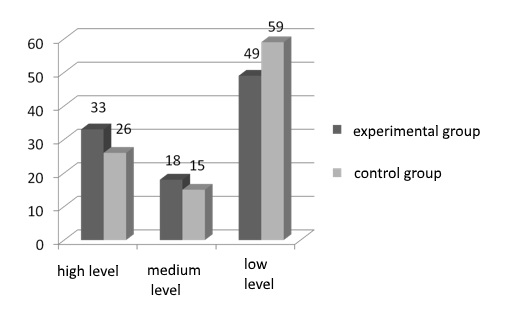
The study of positive-thinking skill component establishment among educating psychologists conducts through the diagnosis of optimistic attitude to life and motivation to success methodic of T. Echlers (Raigorodskyi, 1998). The establishments of positive thinking, motivation to success, optimism and benevolence among the participants were traced. It gave the following result.
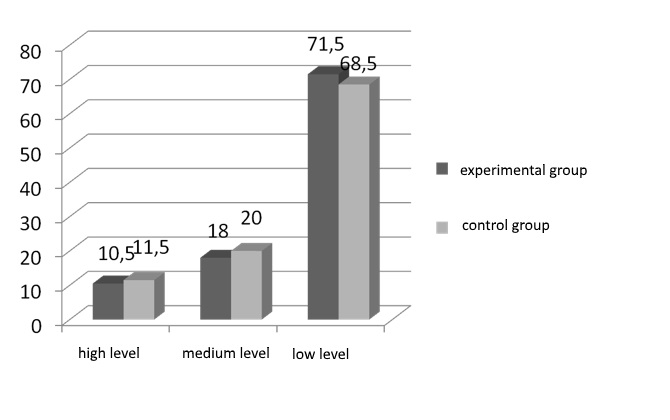
The study of communicative-empathic component assumed the exploration of participants’ capacity to make and maintain contact with clients and with other people, including communicative flexibility, mastering in a range of communicative tactics and strategies, efficiently and proper implemented into their professional activity, the ability to use complicated communicative skills and knowledges, cultural norms application restrictions on communication, customs, traditions, etiquette in the sphere of communication, keeping up appearances and good manners; the ability to focus during communicative strategy choice. These indexes monitors according to the “Methodic of communicative focus diagnosis” of V.V. Boiko (Raigorodskyi, 1998). The results are shown in the figure
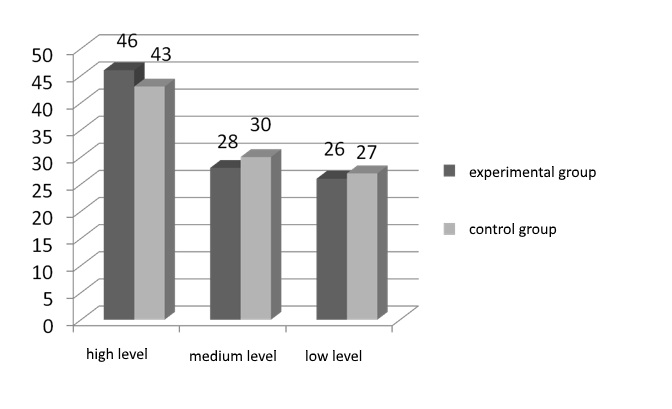
The study of coping-behavioral component revealed the ability of participants to choose efficient forms and actions, to control their own hypnotic state, readiness to solve arising life's problems, eliminate stress impact; the capacity to determine their pathways to self-fulfillment, creating the needed conditions.
While solving the given problem we use the methodic of the type of behavioral activity assessment of L.I. Vasserman and N.V. Gumenyuk (Raigorodskyi, 1998).
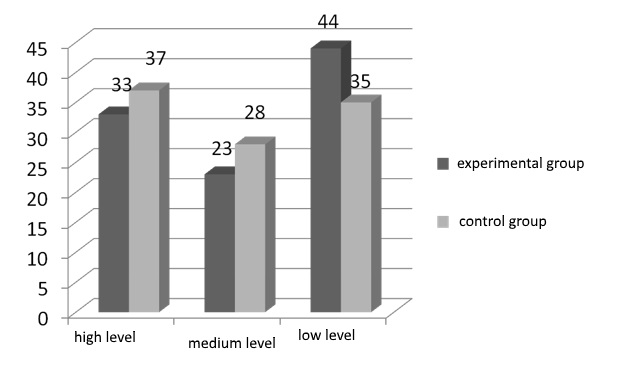
Guided by the provisions that “average amount is the compilating, combining feature of many individual indexes of some quantifiable attribute”, we conducted statistical processing of the data obtained according to the Adolf Ketle theorem (Spirin & Bashina, 2003).
It revealed the average index rate of all components among the future educational psychologist the ability to choose a behavioral strategy in terms of socio-professional adaptation. This data indicates the following indexes of behavioral selection strategy skill during the period of socio-professional adaptation: 30,7% of experimental group members demonstrate high level of skill establishment, 21,7% – medium and 47,6% – low level.
The data of control group members are the similar to data of experimental group members: 29,4% demonstrate high level of skill establishment, 23,3% – medium and 47,3% – low level.
Then there elective course “Educational psychologists chose the behavioral strategy to address difficult life situations in terms of socio-professional adaptation” was carried out in experimental group. The course had satisfied cognitive interests of the participants: formed the needed skills and knowledges, depicts the variety of behavioral strategies while coping with a difficult living situation; provided understanding of possibilities and ways of chosen professional activity realization.
After this elective course there was a repeat study with the implementation of the same diagnosis methodic, which were used during the resulting stage of experiment. The revealed data are shown on Table
With the Adolf Ketle theorem (Spirin, Bashina, 2003) we have calculated the average amount in all components of the skill under study and have got the following results, depicted in the Table
Analysis of the data received suggests the specially developed and implemented elective course “Educational psychologists chose the behavioral strategy to address difficult life situations in terms of socio-professional adaptation” serves as psycho-pedagogical condition and scientific and methodological support for the professional adaptation of educational psychologists, as the factor of establishing the skill of behavioral strategy selection. This is proved by significant decrease in the index of educational psychologists with low rate of skill component establishment – from 47,6% on resulting stage to 10,8% on final stage of the experiment; the amount of educational psychologists, who have the high rate of skill component establishment, is, vice versa, have significantly increased – from 30,7% on resulting stage to 60,0% on final stage of the experiment. The indexes of rate of skill component establishment of control group haven’t considerably changed.
Conclusion
The purpose of organization and carrying out of the pilot study was to evaluate the efficiency of the specially developed elective course “Educational psychologists chose the behavioral strategy to address difficult life situations in terms of socio-professional adaptation”, which suggests efficient ways, means, methods, technics and technologies to ensure the psychologists profession, contains all possible behavioral strategies to adapt to professional psychologists activity. The study suggests that the proposed elective course acts as the sufficient psychological-pedagogical conditions and scientific and methodological support for the professional adaptation of educational psychologists as the factor of establishment of his skill of behavioral strategy selection through different forms of education (additional knowledge) and interactive technologies (technics and technologies).
References
- Abulkhanova-Slavskaya, K.A., Brushlinskiy, A.V. (1989). Philosophic and psychological concept of S.L.Rubinshtein. To the 100th anniversary of his birth. Moscow, Science.
- Antcypov, A.Y, Shipilov, A.I. (2016). Confloctology. Textbook for university. Saint Petersburg, Piter. (6th edition revised and expanded).
- Carver, C.S., Scheier, M.F. (2002). Optimism. Handbook of Positive Psychology. Oxford, University Press.
- Ericson, E. (1996). Identity: youth and crisis. Moscow, Progress.
- Istomina, T.I. (2014). The theory of motivation of A.Masloy: Traditional approach and modernity. IV Ryazan sociological readings. Materials of an interregional theoretical and practical conference. P. 31-37. Ryazan, Publishing house of Ryazan State University named after S.A. Yesenin.
- Karelin, A.A. (2005). Big Book of psychological tests. Moscow, Eksmo.
- Lazarus, R. (2006). Emotions and interpersonal relationships: toward a person-centered conceptualization of emotions and coping. Journal of Personality, 74, 1, 9-43.
- Raigorodskyi, D.Y. (1998). Practical psych diagnosis. Samara, Bachram.
- Spirin, A.A., Bashina, O.E. (2003). General Theory of Statistics: statistical methodology in the study of commercial activities. Student book. Moscow, Finance and Statistics.
- Serdyukova, E.F. (2010). The research of strategies of difficult living situation overcoming from the position of system approach. Russian psychological magazine, 7, 4, 59-63.
- Serdyukova, E.F. (2018). The choice of behavioral coping-strategies during the adaptation to the psychologists profession. Materials of professors and pedagogical stuff conference, dedicated to the 80 anniversary of the Chechen State University. (pp. 299-302) Grozny, Chechen State University Publishing house.
- Shkuratova, I.P., Annenkova, E.A. (2007). Personality resources as the factor of coping with critical situations. Psychology of the crisis and crisis states. Interdisciplinary Yearbook, 4, 17-23.
- Vasilyk, F.E. (1981). The psychology of critical situation overcoming: Abstract of the thesis for the degree. Moscow, Moscow Lomonosov State University publishing house.
- Verzunova, L.V., Serikh, L.V., (2007). Relevant pedagogical issues in professional education: vocabulary. Bjelgorod, Publishing house of Bjelgorod regional Institute of raising professional qualifications and retraining.
- Zeer, E.F. (2003). Professional psychology: study guide for students. Moscow, Academic project; Ekaterinburg; Business book.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-057-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
58
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2787
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Serdyukova, E., Khrebina, S., & Lvovna, S. M. (2019). Behavioral Strategies Skill-Building In Terms Of Socio-Professional Adaptation Of Educational Psychologists. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 58. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1130-1137). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.02.131
