Abstract
In modern conditions, when new technologies are appearing, customers’ preferences are changing. The key factor of success in the market is the right business model. When the economy is moving to the digital economy, new requirements for the business model is formed. It should be unique, profitable; the elements of the model should be adjusted. It should be complex, stable (able to face external and internal changes). The business model reflects the company’s potential, its partners, market competition, key factors, unique abilities and company competences, which determine its success, costs structure choice and value to proposition to the beneficiary. In today's realities, business faces three key challenges: maintaining business acumen; maximizing the use of critical information that is becoming increasingly complex, specific, dynamic for the benefit of the company; and coordinating multifaceted challenges to achieve synergy. These areas are necessary and relevant for any organization, as they form the need to form the basic business model, which is the basis for the development of the organization. The business model development history started more than 100 years ago. The business model is a system which is formed under the direct influence of the environment, the indirect influence of the environment and elements of the domestic environment.
Keywords: Business modelwith industrial company management
Introduction
A modern company is a combination of assets and abilities, most of which are intangible. Companies with unique abilities have a real cutting edge, which cannot be copied by other companies, and due to his fact the companies get a profit, which is higher than an average one. When developing a business strategy, it is important to find out what abilities the company possesses. For this purpose, the company’s assets and abilities should be analyzed. Slywotzky (2006), Christensen when providing justification for a business model, stress the business concept. This attitude makes it easier to understand the researched object. It helps to select and study the main elements of the business model and also the relationship between them, which companies are usually characterized by Slywotzky (2006).
The third research attitude examines particular situations and analyzes the business models of currently working companies like Xerox, Zipcar, Lego, Dell, Innosentive, Toyota, Wal-Mart and others. It should be mentioned that the research differs in terminology when conceptualizing and formalizing the currently working companies’ business models.
The business models are widely used in the age of technology entrepreneurship and venture capital investment. As this tool makes it possible to compare several projects and startups in the short period.
Problem Statement
According to Osterwalder and Pine (2013), the classical shop business model transformation started 20-30 years later. The classical model means a shop being located at the place comfortable for potential customers and demonstrating them the goods and services for sale. The business model, which is called “loss leader” (also, brown as “razor blade” or “related products”), began to be used at the beginning of the 20th century. The business model lies in that the main product should be sold at a very low price, which is lower than real value; then the main profit is obtained selling spare parts, expendable materials and others, related to “loss leader” goods and services (“hook”). For example, razors and blades, mobile phone and communication service, printers and cartridges, cameras and photos. In the 1950s new business models, based on organization, management and marketing innovations developed by McDonald’s and Toyota appear. In the 1960s, Walmart became an innovator. The 1970s brought new business models from FedEx and Toys R US, the 1980s - from Blockbuster, HomeDepot, Intel and Dell, the 1990s - from Southwest Airlines, Netflix, eBay, Amazon. Com and Starbucks. In a rapidly changing economy, business is exhausted because of an old business model of speed and complexity. The problem of using and developing business model in an organization has become important over the current period of global competition, when the stable and sustainable development of the enterprise depends not only on the production and financial resources but also on human re-sources.
In today's reality businesses are faced with three key tasks: to maintain business acumen; to maximize the use of the important information which is becoming more complex, specific, dynamic for the benefit of the company; to coordinate multifaceted tasks to achieve a synergistic effect. Key teams play a fundamental role in the implementation of an integrated approach to management at all levels, the central part of which is dispersed leadership.
Business model become apparent in the process of making strategic and opera-tional decisions. In a low-competitive environment business model are implemented though the passive adaptation of organization to the market changes. In an extremely competitive market the promotion of goods is rather a tough process, that is why the business model become a strategic resource that affects the position of business on the market Business model are essential in reaching strategic goals of an enterprise.
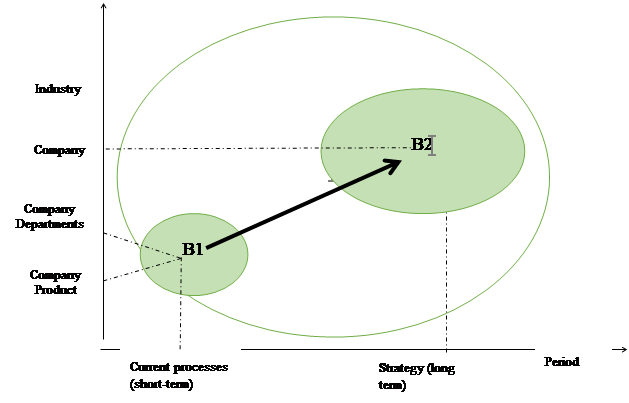
Fundamental changes - both evolutionary and radical - have been forming the economy and the business environment during the last decades that is shown in figure
Information and communication technologies have radically changed the requirements for developing and running business. Revolutionary technologies need perspective business models. In a competitive business environment, the classical model “lead and control” has become less effective. Up to 2000, the business model was developed with a specific product for a short term; at present, it is developed along the company’s strategy.
Research Questions
In the modern hyper competitive world, the business model in itself does not provide a stable competitive edge. In the long run, the companies, which can employ their full potential, will be successful. Only flexible firms, which can rapidly respond to new challenges, seize the opportunities and be able to create use values. The changes in use values should include new methods of pricing, innovations and emotions. These new forms result in customization (turning push industry into a demand pull one).
The main problem is that the classical business model does not conform to the modern business environment. A non-conforming business model can result in a company’s decline and exit from the market (Hamel, 2007; Handy, 1989).
Rapidly growing companies, concentrating on their main competences and corporate abilities, create a business model (picture 2).
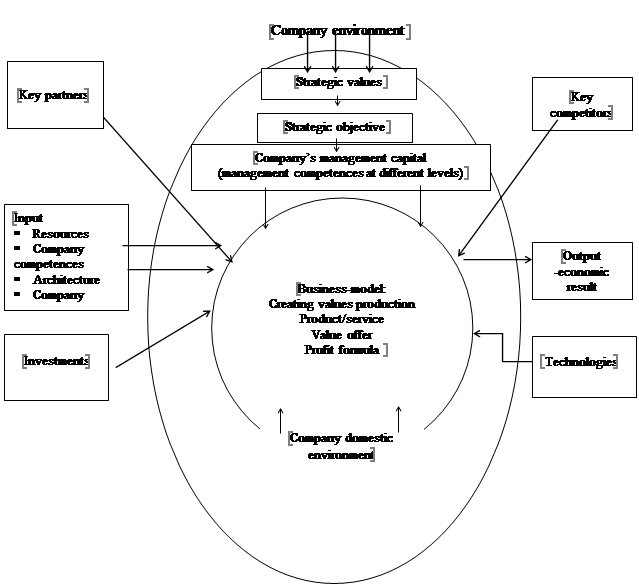
Purpose of the Study
The business model adjusts to the changes, occurring in the environment, and justifies the use of these changes for achieving its strategic objectives, finding out key competences which will be necessary for achieving the strategic objectives and developing these competences. The business model is a system which is formed under the direct influence of the environment (key partners, key competitors, innovations, investments and so on), the indirect influence of the environment (economical, political, social, technological, resources systems) and elements of the domestic environment (perspective vision, mission, values, objectives, strategies, staff, organizational structure, management style and so on). The inputs of the conceptual framework of the business model development are resources and company’s competitive edge (company competences, company architecture, which can add to knowledge that company has, procedures, applied to it, flexibility, ability to quick information exchange, company’s goodwill – the way of communicating with customers). The business model development justifies strategic values; strategic objectives, management contribution (management of different levels), creating values, production, product/service, value offer, profit formula. The economic result is the company’s output (Hodgkinson & Sparrow, 2002; Kim & Mauborgne 2005).
Research Methods
The research was made with the help of general academic and special techniques and methods including systemic comparative analysis. The methods were used to analyze the process of development of new management intellectuals;
Findings
Kotler, Berger, and Bickhoff’s research (2010) showed that such industries like automobile, logistics, healthcare, electronics, machinery and energetics are on the way to digital changes. These changes are due to new opportunities for collecting data and operating, product relations, infrastructure, companies and customers, and more widening ability of components, products and the system to make decisions independently.
The internet technologies development influences all the aspects of the economy greatly. The companies of different industries face quickly changing opportunities and problems, which are due to new internet technologies. Osterwalder, Pine and Prakhalad, (1996) offer three branches where new digital technologies can be used:
The experience of working with customers: firms can use information and communication to attract the customers in a new way. For example, they can make digital users communities to provide additional value.
Operation process: digital technologies allow one to achieve greater results in effective processes at all three stages of creating value;
Business models: to develop new forms when creating and fixing value.
Conclusion
New business models in digital economy are formed and developed according to the following principles:
Demand increasing. In new business models the demand initially is formed and increased by distributing different goods and services free of charge, then it is used.
The management productivity. The ability to effectively use the key competences of the company in real time.
Company’s costs minimization. Cutting down on extra operations and building company’s intellectual capital.
Intellectual networks. Each form of the network can contact and exchange information with other networks, creating a huge and complex global brain. The result of the networks are products, in particular, network intelligence.
The complexity of the system at all levels of management. Increasing technological complexity results in increasing complexity of other forms.
Wide and continuous contacts. Companies are communicating non-stop.
Innovational value creating. Customers value influences everything.
Leadership. The organizational structures have become dynamic with the use of modern technologies. Leadership is the key resource for company growth and its adaptability to the environmental changes.
Continuous training is reflected in a constant development of the ability to build knowledge.
A huge speed. Only fast companies can survive and do well in digital business environment.
Adjustment to an individual. When developing the business model, a manager not only acquires the skills of system vision and strategic thinking, but also practical analysis of the business models (understanding business, cooperation, flexibility, persuasiveness, ability to be proactive and so on)
Acknowledgments
Let us express gratitude to Neretina E. A. for her enormous contribution to the development of science
References
- Hamel, G. (2007). Leading the revolution. SPb: BestBusinessBooks.
- Handy, C. (1989). The Age of Unreason. London:Business Books.
- Hodgkinson, G., & Sparrow, P. (2002). The competent organization, Open University Press, Buckigham, Philadelphia.
- Kim, C.W., & Mauborgne, R. (2005). Blue Ocean Strategy: How to create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
- Kotler, P., Berger, R., Bickhoff, N. (2010). The Quintessence of Strategic Management: What You Really Need to Know to Survive in Business. Springer.
- Osterwalder, A., & Pine, I. (2013). Building of business models. M: Alpina Publisher Series Skolkovo.
- Osterwalder, A., & Pine, I.G., & Prakhalad, K. (1996). Competing for the Future. M: Publishing house "Grebennikov".
- Slywotzky, A.J. (2006). Migration values. What will happen to your business the day after tomorrow? M: «Mann, Ivanov and Ferber».
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 December 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-049-5
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
50
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1464
Subjects
Social sciences, modern society,innovation, social science and technology, organizational behaviour, organizational theory
Cite this article as:
Ksenofontova, K. Z., & Kerimova, O. V. (2018). Business Model And Strategy Of Industrial Company Management. In I. B. Ardashkin, B. Vladimir Iosifovich, & N. V. Martyushev (Eds.), Research Paradigms Transformation in Social Sciences, vol 50. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 639-641). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.78

