Abstract
The article presents the empirical study results of a new form of the teacher–student social networking within “Virtual Market of Educational Services” project that was employed for training students in the master’s programme in Educational Psychology. This paper specifies the pressing issue that lies in overcoming contradictions with global challenges of modernity: the competence of the Person of Tomorrow who needs a broad experience of social interaction facing lack of variety in teaching methods that do not allow such learning experience, its interiorization for the further effective professional engagement in the information age. In this context, social interaction is meant as a dialogue of a coordinator of activity with the Self, the Others, and the Culture in the sense of subjectified values and a way of life. A mixed method design to investigate the effect of using an online community of practice is used to substantiate a way to organize a productive creativity of the community that includes social reflection as a means of understanding the self through the Others, evident in online networking and the system of social relations. The paper then moves on to the resulting character of this method. An idea of continued professional development of graduate students in terms of “Networking modular programme of in-service education” project as a developmental potential for the community is discussed. Invariant nature of the proposed structure raises the possibility to use it in all domains of professional training and interaction including international academia cooperation.
Keywords: Social networkingvirtual market of educational services
Introduction
The modern education is becoming a mechanism producing quite new social and cultural practices and ensuring their diversity (Asmolov, 2015) and it is critically important for educationalists to focus on the future.
In the Information Age, the community is centered around networking rather than individuals (Castells, 2010). Don Tapscott asserts that the world is becoming more open and identifies four main principles: global cooperation; openness; exchanging all types of information; expressing willingness to cooperation. An adoption of these provisions, public demand and the needs of today’s students for a new quality of education require radical updating of educational values and goals (Don Tapscott, 2013; Brooks, 2016).
The social nature of educating and developing a personality puts forward the principles of an orientation to group teaching forms, cooperative learning, variety of interaction forms, interpersonal relationships and communication, increasing of a personality’s origins and, simultaneously, their cooperative activity. For this reason, education and social networking relations are gaining momentum (Holmén & Ljungberg, 2014, Stonebraker, 2016).
Productive type of the teacher-student interaction is related to a modern model of training. Implementation of this model found its justification in concepts of the higher professional education based on the anthropological approach (B.G. Ananiev, V.P. Zinchenko, V.I. Slobodchikov et al.), the humanistic approach (A.A. Verbitsky, I.A. Simnaya, V.A. Slastenin et al.), and the axiological approach (A. G. Asmolov, A.V. Kiryakova, V.A. Petrovskiy et al.).
Problem Statement
In practice, the modern educational University system is largely determined by the subject activity. In educational science, the categories of the teacher-student interaction and synergy are developed least of all. The experience of implementing productive learning ideas in university educational process shows that generally, attention is paid to the positive impact of productive interaction on the improvement of students’ performance, rather than on the development of their individual qualities and their capability to communication (Lyaudis, 1980).
Research Questions
The study tries to answer the following research questions:
How can the new forms of human interaction be implemented in the information and education space of Master’s Degree course in Educational Psychology?
What is the effect of network-based project on engagement and interaction between the teachers and postgraduate students in the master’s programme in Educational Psychology?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to propose an author’s model of social interaction in the educational environment for the master’s degree course as a productive and creative teacher-student cooperative activity. In every sphere of a human life, the interaction is always social by its nature. The mechanism of the social interaction includes individuals who take various actions; changes in the outside world, caused by these actions; the influence of these changes on other individuals; feedback of the individuals, who were influenced on (Osipov & Moskvichov, 2015).
On defining the essence of social interaction, P. Sorokin includes the following components in its structure: a personality as a subject of interaction; society as a combination of interacting individuals with its socio-cultural relationships and processes; culture as a set of conditions, values and norms that interacting individuals have (Pochebut & Meyzhis, 2016; Sorokin, 1994). In the network society, virtuality takes on a dimension of reality where new forms of online networking become applicable (Brey, 2014) which, in our opinion, necessitates appeal to values.
In relation to the issues mentioned above, social interaction can be understood as a dialogue that a subject of the activity is having with oneself, with others and with the Culture as a set of acquired values and a context of life.
At present, the educational process is much more often considered as a process of interacting and cross-penetrating a personality’s meanings, as well as an initiation into cultural values, into a humane style of communication and interaction between participants of the educational process. In his seminal work, A.V. Petrovsky confirmed the hypothesis, that relationships in communities, bringing their members together not only through the shared activity, but through a social environment important for every community member, are influenced by the content and values of this activity (Petrovskiy, 2006).
The idea of developing an attitude towards human’s values has become a basis of the educational project “The virtual market of educational services” designed for the postgraduate students in the master’s degree course.
The educational interaction of learning process participants has a form of activity or communication, influenced by interpersonal relations and a collectively created product. The cooperation, with such characteristics as mindful activity, ability to goal setting and reflection, freedom of choice and responsibility for it, corresponds to the “subject-to-subject” level interaction (Linnik, 2013).
The participation of teachers in the whole system of students’ life is characteristic for the real cooperation. For teachers and students it is a process of mutual sharing the meaning and content of their activity, experience, emotions. As a result of a dialogue, its participants' positions are converted into the ones of equal partnership. The main characteristic of this interaction are: common changes on both sides of learning process resulted by their cooperative action and mutual influence; the emergence of new values that are becoming a base of socially important group activity. The objective of the educational interaction is to create the best conditions for the self-presentation of one individual of learning in the counter activity of another one, to help develop the creative learning motivation, to support efforts of creating a new product that doesn’t exist in the world yet (Ryan & Deci, 2017).
The creative nature of activity is associated with the notion "productivity". The term “productivity” refers to an individual’s ability of using his strength and implementing his inner capabilities. This suggests some freedom and independence of the individual from the external management but assumes the inner mind control. Productivity means that an individual perceives himself as the embodiment of his forces as "a creator" (Fromm, 1964). The individual’s contribution to a productive cooperative activity, his position as a subject of this activity, determining the possibility of creative achievements become a necessary condition for further self-development and self-realization. The essence of the cooperative productive and creative activity is to provide the leading role for creative and productive tasks on all stages of teaching (Lyaudis, 1980). Successful cooperative teacher-student activity changes the whole system of cultural environment of learning, the type of teacher’s control, because this system center becomes the developing personality of the student. Teaching creativity is to form a personality’s capability to change the basics of his own activity and interaction, to build and transform his implementation programmes in cooperation with other participants, to develop skills of taking responsibility, to agree with other people about values of their mutual experience and "significant Other".
V.I. Slobodchikov describes productivity as a culture of self-comprehension, self-development, self-revealing one’s own human potential that are not engaged enough in the processes of the modern education (Slobodchikov & Isaev, 2013).
Efficiency as a creating disposition (creative relations in all horizons of experience) being a core of cultural distinctness of a person, together with well-educated intellect and intrinsic motivation to productive work, form a bedrock of human potential. The criteria of the outcomes and quality of the creative educational process are: integrity, soft competencies, creative energies that offer the prospect of self-actualization and self-development in socio-cultural environment, social health and social mobility of a person.
Each student personality development and small group uniqueness arise from learner-friendly attitude of mind, supportive, calm and secure atmosphere in the classroom, a feeling of belonging to a group, building communication with a variety of technology means (telephone, Skype, E-mail, etc.), individual and collaborative creative activities. Based on the findings from earlier studies, the practice comprising online search, understanding and evaluation promotes development of foundational skills and dispositions for learning (Caviglia & Delfino, 2016).
Research Methods
Findings
The outcome of the project is developing a system of values and attitudes during the interaction of the master’s degree students. During the learning activity in the “market format”, different models of interaction were used; mastering different positions, functions and roles by the students who are involved in a cooperative project; forming initiative and doing joint actions on one’s own initiative; developing different ways of reflection.
The developmental model pursuing efficient social interaction in the cultural form of "The virtual market of educational services" was examined within the framework of educational experiment. The proposed mode of interaction employed the master students’ intellectual and activity resources that were concretized in the individual projects. In connection with the development of the open education and according to the Act "On Education in the Russian Federation," some new categories have been introduced into an educational practice. They are: "a networking form of educational programmes realization ", "e-learning", "distant learning technologies». The concept of "collaborative learning" or "cooperative learning” belongs to the main concept of networking interaction in which two or more people study or try to learn something together.
A networking training programme carried out in collaboration can be an example of the participation and cooperation of teachers and students. A group of teachers has taken a refresher course “Tutorial systems in the field of financial competence" within a joint project of Interregional Tutors Association and the University of Finance under the Government of the Russian Federation. Some modules of financial competence improvement (like “Personal master’s finance”) proposed as a base of management by the students were included into the programme “Financial and business activity of students trained for the master’s degree” in Pedagogy”. This is an example of how important is information literacy in terms of “driving the process of students’ making financial management decisions (Stonebraker, 2016).
Positive conditions for developing the student's individual characteristics and uniqueness of a small working group contribute to a good emotional mood, an atmosphere of support and mutual aid, implementation of communication with students through a variety of media (phone, Skype, e-mail, etc.), individual and collective creativity. A mode of exchanging views, ideas, positions, productive discussions, collective generation and opposing ideas, proposals, evidence is set for dialogue. The students’ personal intellectual resources have served as content of the proposed interaction form (personal projects as modules of a networking advanced training programme for master’s degree students, teachers and those individuals who need it).
Examples of educational services proposed by the students
Educational service: "The bio-adequate method or the way of an adequate life." How to use both cerebral hemispheres by developing not only the left hemisphere but also the right one, while using its enormous creative potential?
Educational service “Accessible environment”. How to let a child a good chance to choose anything attractive?
Here is an example of a module annotation "Creative English”, written by a student for a networking module programme of advanced training:
"After studying the content of the module you'll be able: to use spoken and written Russian and English in professional communication; to write abstracts in English of your scientific articles; to prepare multimedia presentations in accordance with standards and formats of the professional community.
The organization forms of learning: group work, discussions, games, Web quests, dramatization, and individual work with Internet resources. The methods and techniques of learning: creating exercises, staging scenes, dramatization of dialogues, writing abstracts, writing article reviews, making a glossary, investigating word origins, etc.”
The students made a mutual assessment of their educational services presentation. Feedback and suggestions were accessible to everyone on the site https://sites.google.com/site/magistraturanevzorovmn/tablica-prodvizenia-studentov-po-nis/-firma-odnodnevka-delovaa-igra
Considering the social interaction of master’s students and their teachers from a position of cultural approach, we used the values, regulatory components of culture (standards, norms) that make an activity motivated and thoughtful. Viktor Frankl, describing values as semantic universals that define the meaning of a human life, distinguishes:
• values of experience: studying the deep essence of other people in their originality and uniqueness on the level of spiritual and semantic dimensions;
• values of creativity: the meaning and value of a human labor as a contribution to the society’s life (Frankl, 1990).
To determine the values in the process of project realization, we used a diagnostic technique "The wheel of values". The study involved 120 students. They were asked to identify the most important values that had been identified in the process of social interaction.
Using a “wheel” axis (in the range of 1 to 10) the students were asked to mark the values which they find the most important in social interaction; label each axis and indicate a degree of its importance; join the points.
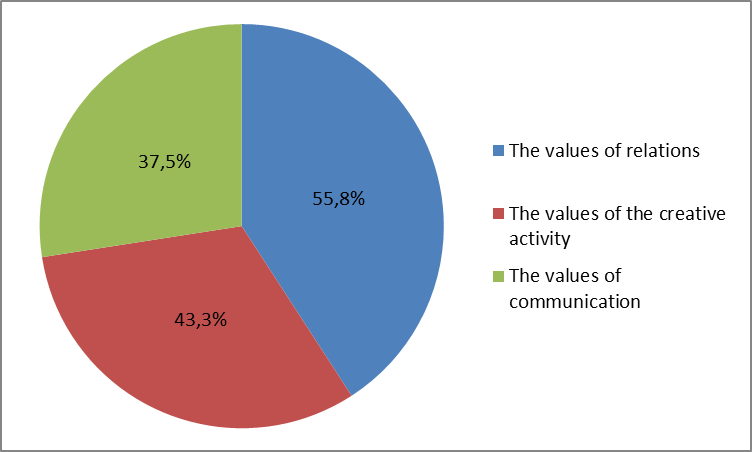
The results of the diagnostic study show that 55.8 % of respondents attach importance to the relationships developed in the process of training (decency, honesty, sociability, peering); and consider them the major purpose of social interaction in vocational training.
43. 3 % of respondents highlighted creativity development throughout “The virtual market of educational services" project.
37.5 % of respondents are certain that reciprocal social interaction (group cooperation) create the values of communication (expressing oneself and carrying one’s point in front of the group, an ability to listen and willingness to hear; endorsing alternatives; reflectivity, teamwork skills), encourage building cooperation relationships and handling problems.
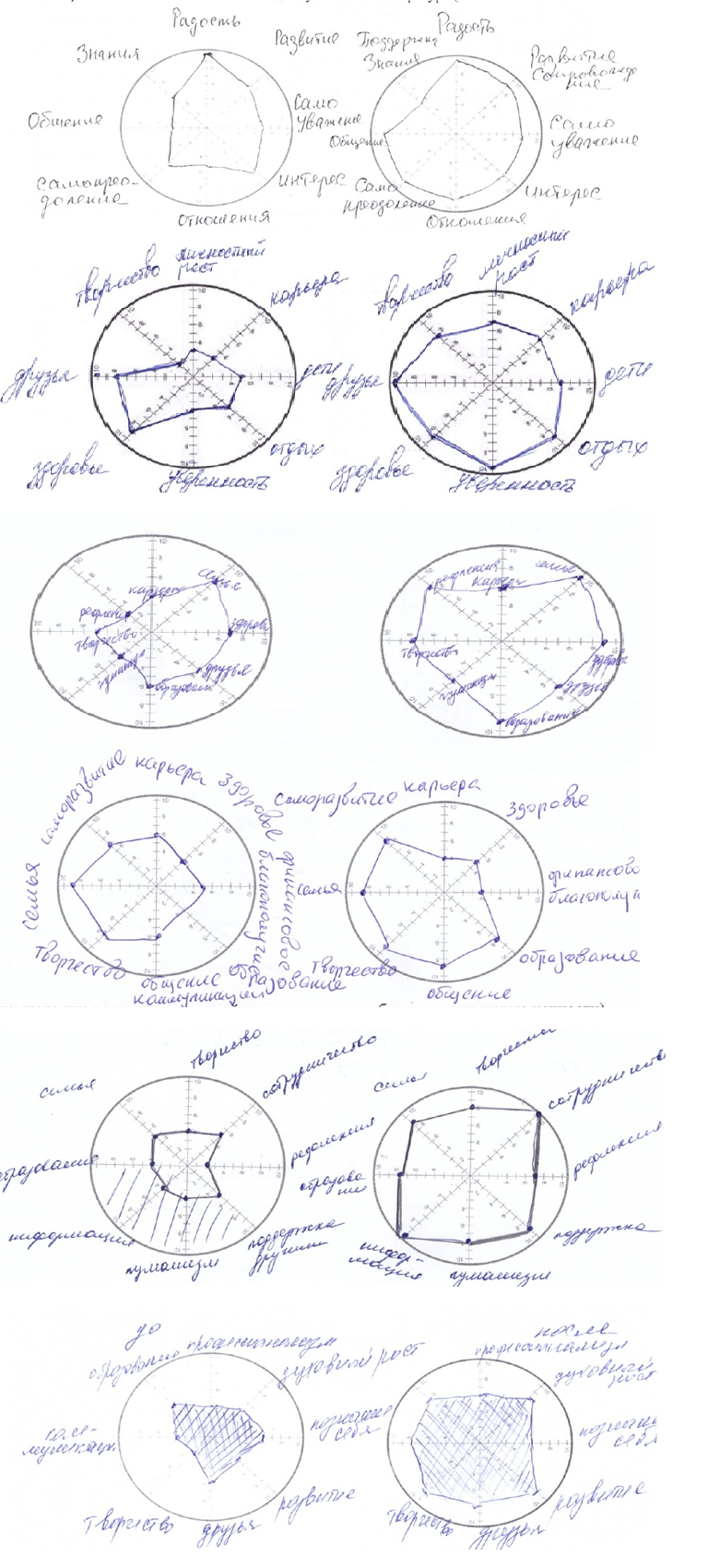
The value changes, identified by the students in the process of preparation and realization of the project “The virtual market of educational services ", are shown in Figure
One of the main survey methods is a sophisticated analysis of the activity products. In the process of the project realization the students carried into effect more than 40 projects designed for the population in the Far Eastern Region.
The students posted their projects on the site
https://sites.google.com/site/magistraturanevzorovmn/tablica-prodvizenia-studentov-po-nis/-firma-odnodnevka-delovaa-igra
The product of the group work is a “Networking modular programme of in-service education” project, a social network of master students in the field of Psychology and Education, School of Pedagogy. Online community members are always willing to provide tailor-made educational services within the range of the professional competences cultivated in the master courses.
The final product of the social interaction in the postgraduate students’ community, within the project, became the idea of the networking modular advanced training programme aimed at providing educational services for the population of the Primorsky Krai, the Far Eastern and Asian-Pacific Regions.
Conclusion
Sharing activity and cooperation, involving in the dialogue, supporting a network community provided an opportunity for every student to find an appropriate niche for his interests, expression style and for making important contribution to the establishment of a common product. This is compliant with the global challenges and the needs for the change in the higher education (Black & Muddiman, 2016; Burford, Partridge, Brown, Hider & Ellis, 2014). A student’s creative initiative in producing a new educational product has made it possible to go beyond cultural items of traditional patterns of students’ life and activity and defined significant increment in value-meaning and personal spheres.
The prospects of developing the virtual market of educational services are as follows. First, the Department of the theory and methodology of professional education in FEFU becomes a resource center, implementing advanced training programmes and, on that basis, forming a professional networking community. The development of cooperative modular advanced training programmes by master’s course students and their teachers provides the continuity of education and allows their participants, who live not only in Russia but also in other countries, to design an individual way of education. Besides, the students of the master’s degree course and their teachers take an opportunity to generate their order for the advanced training programmes.
Second, the virtual market of educational services is converted into a network model of advanced training that allows to expend the boundaries of professional communication of students and master’s graduates, and to ensure cooperation in the international educational community.
In this way the contradiction is resolved between lifelong self-education needs, education programmes tailored to the needs of the present-day students and educators, and a lack of those meeting today’s requirements.
The education area of networking community, for the most part, stipulates success in pursuing the main goal: the creation of the centre of excellence for graduate students and faculty members. The graduate students’ intellectual and activity resources concretized in the individual and group projects provided the content of modular networking programme of professional development.
Thus, while meeting the challenges of the future, the networking model of advanced training extends the set of teaching forms and methods, makes it possible to use the proposed forms in all fields of training and professional communication, meets individual learning needs of teachers, students and workers in various fields through the various resources at the level from an individual to the global world.
References
- Asmolov, A.G. (2015). Optika prosveshcheniya: sociokul'turnye perspektivy. Moskva: Izdatel'stvo «Prosveshchenie» [in RUS.]
- Black, A., Muddiman, D. (2016). The early information society: Information management in Britain before the Computer. Retrieved from: https://books.google.ru/books?id=AzOCwAAQBAJ&hl=ru&source=gbs_book_other_versions
- Brey, P. (2014). The Physical and Social Reality of Virtual Worlds. In M. Grimshaw (Ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Virtuality (pp. 42-54). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Brooks, C.F. (2016). Disciplinary convergence and interdisciplinary curricula for students in an information society. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14703297.2016.1155470].
- Burford, S., Partridge, H., Brown, H., Hider P., Ellis, L. (2014). Education for Australia's information future. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/07294360.2014.973380
- Castells, M. (2010). The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture. V.1: The Rise of the Network Society. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell.
- Caviglia, F. & Delfino, M. (2016). Foundational skills and dispositions for learning: an experience with Information Problem Solving on the Web. 487-512. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1475939X.2015.1080756
- Don Tapscott, Anthony, D. W. (2013). Radical Openness: Four Unexpected Principles for Success. Technology, Entertainment, Design: collection of articles based on materials from the international Internet conference. Long Beach: LLC. Retrieved from: https://www.ted.com/talks/don_tapscott_four_principles_for_the_open_world_1
- Frankl, V. (1990). Chelovek v poiskah smysla: Moscow: Progress. [in RUS.]
- Fromm, E.H. (1964). Man For Himself. An inquiry into the psychology of ethics. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Holmén, M. and Ljungberg, D. (2014). The teaching and societal services nexus: academics' experiences in three disciplines. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13562517.2014.978751].
- Linnik, E.O. (2013). Sushchnostnaya harakteristika ponyatiya «sub"ekt-sub"ektnoe vzaimodejstvie»: psihologo-pedagogicheskij aspect. Innovacionnye obrazovatel'nye tekhnologii, 4 (36), 48-54. [in RUS.]
- Lyaudis, V.Y. (1980). Struktura produktivnogo uchebnogo vzaimodejstviya. In A.A. Bodaleva, V.YA. Lyaudis (Eds.), Psihologo-pedagogicheskie problemi vzaimodejstviya uchitelya i uchashchihsya. Moscow: NIIOP APN SSSR, 37-52. [in RUS.]
- Osipov, G.V., Moskvichov, L.N. (2015). Sotziologiya. Osnovy obschey teorii. Moscow, INFRA-M Publ. [in RUS.]
- Petrovskiy, A.V. (2006). Psihologiya i vremya. St. Petersburg: Izdatel'stvo «Piter» 368. [in RUS.]
- Pochebut, A.G., Meyzhis, I.A. (2016). Social psychology. St. Petersburg: Piter Inc. [in RUS.]
- Rheingold, H. (1993). The Virtual Community: Homesteading on the Electronic Frontier. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Ryan R.M., Deci E.L. (2017). Self-Determination Theory: Basic Psychological Needs in Motivation, Development, and Wellness. New York: The Guilford Press.
- Slobodchikov V.I., Isaev, E.I. (2013). Psikhologia razvitiya cheloveka. Moskva: Izdatel’stvo Pravoslavnogo Sv’ato-Tihonovskogo humanitarnogo universiteta. [in RUS.]
- Sorokin P.A. (1994). Obshchedostupnyj uchebnik sociologii: Stat'i raznyh let. Moskva : Nauka. [in RUS.]
- Stonebraker, I. (2016). Toward informed leadership: Teaching students to make better decisions using information. 229-238. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08963568.2016.1226614].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
21 September 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-045-7
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
46
Print ISBN (optional)
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-887
Subjects
Education, educational equipment, educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), Study skills, learning skills, ICT
Cite this article as:
Borovkova, T. I., Kravtsov, V. V., Lavrinenko, T. D., Savelyeva, N. N., Petrova, G. N., & Stepkova, O. V. (2018). Productive Student-Teacher Interaction On The Virtual Market Of Educational Services. In S. K. Lo (Ed.), Education Environment for the Information Age, vol 46. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 108-119). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.09.02.13

