Abstract
Urbanization is associated with urban transformation based on the development of industry, transport and communications, construction, infrastructure and affects not only the social, demographic structure of the population, but also his career, distribution of productive forces and culture. Urbanization has a huge impact on the development of various socio-economic processes and phenomena, including the labour market. This study is dedicated to reviewing and identifying the characteristics of the labour markets of the largest cities in Russia. Methodical approaches to the study of this problem are analytical, statistical, comparative methods, content analysis, allowing identifying the features of the labor markets of the largest cities in Russia. The article presents a comparative analysis of the labor markets of the largest cities in Russia. The authors analyze the state of the labor market in terms of unemployment, tension, wages and career opportunities. The authors conclude that the labor markets of the largest cities in Russia are characterized by low unemployment and tension, high wages, and good career opportunities. The development of industries to ensure the financial well-being and confidence in the future, stable employment, a belief in the existence of career prospects explains the process of urbanization. It is possible to influence the competitiveness of the territory at the level of the federal and regional leadership in terms of the redistribution and use of the main factors of production and the use of socio-political factors as a mechanism for building links between regions.
Keywords: Labour marketurbanizationlarge cityunemployment
Introduction
The problems of employment of the population and the formation of labour markets in the conditions of growing urbanization are relevant and require close attention of researchers in the field of regional economics, labour economics, urban studies and economic geography. The topic of urbanization is relevant now, both for Russia and for the entire world community. The problem of employing incoming labour resources from rural areas to cities, from small and medium-sized cities to large cities, is concerned today by scientists and practitioners from all over the world about the quantity and quality of incoming labour. For Russia, the study of urbanization impact on the various areas of social development is also of great importance. The distinctive characteristics of the labor markets of the largest cities of Russia are especially interesting to study. For Russia, the study of the impact of urbanization on various spheres of social development is also extremely important. Particularly interesting for the study are the distinctive characteristics of the labor markets of the largest cities in Russia.
Problem Statement
According to UN forecasts, by 2050, 68% of the world's population will live in cities. (World urbanization, 2018). Urbanization is associated with urban transformation based on the development of industry, transport and communications, construction, infrastructure and affects not only the social, demographic structure of the population, but also his career, distribution of productive forces and culture. Urbanization has a huge impact on the development of various socio-economic processes and phenomena, including the labor market. This study is dedicated to reviewing and identifying the characteristics of the labor markets of the largest cities in Russia.
Research Questions
The article examines the labor market of million-plus cities. Labor markets Russia's largest cities have distinctive features in comparison with the labor markets of medium and small cities. In the theory of urbanism, there are several classifications of cities by population (World urbanization, 2018). The very first classification of cities in terms of population was proposed by V.P. Semenov-Tian-Shan. According to his classification, cities with a population of over 1 million inhabitants were called metropolitan (Animnitsa & Vlasova, 2010). In urban planning practice, a classification of cities is used, in which cities with a population of more than 1 million people are called the largest ones. Some authors call cities, in the administrative and territorial borders of which more than 1 million people are concentrated - cities with a million-plus population (Gontareva, 2012). A number of authors classify cities with more than one million people in a slightly different way (Bogomolova & Bogomolov, 2016). In this study, the terms «major cities» and « cities with a million-plus population» are used interchangeably, meaning cities with a population of more than one million.
The study of socio-economic indicators, territorial characteristics and production capabilities of the largest cities in the country allow to analyze their situation at the present stage and to formulate priority directions for their further development.
At present, there are lots of the ratings of Russian regions as a whole in terms of their socio-economic development and for the formation of individual sectors of the economy. Some ratings are presented in this study. Ratings on the socio-economic development of Russian cities are not so much. There are several studies on the rating of sustainable development of Russian cities. For example, E.V. Antonov, E.I. Dolgikh, V.A. Yerlich, BY. Kuznetsova was rated the sustainable development of Russian cities, which is on the basis of international experience and the principles of sustainable development of the territory, defined by international organizations and the scientific community. To build the rating of cities, an integral indicator was used - the index of sustainable urban development. This index is calculated on the basis of 30 statistical indicators characterizing the sustainable development of cities in three main blocks: economic, environmental and social unit (Dolgikh, 2015; Dolgikh, Yerlich, & Kuznetsova, 2018). Assessment and analysis of the socio-economic development of cities in various fields are presented in the works of domestic scientists and are of great scientific interest (Malykh, 2012, Konstantinov, 2018; Khamidullina & Sitdikova, 2017; Anisimova, 2014; Sokolov & Rudneva, 2017; Volkov, 2016). Problems of functioning and regulation of the labour market's largest cities are discussed in N.G. Vishnevskaya, A.V. Yakovleva, B.L. Tokarsky, Yu.B. Sosulnikov, R.R. Nasibullin and others. (Yakovleva, 2013; Zubarevich, 2013; Nasibullin, 2007; Sosulnikov, 2008; Vishnevskaya, 2014).
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to identify the characteristics and basic characteristics of the labour markets of the largest cities in Russia by studying socio-economic indicators: population size, unemployment rate, labour market tension, average wage, the ratio of wages to the cost of living, career growth opportunities. Based on the study of these indicators, the authors aim to draw conclusions about the competitiveness of the largest cities in Russia.
Research Methods
Methodological approaches to the study of this problem are the analytical, statistical, comparative methods, content analysis, allowing analysing the characteristics of the labour markets of the largest cities in Russia.
Findings
On January 1, 2018 according to the Federal State Statistics Service, in Russia there were 15 cities with a permanent population of a million or more people. For 2017 decrease of the population was registered in Nizhny Novgorod, Omsk, Samara and Volgograd. In the rest of the cities with a population of over one million people, population growth has been registered.
The main reasons for the decline in population in these cities are: the outflow of young personnel to the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg due to the lack of employment opportunities; low birth rate and high mortality rate due to the low level of medical and social services for the population, ineffectiveness of the activities carried out in these areas, despite the existing federal and regional social programs.
We are analyzing the situation on the labor markets of large Russian cities.
At the beginning of 2018 the level of registered unemployment in the Russian Federation amounted to 1.02%. The lowest unemployment rate was in Moscow (0.3%). Nizhny Novgorod, St. Petersburg, Omsk and Krasnoyarsk also entered the top five with low unemployment among cities with a million-plus population. The high unemployment rate among the largest cities of Russia was formed in Voronezh (0.8%) and Ufa (0.86%). It is worth noting that even in the largest cities-outsiders in terms of the registered unemployment rate; this indicator is below the national average (Table
A decrease in the number of unemployed in 2017 compared with 2016 was observed in all million-plus cities: Volgograd in 984 people, Voronezh in 551 people and Yekaterinburg in 1 324 people. In Kazan in 608 people, Krasnodar in 196 people, Krasnoyarsk in 1127 people, in Nizhny Novgorod in 787 people, Novosibirsk in 977 people, Perm in 83 people, Rostov-on-Don in 497 people, Samara in 1161 people, Chelyabinsk in 1806 people. Only in Omsk there was growth in the number of registered unemployed people in comparison with the year 2016 in 758 people. The reasons for reducing the official unemployment rate may be: creation of additional jobs, labor migration to larger cities, the aging of the working force . This is evidenced by the fact that reducing unemployment does not lead to an increase in the number of people employed, which is necessary for a technological breakthrough and economic growth.
By the number of vacancies declared by employers, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Krasnoyarsk, Kazan and Omsk demonstrate the best performance. The coefficient of tension in the labor market (the ratio of the number of registered unemployed to the number of vacancies) on 31.12.2017 on average was 0.62. Perm is the only largest city in which the intensity ratio exceeded the average value. The lowest rates of labor market tensions were recorded in Moscow, Omsk, Volgograd, Samara and Ufa. Tensions in the labor market have declined compared with 2016 in Volgograd, Yekaterinburg, Kazan, Krasnoyarsk, Novosibirsk, Rostov-on-Don and Chelyabinsk. In the cities of Voronezh, Krasnodar, Nizhny Novgorod, Perm and Samara there was an increase of tension in the labor market compared with the year 2016. In Omsk, tensions remained at the level of 2016.
Thus, it can be noted that the registered labor markets of cities with a million-plus population in Russia are characterized by low unemployment and a low tension ratio.
The main characteristic of the labor market is its salary. The agency «RIA Rating» conducted a study on the level of salary among Russian cities (Table
If we analyze the data on average salary in major Russian cities, it may be noted that the situation is better than the national average Moscow ranks the fifth place in the overall rating, and the lowest position is Volgograd, which is located on the 59th place. Besides Volgograd, another city among the largest (Voronezh) takes place below the fiftieth, and all other million-plus ones are located above. If we consider the rating in terms of salary only among cities with a million-plus population, the leaders here are Moscow, St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg and Krasnoyarsk .Outsiders are Volgograd and Voronezh.
As to the ratio of average salary and the cost of the consumer basket, Moscow is the most prosperous from this point of view. There, on an average salary one can buy almost three consumer baskets. Next in the rating is St. Petersburg with a ratio of the average salary and the cost of a standard consumer basket of 2.44, Krasnoyarsk (2.4), Kazan (2.28), as well as Ekaterinburg (2.25), Ufa (2.21), Chelyabinsk (2.16) and Omsk (2.16). That is, with the exception of Moscow, Russia's largest cities showed quite a similar result on the purchasing power of wages. The difference is about 28% between «leaders» and «outsiders».
Analysts of the Superjob.ru research center (IT service for job search and recruitment) have been conducting labor market surveys in the Russian Federation since 2005 to monitor the economic situation. Cities of Russia are being studied for employment attractiveness and career development opportunities for residents. Assessment is based on the following parameters:
salary level;
ratio of salary expectations and salary offers;
level of professionals remaining in the city;
gross regional product ;
the volume of investment in fixed assets;
rental housing affordability.
In 2018, a survey was conducted in 37 cities by the Research Centre of the Superjob.ru portal to assess career prospects. According to the results of the survey, the situation in cities with over one million people was analyzed and very interesting data was obtained (Figure
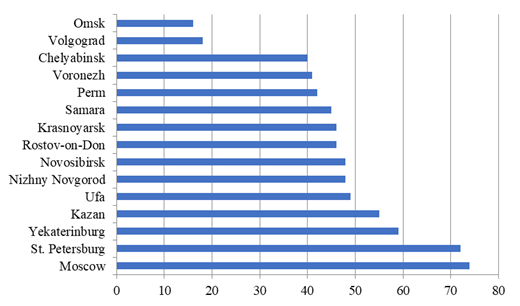
As the research data show, the highest positive expectations in terms of building a career are shown by residents of Moscow and St. Petersburg (74 and 72%, respectively). Ekaterinburg is located on the third place (59%), then Kazan (55%). From Ufa to Chelyabinsk, the ratio of optimists and pessimists regarding the prospects for career advancement is reduced from 49 to 40%. Volgograd (only 18% believe in career success) and Omsk (16%) are of particular concern in the list of cities studied. This allows us to conclude that large metropolitan cities are more economically developed than others and, therefore, more attractive to the working-age population in terms of career opportunities and professional development.
Conclusion
Thus, the analysis of various research approaches to understanding the characteristics of the labour market of large cities allows us to conclude that the situation in the labour market of the largest cities directly depends on the characteristics of their economic and social development, local policies, programs implemented and the creation of quality living conditions and prospects for further development. The labour markets of cities with million-plus populations in Russia differ from the rest by low levels of unemployment and tension, high salary, living standards and prospects for career growth. The development of industries guaranteeing financial well-being and confidence in the future, stable employment of the population, and belief in the presence of career prospects explain the process of urbanization. The competitiveness of territories and major cities can be influenced by federal and regional authorities through the redistribution and use of the main factors of production and the use of social and political tools to establish links between regions. Thus, it seems possible to equalize the regions and stabilize the situation on the labor market of the Russian Federation.
References
- Anisimova, E. A. (2014). The level of migration as an indicator of the assessment of the socio-economic attractiveness of cities (on the example of the cities with a million-plus population of Russia). Economy and entrepreneurship, 4-1, 45, 278-281.
- Animnitsa, E. G., Vlasova, N. Yu. (2010). Graduation. Ekaterinburg: Publishing House of the Urals State Economic University.
- Bogomolova, I. V., Bogomolov, S.A. (2016). Major cities as a socio-economic system: features, trends and prospects of sustainability. Sociology of the city, 3, 16-17.
- Dolgikh, E. I., Antonov, E. V. (2015). Rating of sustainable development of cities in Russia. Urbanism and real estate market, 1, 17-32.
- Dolgikh, E. I., Yerlich, V. A., Kuznetsova, P. O. (2018). Rating of sustainable development of cities in Russia for 2016. Demoscope Weekly. 765-766, 1-30.
- Gontareva D.N. (2012). The influence of million-plus cities on the development of national economic space. Economy of regional development: problems, searches, prospects. 13, 209-217.
- Khamidullina, A. M., Sitdikova, R. R. (2017). Analysis of the competitiveness of million cities in Russia. Economy and entrepreneurship, 12-3, 89, 906-911.
- Konstantinov, I. S., Zvyagintseva, A. V., Ivashchuk, O. A. (2018). Rating of Russian cities by the level and pace of housing development. Housing construction, 1-2, 34-37.
- Malykh, O. E., Polyanskaya, I. K., Shamsutdinova, A. F. (2012). Assessment of the level of socio-economic development of million-plus cities as the degree of realization of the administrative resource. Bulletin of the South Ural State University. Series: Economics and Management, 30, 289, 14-20.
- Nasibullin, R. R. (2007). Young people in the labor market of a large city. Sociological research, 11, 283, 143-144.
- Sokolov, A. A., Rudneva, O. S. (2017). Rating of the largest and largest cities of Russia in terms of the comfort of living. Population. 3, 77, 130-143.
- Sosulnikov, Yu. B. (2008). Labor markets in large cities. Scientific research in education, 1, 52-54.
- Volkov, V. N. (2016). Ratings of Russian cities by the quality of life of the population as a reflection of the effectiveness of educational systems. Continuing education: XXI century. 1, 13, 50-60.
- World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision. Retrieved from: un.org.
- Yakovleva, A.V. (2013). Features of unemployment in a large city. Economy and environmental management, 4, 18.
- Zubarevich, N. V. (2013). Major Russian cities: leaders and outsiders. Demoscope Weekly, 551-552,117.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-057-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
58
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2787
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Vyacheslavovna, A. O., Valeryevna, A. K., Gennadievna, V. N., Eduartovna, G. A., & Anvarovna, K. Z. (2019). Labour Markets Of Largest Cities Of Russia: Comparative Analysis Of Main Indicators. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 58. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 94-101). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.02.11
