Abstract
The study of factors and motivesfor forming qualification deficits and educational demands of University middle managers in the context of knowledge management, practical significance, the results of which is the solution of the problem of management accounting and the effectiveness of professional interaction of managers in the transition to the project type of professional activity and obtaining additional resources for the development of the University. Innovation, in the context of the non-linear nature of the University as an educational organization and the basic processes of its life, the article postulates as a non-linear phenomenon that is required for the generation and implementation of adequate forms of University management, which provides project management. The process of updating the sources of University managers qualification as the basis of efficiency and productivity of University management, considered in the article to the context of knowledge management, allowed not only to offer ways of direct overcoming of the identified qualification deficits that can be overcome with the help of certain educational programs, but also to determine the basis for the formation of productive management project teams based on the use of the strengths of University managers, which in turn contribute to the generation of, develop and implement internal and external innovative university projects.
Keywords: Educational requestinnovationactivityknowledge managementproject managementqualification deficittrigger
Introduction
The system changes taking place in the sphere of University management are connected, first of all, with the introduction of the principles and mechanisms of project management. This means that the role of project activities (both "external and "internal") increases dramatically. On this basis, the professional interaction of managers of modern educational organization is built.
In addition, the following innovative contexts are typical for the management of a modern Russian University:
consolidation of universities, as a result of which there are Federal and supporting universities (Order of Russian Federation Ministry, 2010);
the emergence of globally successful research universities (Project Managment Institute, 2018);
the manifestation of international development trends in the educational activities of Russian universities ("bolonization", "digitalization", the increasing role of online education, the formation of universities as centers of innovative research and development, internationalization and growth of "export" potential of Russian higher education, the development of "network" and the entry of Russian universities into international University corporations and other associations, etc.) (Resolution of Russian Federation Government, 2017);
participation of universities in a number of strategic, state-supported projects for the development of universities, aimed at strengthening their global positions (project "5 in 100"), and to turn universities into drivers of innovative development of regions and digital economy and new information culture in General (Kuzminov, 2018; Decree of Russian Federation President, 2018);
professional standardization in the Russian higher education as a manifestation of global and all-Russian trends characteristic of society and the economy as a whole (Leibovich, 2014);
the introduction of a professional standard describing the activities of teaching staff, the completion of the discussion of the professional standard "Head of the educational organization", regulating, in particular, the professional activities of University top management (Order of Russian Federation Ministry, 2010, 2011, 2013, 2015, 2016; National Council of the President, 2017).
Problem Statement
It turns out that to manage projects and with the help of projects is to manage the professional knowledge of managers with the relevant project competencies. And project activities are carried out in project teams, for which objective criteria are necessary. We assumed that this is a "strong" professional knowledge of University managers. And a mechanism for their detection is necessary.
In addition, the specificity of knowledge management managers at the University, determined by the fact that the University, like any educational organization – an organization with "weak ties." We are talking about the weak links between the basic processes (teaching, teaching, scientific, innovative, social activity etc.). In such organizations, as is known from the theory of management, in a state of permanent crisis, with a very high degree of resistance to systemic changes. This is due to the fact that the weak links suggest different degree of impact on different parts of the system in the context of external change, and, as a consequence, uneven passage of management signals within the organization. That is, we can state the presence of a paradox that determines the essence of the process of development of educational systems: the weaker the relationship between the basic processes in the organization, the higher the degree of its stability during the crisis. But such an organization, as a rule, is poorly managed from a single center, with a simple change of regulations.
We believe that it is possible to increase the controllability of such a system only within the framework of a matrix scheme, which is based on projects that create a horizontal management space.
Research Questions
Thus, we propose the following paradox as the main management hypothesis of our research: an adequate approach to the management of an organization with weak ties can be a project approach, the tool of which is the work of project teams formed from managers with strong knowledge.
Another. In a "normal" organization-an organization with strong ties (company, enterprise), the management signal is able to simultaneously change the nature of all the basic processes and the behavior of the organization as a whole. Such organizations in the managerial sense are "linear". "Output" is determined by "Input" (Kurnosov, 2017).
We assume that the University should have a different picture-the" Output " is determined by the results of the system synthesis, in which the input management information is transformed. In the context of the above, project activities are processes of management information transformation that take place in the "Black Box". In this sense, the project management of an educational organization is nonlinear.
So, the objectives of our research:
to determine the qualification deficiencies, the motives for overcoming them, "strong" and "weak" knowledge (actual competence) of University managers;
to develop a mechanism for the formation of project management teams at the University;
to substantiate the role of project management as a trigger of innovation at the University.
We gave preference to middle managers, as we suggested that in the context of the global process of "management" of University management, their activities in the implementation of the development strategy of the organization becomes very significant. It is obvious that in the situation of project management increases the degree of their autonomy in the preparation of management information of a strategic nature, as they traditionally lead the formation and actual activities of University project teams that implement both "external" and "internal" strategic projects, while the representatives of the top management are, as a rule, coordination and external motivation.
Development of action plans, project activities aimed at achieving strategic objectives and obtaining effective results is currently not so much the responsibility of management as a vital necessity, as in the context of the ideology of project management there is an opportunity to attract additional development resources (primarily financial), through competitive participation in Federal projects implemented within the framework of the State Program "development of education in the Russian Federation" for 2018-2025 and the decree of the President of the Russian Federation from May 7, 2018 (Decree of Russian Federation President, 2018).
The theoretical and methodological basis of the study was primarily the works on the theory of knowledge management (Wiig, 1997; Foss, 2006; Blackler, 2002; Thomas, 1989) the theory of socio-cultural trigger (Goldsmith, 2012, 2015), innovative development of universities (School management and organization, 2014; Curlee, 2010; Blinov, 2008), as well as practices in the field of University management (The Open University, 1998; Project Managment Institute, 2018).
By the way, the application of the stage theory of socio-cultural trigger (Goldsmith, 2015) allows to use this concept not only as a metaphor (antithesis of the definition of "barrier"), but also as a real research tool. These authors consider the socio – cultural trigger as a process that includes the unity of three stages-reaction, awareness, action. Project practice of University management teams demonstrates the coincidence of the primary cycle of decision-making and implementation of management decisions in the generation, development and implementation of innovative projects, both "internal" and "external", with the above basic cycle of socio-cultural trigger.
Purpose of the Study
Thus, we describe further the research work to identify the existing qualification deficits and the nature of their occurrence, the educational needs of middle managers of modern educational organizations, as well as the motives for their occurrence in order to determine the educational programs to meet the "weak" actual competencies and identify the "strong" actual competencies that contribute to the formation of specific professional interactions of managers of educational organizations in the main areas of its activities.
The theoretical and methodological basis of the study was the works of researchers in the field of sociology and sociological research, the concepts of the theory of knowledge management and human resources management, the foundations of management theory, organization and practices in the field of management.
The study was conducted in three stages. The first stage consisted of a survey of 310 respondents from 8 Federal districts of the Russian Federation, 12 profiles of educational institutions of higher education, which are represented by specialists, middle managers, top managers, as well as teaching staff. The program requirements to achieve the representativeness of the sample were gender, age, social and professional composition of the surveyed and their spatial localization with restrictions on professional and qualification composition. The planned conclusions of the study are aimed to a greater extent at the qualitative representation of the sample.
The second stage was the processing of the data, analysis of the results and their interpretation. The third is to conduct 2 focus surveys in the academic community with the participation of 5 expert respondents, 4 participant respondents to interpret the results and interview 10 experts-heads of educational organizations to obtain an expert evaluation of the results.
Analysis of primary questionnaire data was carried out with the help of mathematical statistics univariate, bivariate descriptive analysis, the obtained results are processed using regression, factor and cluster analyses of survey data using computer software packages SPSS, Microsoft Office, and some open questions we have conducted a quantitative content analysis using the software QDA Miner and Wordstat Lite.
Research Methods
One of the tasks of the analysis of personal data was to determine the request for the necessary educational programs from the point of view of managers of educational organizations. The task of identifying the causes of their occurrence was also carried out. Thus, there were 10 main programs in the main areas of requirements for managers of any level: the theory of management, marketing, office management, work with IAS, psychology, conflictology, business and interethnic communication, social networks and career guidance.
However, this preference was observed in 50 % of the respondents, therefore, the focus of searching for the causes moved to the analysis of the responses about the shortcomings of the qualifications that respondents managers and their subordinates. As a result, 7 areas were identified in 60% of respondents, which did not coincide with the previously 10 requested programs. According to the results of the survey on the existing qualification deficits in managers allocated 7 programs to overcome them: the theory of management, including strategic, knowledge of the functioning of the organization, including control, information Analytics, psychology, self-management, including time management, management decisions, change management.
To solve the problem of determining the causes of qualification requests was carried out factor analysis, according to the methodology of which the analysis of 28 questions on the semantic differential on a scale of "has not changed – not much – very noticeable– I find it difficult to answer (not doing)".
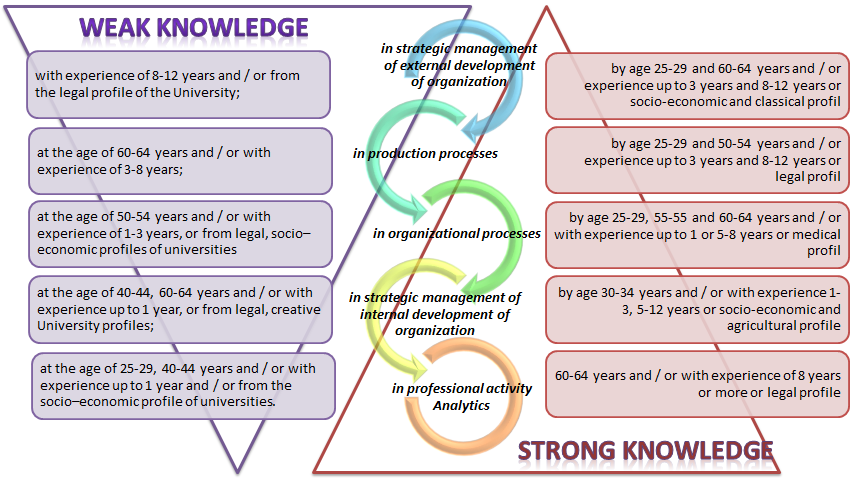
As a result, 5 factors with a statistically significant result (1> p > 0.5, p=0.712) correlated with the conceptual levels of knowledge (Wiig, 1997) and such areas of professional activity of the Manager according to the management theory: the first factor is associated with the strategic management of the external development of the educational organization, the second – with strategic management of internal development, the third – with organizational processes, the fourth – with production, the fifth – with the analysis of professional activities of the Manager.
Then the factor values for each Respondent were calculated by age, work experience, type and level of position, profile of professional activity, status and profile of educational organization. During the calculation were identified as "weak" and "strong" knowledge of managers of educational organizations.
By means of calculation of the received values of factors it is defined that qualification deficits of heads at the time of poll are not connected neither with a profile of professional activity, nor type and level of a position, nor with the status of the educational organization, and are connected with age, experience of the head and a profile of the educational organization. At the same time, in each of the 5 spheres of activity there are certain ranges of formation of the lack of knowledge in the strategic management of the external development of the University, in the strategic management of the internal development of the University, in the organizational processes of the University, in the production processes of the University and in the Analytics of professional activity of the employee (Fig.
Thus, the obtained factor values allow to distinguish the directions of development of educational programs. But what was the reason for such qualification deficits?
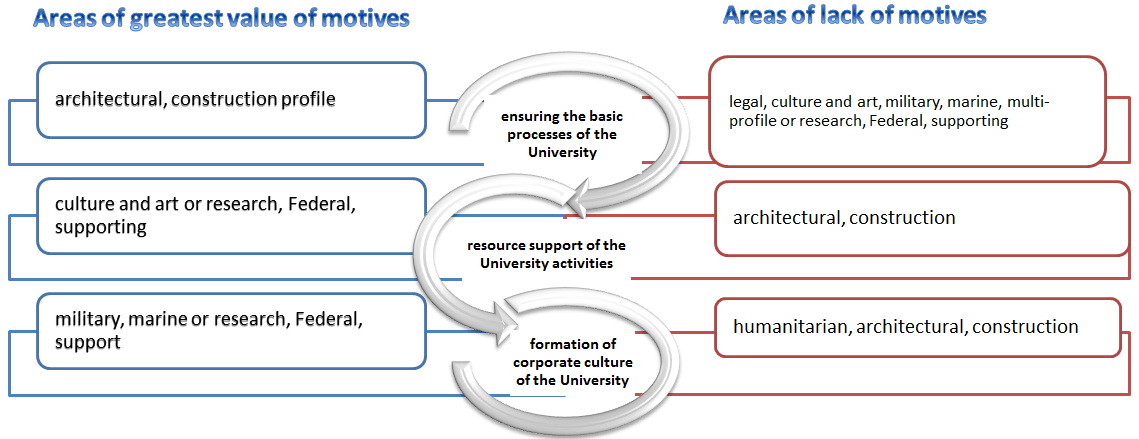
To determine the motives, based on the factor values, the cluster analysis by the analysis of cluster centres, which resulted in 3 groups of respondents, the motives of which can be interpreted as: providing the basic processes of activity, resource support activities and the formation of corporate culture of the educational organization (Fig.
Using the obtained data was calculated and analysis of the affiliation motives of the respondents.
The values calculated on the basis of the data characterizing the profile of activity and the status of the educational organization turned out to be informative, it turned out that the motives for the emergence of qualification deficits in managers of architectural, construction profile (100%) lie in the field of ensuring the main processes of the educational organization, but are absent in the resource support of its activities (0%) and the formation of corporate culture (0%), when both in educational organizations of culture and art (86%), scientific and research organizations, Federal and support (58%) motives lie in the field of resource support of the educational organization, but there are no basic processes, and the military, marine (50%), research, Federal and support (42%) lie in the formation of corporate culture of the educational organization, but also absent in the provision of basic processes.
It is possible to state that the received values allow to formulate not only directions of development of educational programs, but also to define target audience.
Findings
The results of the study allow us to state that with the revealed significant strengthening of the role of University managers in the context of the trend of "managerization", the qualification requirements for them have not changed, training, advanced training or retraining were carried out on programs that do not meet the identified educational needs.
One of the tasks of the analysis of personal data was to determine the request in the necessary educational programs from University managers, as a result of which 10 directions were allocated for the basic requirements for managers of any level. However, the analysis of the noted qualification deficits in respondents, their management and subordinates revealed 7 areas (management theory, including strategic, knowledge on the functioning of the organization, including the implementation of control, information Analytics, psychology, self-management, including time management, management decisions, change management), which, in General, did not coincide (except for the General theory of management and psychological knowledge) with the previously requested 10 respondents programs (theory of management, marketing, office work, work with information management systems, in particular, with information automated systems, psychology, conflictology, business and interethnic communication, social networks and career guidance).
This circumstance is explained by the fact that in the allocated qualification deficits there are competencies, which are based on “weak” knowledge. Therefore, the next step was to determine the factors of their formation.
As a result of the factor analysis of sociological data of 28 questions based on semantic differential, 5 factors correlated with conceptual levels of knowledge on Wiig and areas of professional activity of University managers are received.
Identified as "weak" and "strong" knowledge of University managers, which (which greatly surprised the experts) are not associated with any profile of professional activity, nor the type and level of their positions, nor the status of the University, and are associated with the age, experience and profile of the educational organization. At the same time, in each of the five areas of activity, there are certain ranges of formation of the lack of knowledge (Fig.
On the basis of the obtained values of factor analysis, three groups of respondents were identified, the motives for the emergence of qualification deficits are associated with the profile of activity and the status of universities and are grouped into three groups: ensuring the basic processes of activity, resource support of activities, the formation of the corporate culture of the educational organization (Fig.
Conclusion
Thus, on the basis of the obtained results, it was possible to identify the motives for the emergence of "weak" knowledge of University managers, to correlate this knowledge with the subject and content of additional professional programs, training on which should contribute to the transformation of" weak "knowledge into" strong", and the development of professional interactions of managers on a project-functional basis could be correlated with the identified "strong" knowledge of University managers, which will allow to form project teams on the basis of "strong" knowledge, both on the internal and network basis, inter-University based.
Interaction of such project teams takes place at different stages of preparation and execution of the project, for example, the project team of external development conducts analysis of the causes of external changes and the data obtained correlates with the strategic objectives of the University, forms problematic issues, and in the subsequent, the fourth stage is the interaction with the second team - internal development - the exchange of data, information and knowledge. Further, the analysis of external and internal development of the project is formed, at the fifth stage, the analysis of the project implementation and ways of development and transfer of the acquired and accumulated knowledge to the third team - organizational support, which, in turn, analyses the organizational processes and transmits the information to the fourth team to analyse the establishment of production processes. As for the fifth team-analysts, they can conduct an audit and examination of the project at any stage of implementation - they can be highly specialized representatives of different areas.
References
- Blackler, F. ( 2002). The Strategic Management of Intellectual Capital and Organizational Knowledge. USA: Oxford University Press Inc.
- Blinov, V. I. (2008). Natsional'naya sistema kvalifikatsiy Rossiyskoy Federatsii [The national frame of qualifications of the Russian Federation: Recommendations]. Moscow: Federal Institute of education development [in Rus.].
- Curlee, W. G. (2010). Complexity Theory and Project Management. US: John Wiley & Sons.
- Decree of Russian Federation President (2018). On the national goals and strategic objectives development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2024. Retrieved from http://www.kremlin.ru/acts/bank/43027 [in Rus.].
- Foss, N. (2006). Strategy, economic organization and the knowledge economy. N.Y.: Oxford University Press.
- Goldsmith, M. R. (2015). Triggers: Creating Behavior That Lasts--Becoming the Person You Want to Be. N.Y.: Crown Publishing Group.
- Goldsmith, M. R. (2012). Understanding Health Care Management. U.S: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
- Kurnosov, Y. (2017). Azbuka analitiki. [The ABCs of Analytics]. Moscow: Litres. [in Rus.].
- Kuzminov, Y. I. (2018). Dvenadtsat' resheniy dlya novogo obrazovaniya: doklad Tsentra strategicheskikh razrabotok i Vysshey shkoly ekonomiki [Twelve solutions for new education: the report of the Centre for strategic research and Higher school of Economics]. Moscow: Centre for strategic research ; Research University "Higher school of Economics".[in Rus.].
- Leibovich, I.A. (Ed.) (2014). Nezavisimaya otsenka i sertifikatsiyakvalifikatsiy: Sbornik dokumentov i materialov [Independent Evaluation and Certification qualifications: Collection of documents and materials]. Moscow: Publishing House ''Pero' [in Rus.].
- National Council of the President (2017). The layout of the professional standard. Retrieved from http://nspkrf.ru/ [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Government, no. 1696-R (2010). Retrieved from http://government.ru/docs/30280/ [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Ministry (2016). Retrieved from http://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/56574265/ [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Ministry, no 1n (2011). Retrieved from https://rg.ru/2011/05/13/spravochnik-dok.html?utm_source=rg.ru&utm_medium=offline&utm_campaign=back_to_online [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Ministry, no 761n (2010). Retrieved from https://rg.ru/2010/10/20/teacher-dok.html [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Ministry, no. 148н (2013). Retrieved from https://rosmintrud.ru/: https://rosmintrud.ru/docs/mintrud/orders/48 [in Rus.].
- Order of Russian Federation Ministry, no.608н (2015). Retrieved from http://profstandart.rosmintrud.ru/obshchiy-informatsionnyy-blok/natsionalnyy-reestr-professionalnykh-standartov/reestr-professionalnykh-standartov/index.php?ELEMENT_ID=48584 [in Rus.].
- Project Management Institute (2018). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. US: Project Management Institute.
- Resolution of Russian Federation Government, no. 1642 (2017). Retrieved from http://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/71748426/ [in Rus.].
- Resolution of Russian Federation Government, no. 1242 (2017). Retrieved from http://economy.gov.ru/minec/activity/sections/govprograms/201711117 [in Rus.].
- School management and organization. (2014). Current Problems of University Management. Wydawnictwo, UJ: School management and organization.
- The Open University (1998). Project management. UK, Kents Hill: The Open University.
- Thomas, V. B. (1989). Lawler Chutes and Ladders: Growing the General Manager. Cambridge, MA: Sloan Management Review.
- Wiig, K. (1997). Knowledge Management: Where did it Come and Where will it Go? Expert System with Applications. London: Pergamon Press.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 December 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-050-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
51
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2014
Subjects
Communication studies, educational equipment,educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), science, technology
Cite this article as:
Verkhovskaia, I., & Prikot, O. (2018). Project Management In Context Of Knowledge Management As Trigger Of Innovation University. In V. Chernyavskaya, & H. Kuße (Eds.), Professional Сulture of the Specialist of the Future, vol 51. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2006-2014). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.02.213

