Abstract
The article discusses the meaning of the future specialist’s personality. Our modern society needs competitive professionals, who are in a high demand on the labor market. It was conducted ananalysis of higher education where it was considered as a specific social institution in the socialization of the individual. I was analyzed through different forms of education, upbringing, self-education through the mechanisms of socialization, adaptation, integration, and cognitive processes. In fact, the effectiveness of the system of professional training, first of all, is determined by the demand of the society of the specialists with different professional profiles, and with the required level of qualification, including social order. The volume of social order for professional training and its content is regulated by the needs of the regions. The process of formation and development of personality is called socialization. It’s a process of individual assimilation of social norms and values of society, the transformation of social experience into personal attitudes, orientations, values - the internalization of accumulated human culture. The main factors of socialization of the personality are pointed. A lot of attention is given to the aspect of information demand. Info interaction acts as an informational mechanism of socialization and activates its dynamics as a whole process. Investigating the statistical data on the state of the infrastructure of higher education, the role of the higher school in the formation of professional socialization of specialists in the regions of the Russian Federation was defined.
Keywords: Determinationinteriorizationprofessional socializationsocial institution
Introduction
Knowledge, intellect, culture, education, intelligence should become a priority in human life. Democratization, humanization, fundamentalization, informatization, integration, multivariance - are the main directions of modern reforms in the field of education. That is why modern society needs competitive professionals who are in demand on the labor market. Education as a social phenomenon is focused on the formation of personality. It fulfills the main functions of professionalization and socialization. Consequently, the education system is a strategically important area of human activity, it’s one of the social institutions whose importance increases as society is constantly moving along the path of information, technological and socio-economic progress. As the society develops, the correspondence of the level of specialists produced by higher education institutions to the needs of the society, the dynamics of its development, the demand on the labor market is becoming more transparent.
The effectiveness of the system of professional training, first of all, is determined by the demand of the society for specialists of a particular profile at the required level of qualification, i.e. social order. The volume of the social order for professional basic education and its content is determined by the needs of the regions. Therefore, the problem of professional socialization of the personality of a specialist in the future requires comprehensive research and the solution will be highly important for the stabilization and sustainable development of modern society, which determines the relevance of the topic. The problems of education are included in the field of sociological, pedagogical, sociolinguistic research at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries within the framework of the general theory of socialization, and, more fully, in the 1920s and 1930s within the framework of the structural-functional theory. Considerable attention is given to the theory of socialization of the individual. In the development of the theory of socialization, T. Parsons contributed his contribution, which applied the concepts introduced by Freud of the theory of social action and social systems (Parsons, 1965). Smelzer (1994) considers socialization from the point of view of the structural and functional approach. Socialization is an object of interdisciplinary study, and today its the intersection of various sciences. In general, it is customary in sociology to define socialization as a process (a set of processes) by which an individual absorbs social norms and values. The agent of socialization of the individual is the institutions and, above all, the institution of education. The authors’ researches allowed us to analyze education as a specific social institution in the socialization of the personality of the future specialist through forms of education, upbringing, self-education through the mechanisms of socialization, adaptation, integration, cognitive processes.
Problem Statement
The research tasks are defined:
consider the education system as a social institution for the performance of socialization the personality of the future specialist;
describe the factors of socialization the personality of the future specialist in the process of professional education;
determine the role of higher education in the professional socialization the personality of the future specialist
Research Questions
-
Professional socialization is considered as the main component of the social development of the individual, it determines the most important, socially significant characteristics of a person.
-
The main subject of socialization the personality of the future specialist is higher education considering as asocial institution of society.
-
The relationship between the institution of education and the socialization the personality of the future specialist is a regularity aimed at satisfying the needs and vital values of a person.
The model of educational conditions and means of socialization the personality of the future specialist is justified as a set of goals, structural and content aspects of the activity of the educationalinstitution.
Purpose of the Study
The main goal is to study the process of professional socialization the personality of the future specialist in the education system as a social institution.
Research Methods
To achieve the purpose of the research and solve its problems usingtraditional methods of research: system analysis, method of historicism, comparative, analytical and pedagogical methods, and methods of statistical analysis.
[In order to achieve the research goal and solve problems, traditional methods of research are used the following: system analysis, historicalism, comparative, analytical, pedagogical, statistical analysis methods. Clinical Method in Professional Pedagogy and in Social Sciences (Blezza, 2017). Clinical method in professional pedagogy and social sciences.
Socialization is the process of formation and development of the personality. This is the process of assimilation by an individual of social norms and values of society, the transformation of social experience and personal attitudes, orientations, values - the internalization of the accumulated human culture. In the course of socialization, the connection between society and the individual and its adaptation to the world is established and developed. There is a process of man's entry into society, including social ties with the integration of various types of social communities, as a result of which the socialization of the individual is taking a shape. There is an active interaction with her/him or confrontation with it. The environment is also active. At the same time, socialization means not only the entry of an individual into society through the assimilation of a certain system of values, but also the acquisition of one's own social experience. In sociological literature, the main factors of socialization of the individual are:
totality of roles and statuses that society offers to a person;
set of social institutions and organizations, social communities within which certain social roles are realized and the desired social status is acquired;
totality of values, social norms, knowledge, skills, skills, qualities that a person possesses;
set of social structures, technologies for the production, reproduction and transfer of cultural samples, values, norms;
specific events.
Considering the development of personality, Frolov (1996) identifies five factors that affect the formation of personality: 1) biological heredity; 2) the physical environment; 3) culture; 4) group experience; 5) unique individual experience.
It should be noted that some personality qualities are actualized in certain life stages of a person. Thus, for example, according to Ebzeeva, Mitrofanova, & Dugalich (2017) adolescents and young people tend to be aggressive and demonstrate a protest mood.
The approach to the allocation of the system of factors of socialization is peculiar Andruschenko & Gorlach (1996). The author presents such elements as: 1) totality of roles and statuses that society offers to a person; 2) aggregate of social institutions, social organizations, social communities, within which the individual realizes certain social roles and acquires statuses; 3) totality of values, social norms, knowledge, skills, qualities, qualities that a person masters in order to fulfill the appropriate roles and maintain the acquired status in accordance with the needs of society; 4) et of social institutions and social technologies for the production, reproduction and transfer of cultural samples, values, norms; 5) specific events.
Interest is also proposed by Asmolov's (1990) scheme of determining the development of the personality, which includes the individual properties of a man as prerequisites for the development of the personality, socio-historical lifestyle and joint activity as the basis for the realization of life for the individual in the system of social relations. Thus, approaching one of the forms of connection between the way of life of the individual and its socialization - the impact of labor activity, which is one of the structural elements of the way of life, on the professional socialization of the personality of the future specialist. Similar links can be found between other structural elements of the way of life and the corresponding types of socialization. Proceeding from the above, it can be concluded that everything that a person does - all this forms the characteristic features of her/his personality. That’s the main principle of the mechanism of the impact of the way of life on the socialization the personality of the future specialist.
The factors of socialization Mudrik (1991) distinguishes in three groups. The first - macrofactors (Space, planet, world, country, society, state), which affect the socialization of all the inhabitants of the planet or very large groups of people living in certain countries. The second is mesofactors (meso - intermediate), the conditions for the socialization of large groups of people allocated: on a national basis (ethnos as a factor of socialization); in the place and type of settlement in which they live (region, city, village); by belonging to the audience of certain mass communication networks (radio, television, cinema, etc.). Mesofactors influence socialization both directly and indirectly through factors of the third group - microfactors. These include family, peer groups, micro society, organizations in which social education is provided by educational, professional, public, religious organizations. All these factors belong to the elements of the social environment.
In addition to them, personal factors also play an important role for the person, there are potential abilities and opportunities to develop the cultural layer of society, needs and interests, the direction of social activity. Information needs can also be attributed to the factors of socialization, as it includes the specific conditions of the social environment. The social environment through the transmission of directed information seeks to educate the individual in such a way that he effectively realizes the goals are set by this environment. The individual, in turn, consumes, transmits and produces information for the purpose of her/his own self-realization in the conditions of a given social environment. The degree of activity of the individual in a given process depends on the level of development of her/hisinformation needs. Thus, social environment activates the information needs, stimulates the entry of the person into infotainment, which, at the same time, acts as a mechanism of socialization. According to the degree of development of human information needs it determines the intensity and quality of its interaction and, consequently, determines the dynamics of its socialization. The developed information needs activate infofamidity and speeds up the process of entering and changing information. Thus, a person periodically finds himself in an innovative information field, which causes his new information content to change stereotypes, abolish previous ones, or form new installations. One of the most significant milestones of socio-cultural development in the information society is the priority of the individual. It is the change of personality that precedes the change in society. Individuals influence the changes in society no less effectively than social institutions. Knowledge of foreign languages in the modern world is an indicator of the culture and active communication of the future specialist (Mitrofanova, 2018).
A bright, creative person is always in high demand. The phenomenon of such a person is that it is capable of exerting an integrating influence on various spheres of social life. A person of this type is formed in the conditions of collective efforts, taking in a wealth of results and methods for obtaining them. The main thing is that it is the instrument of the process of socialization and communication, as it means to solve the creative task is not simple summation of information, but the dialectical assimilation of experience which is accumulated in the culture and the formation on this basis of new principles of scientific, artistic, technological activity.
Let’s discuss our second question and consider higher education and its role in the professional socialization the personality of the future specialist.
"Higher education means all types of training courses for training or training for post-secondary research submitted by universities or other educational institutions that are recognized as higher education institutions by competent public authorities;" (UNESCO, 1993).
High school is not only an institution responsible for the inheritance, accumulation and reproduction of scientific knowledge, values and norms, but also ensures the fulfillment of pragmatic tasks - from the training of specialists and the conduct of scientific research to the formation of public opinion. In Russia there are universities of the following types: university, academy, institute. At the level of higher education there are three levels: Bachelor (4 years); specialty, diploma "specialist" (training lasts at least 5 years), master's degree. Bachelors and specialists can apply for master's programs. Training lasts at least 2 years and provides for the preparation of a student for research different activities. Graduates defend their master's thesis, which results in a master's degree and is awarded the "master's" qualification. The third level – training of highly qualified person is postgraduate studies, residency, assistant training, - the form of training of highly qualified workers in the field of arts. Having mastered the program of the third level, and defended the thesis, they receive the scientific degree of Candidate of Science.
The data in Table
Analysis of Table
Education system provides for students a transfer of a certain set of knowledge in the social sciences, as well as related practical skills and abilities. It is humanitarian education, humanization that are the most important means of shaping the worldview, play a huge role in the overall development of people in their moral and ideological and political education. Social promotion of the personality is conditioned by the level of development and quality of higher education, the adaptation of the individual to the education system, which affects the professional and unprofessional socialization of the individual.
Profession is a complex inherent in a person of special knowledge, skills and skills acquired as a result of special training or long-term practical activity and enabling him to fulfill established labor traditions. Profession is characterized by a number of significant signs. First, it is always personalized, that is, it belongs to a person. Secondly, the basis of any profession is a person's professional experience - his knowledge, skills, skills, sensory experience. Thirdly, the profession is the main form of personal self-expression and the satisfaction of the needs of man and society. Fourthly, the profession can be acquired in two ways: through organized forms of education (training in educational institutions of various levels and profiles, other forms of education - so-called "school education") and as a result of long-term practical activities ("extracurricular preparation"). Fifthly, any profession has objective grounds for its emergence, that is, its emergence is possible only when a certain set of labor functions is laid down in objective factors of labor, which is the reason for its objective need for social labor. At the same time, the possibility of its objectification as a qualitative form of labor is related to the person, his abilities. At any moment of the development of society there is a need for a certain number of people with certain social qualities. At the same time for the smooth functioning of the social organism it is important that it is occupied by a person fulfilling his role in accordance with social order. An important element of pedagogical activity in the university is "to teach the student to study" (Mitrofanova, 2018, p. 187).
It is important to take into account the fact that in Russian education social institution is being modernized, and people adapt to it in accordance with the system of certain norms and values. The social institution of higher education is formed together with a person, with a new professional type of personality (Figure

Probable character of placing individuals in social positions is a property of social relations. The patterns of such a placing are of a static nature, that is, a person endowed with certain social qualities may take a particular position, to a greater or lesser extent.
Findings
In the course of the study, statistical documents were analyzed: compilation of the Federal State Statistics Service; Russian statistical yearbooks (2017, 2018). On the basis of these documents, studies were carried out, the purpose of which:
determine the role of higher education in the formation of professional socialization of future specialists in the regions of the Russian Federation;
compare the process of professional socialization of the personality of future specialists in the system of higher education in different regions of the Russian Federation.
The following regions served as the object of the study:
The Central Federal District - Moscow;
The North-West Federal District - St. Petersburg;
The Southern federal district-Krasnodar Territory;
The Volga Federal District - the Ulyanovsk Region;
The Ural federal district - the Tyumen region;
The Siberian Federal District - Krasnoyarsk Territory;
The Far Eastern Federal District- Khabarovsk Territory.
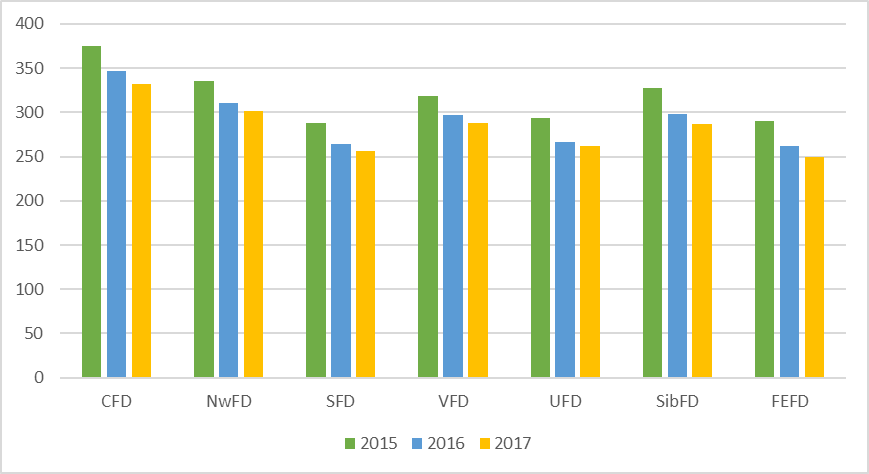
Analyzing the data of the table
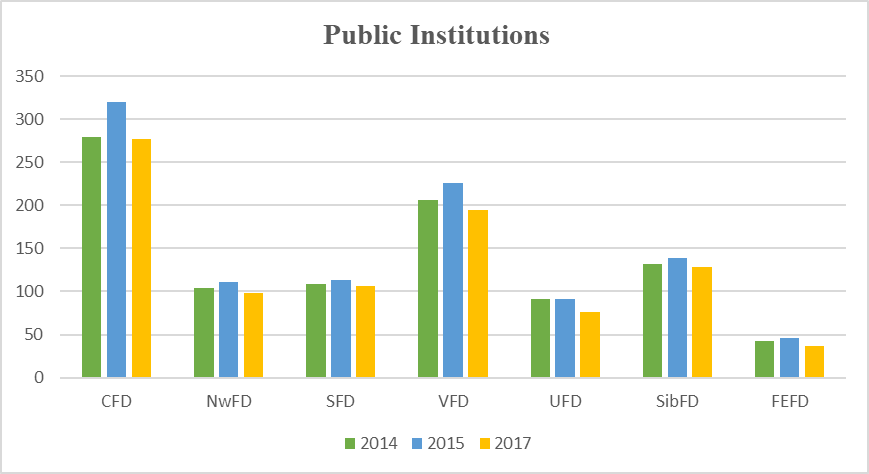
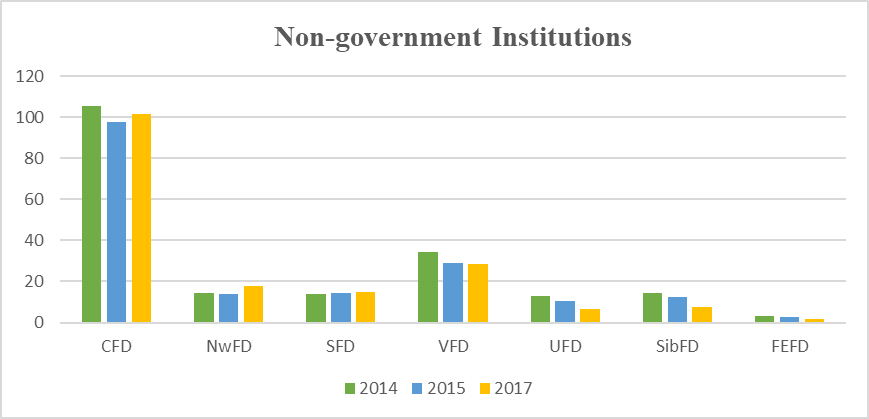
The results of Table
The Central Federal District - there is a decrease of 1.1% in state universities, in non-state higher education institutions is reduced by 3.8%. The North-West Federal District, the decline is 5.1% in public institutions of higher education, in non-state universities - 23.6%. The Southern Federal District is down 2.3% in state universities, while in non-state ones there was an increase of 10.2%. In the Privolzhsky Federal District, we see a 5.6% reduction in public institutions of higher education, 17.5% in non-state higher education institutions. The Urals Federal District is down 15.6% in public institutions of higher education, in non-governmental institutions 50% (the highest indicator). In The Siberian Federal District there is a decrease in state universities by 2.9%, in non-governmental institutions by 45.8%. The Far Eastern Federal District is down 48.5% in state universities, in non-state - 13.4%. It should be noted that in 2015 there was an increase in the output of specialists by state universities in all regions of the Russian Federation, as well as a decrease in the growth in non-state universities in all regions of the Russian Federation.
The total number of educational institutions of higher education and scientific organizations that carry out educational activities under the bachelor's, specialist and master's programs in 2017, as compared to 2016, decreased by 6.4% (or by 52 units), the number of state and municipal organizations decreased by 0, 4% (2 units); private - by 15.8%.
Conclusion
Summarizing the statistical data, the following tendencies are revealed: firstly, within three years the "attractiveness" of higher professional education has grown; Secondly, the rating of state education is still higher than non-state education; thirdly, the process of professional socialization of the future specialist is evolutionary for all regions of the Russian Federation, in connection with the introduction of new technologies, innovations in the production and market demand. According to the Minister of Education and Science of the Russian Federation Olga Vasilieva: “We have one of the highest levels of education in the world .... , the proportion of the population that graduated from college or HEI is 56%. .For comparison: in the countries-members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation (OECD) -37%. People aged 25 years who have not finished school are less than 5%, and in the OECD countries this figure reaches 18%” (ТАSS, 2017).
Acknowledgments
The article is published within the initiative theme 050323-0-000 Russian Language in Different Linguistic and Cultural Surroundings.
References
- Andrushchenko, V.P., & Gorlach, N.I. (1996). Sociologiya. Nauka ob obshhestve [Sociology. Science about Socium]. Kharkov: Har'kovskij kollegium [in Rus].
- Asmolov, A.G. (1990). Psixologiya [Psychology]. Moscow: MGU. [in Rus].
- Blezza, F. (2017). Clinical method in professional pedagogy and in social sciences Studies in Systems. Decision and Control, 66, 387-397. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-40585-8_34
- Ebzeeva, Yu. N., Mitrofanova, I. I., & Dugalich, N. M. (2017). The image of a migrant in the contemporary Russian TV journalism discourse. Man in India. 97(23), 525-532.
- Frolov, S.S. (1996). Sociologiya. [Sociology: Textbook for higher educational establishments] Moscow: Logos. [in Rus].
- Kon, I.S. (1998). Nauchno-texnicheskij progress I problemy` socializacii molodezhi [Scientific and Technological Progerss and Youth Socialization]. Moscow: Znanie. [in Rus].
- Mitrofanova, I.I. (2018). Mnemonik techniques of working with a vocabulary in Russian classeswith a foreign audience. Science and Society, 13, 186-196. Retrieved from http://scieuro.com/science-and-society-february-2018/?preview=true
- Mudrik, A.V. (1991). Socializaciya v smutnoe vremya [Socialization in Troublous Times]. Moscow: Znanie [in Rus].
- Obrazovanie v Rossii [Education in Russia] (2017). Statisticheskij sbornik. [Statistics Digest]. Moscow: GoskomstatRossii.[in Rus].
- Parsons, T. (1965). Obshcheteoreticheskie problemy` sociologii. Sociologiya segodnya. Problemy`i perspektivy`[General Theoretical Problems of Sociology. Sociology Today. Problems and Prospects]. Moscow: Progress.
- Regiony` Rossii. Social`no-e`konomicheskie pokazateli [Regions of Russia. Social and Economical Indices]. (2017). Moscow: Rosstat. [in Rus].
- Rossijskij statisticheskij ezhegodnik. [Russian statistical yearbooks]. (2017). Moscow: Goskomstat Rossii. [in Rus].
- Rossijskij statisticheskij ezhegodnik.[Russian statistical yearbooks] (2018). Moscow: Goskomstat Rossii. [in Rus].
- Smelzer, N. (1994). Sociologiya. [Sociology]. Moscow: Feniks. [in Rus].
- TASS. (2017, November 20). My ni ot kogo ne otstavali i otstavat' ne sobirayemsya. [We are not lagging behind anyone and are not going to lag behind]. [in Rus]. Retrieved from https://tass.ru/interviews/4703617
- UNESCO (1993). Rekomendatsiya o priznanii issledovaniy i kvalifikatsiy v vysshem obrazovanii) [Recommendation on the Recognition of Studies and Qualifications in Higher Education]. Retrieved from http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=13142&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201.html
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 December 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-050-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
51
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2014
Subjects
Communication studies, educational equipment,educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), science, technology
Cite this article as:
Mitrofanova, I. (2018). Professional Socialization Of Future Specialist’s Personality. In V. Chernyavskaya, & H. Kuße (Eds.), Professional Сulture of the Specialist of the Future, vol 51. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1809-1820). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.02.192

