Abstract
This study investigates the dynamic relationships amongst the total of housing loan and macroeconomic variables (inflation, interest rate, and Growth Domestic Product) in Malaysia. A sample of this study are time-series data, which covered the period from 1991 to 2014 (23 years) from Department Statistics and Bank Negara. This paper analysed by using correlation and regression in SPSS. There are two (2) methods of analysis are picked to evaluate the results, consists of correlation model and regression model. The empirical results show that only inflation, interest rate, and GDP have negative significant impact with increasing of total housing loan while unemployment rate are not significant impact with the increasing of total housing loan. The correlation results show the inflation rate, interest rate, and GDP are having a strong relationship with total of housing loan. As a conclusion, only three (3) out of four (4) macroeconomic indicator are having a relationship with the housing loan and the strongest relationship is inflation and interest rate. As the result which inflation rate, interest rate and GDP have a significant relationship towards total housing loans, the company and government can predict and making decision about loan approval in construction sector
Keywords: Housing Loaninflationinterest rateGDPunemployment rate
Introduction
Housing loan that been offered by a financial intermediaries such as banks, government society, and so along. Housing loan also can be seen as a totality of money that has been borrowed from a financial establishment in order to buy homes. Housing loan consists of adjustable or fixed interest rate in payment term. There have some factors that need to be considered by the financial institutions in order to approve a housing loan because to avoid default payment. For example, income.
More often than not, a person considered many factors in order to decide to purchase a home such as the income that they earn, loan interest rate, inflation, and etc. The general level of prices for goods and services is rising (inflation), and, later, the buying power is passing. The person who not employed will affect their income. Thus, will bear upon the demand of goods and products and from that it will chew over the inflation rate. By that, unemployment might help in providing better findings towards this field.
According (Yuval, Peter, & Jan, 2012), they found that relationship between home ownership and unemployment levels is inverse in cross-section and GDP significance of the relationship is small. Prior literatures (e.g. Oliver, 2010; Sabri, 2005; Theodore, 2015) found that significant relationship between interest rate and housing loan. Investigated a significant multidirectional link between house prices, and GDP and inflation. Furthermore, Ong (2013) found that GDP a significant and strongest relationship with the house price index not inflation.
Problem Statement
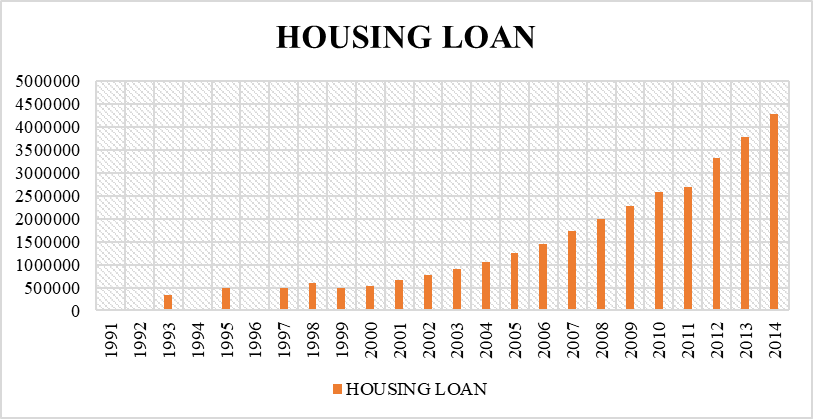
Based on the figure
Research Questions
How does inflation, interest rate, unemployment and GDP influence the amount of housing loan that will be made in a year?
Purpose of the Study
The study might improve a knowledge on housing loan and the economics factor influenced the total amount of housing loan increased or decreased.
Research Methods
A sample of this study are time-series data, which covered the period from 1991 to 2014 and sources of data from Department Statistics and Bank Negara.
Regression analysis is given of the following examples
Whereby;
Y =total of housing loan (Dependent data)
a = constant
B1 = inflation (Independent data)
B2 = interest rate (Independent data)
B3 = GDP (Independent data)
B4 = unemployment rate (Independent data)
e = error
Findings
The table below shows a Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) test. VIF measure how much the variance of the estimated regression coefficients is inflated as compared to when the predictor variables are not linearly related. It is practiced to identify how much multicollinearity (correlation between predictors) exists in regression analysis. Multicollinearity is problematic because it can increase the variation of the regression coefficients, making them unstable and hard to understand.
Inflation rate and housing loan have a negatively correlated relationship with a magnitude -43.9%, accepted at the 5% level of significant. Interest rate and housing loan have a negatively correlated relationship with a magnitude -37.2%, accepted at the 5% level of significant. Unemployment rate and housing loan have a positively correlated relationship with a magnitude 0.3%, accepted at the 1% level of significant. GDP and housing loan have a negatively correlated relationship with a magnitude -36.9%, accepted at the 5% level of significant.
REGRESSION MODEL
Y = Total of Housing Loan
Β0 = Constant Parameter
INF = Inflation
IR = Interest Rate
UR = Unemployment Rate
GDP = Gross Domestic Product
ϵ = Error Term
Model shows that all the independent variables which is inflation rate, interest rate, GDP, and the unemployment rate has a negative result on housing loan as the estimated correlations is negative. In other words, if housing loan increase by 1 unit, then inflation rate also decrease by 0.262 units, interest rate will decrease on 0.090 units, while GDP will decrease 0.074 units and for the GDP, it will decrease 0.096 units and vice versa depends on the estimated coefficient value. This makes a negative reflects to housing loan.
Based on the probability value, inflation rate has a significant value because the probability value is less than the significant value of 5%. The probability value of inflation rate respectively is 0.003, which is lower than 5%. Furthermore, it indicates that there is a negative impact between inflation rates towards housing loan. (Chong, 2007)
It also same with the other independent variables which is interest rate and GDP because the probability value of these variable are 0.004 and 0.012 which is lower than 5% and 1%. However, it still shows that there have a negative impact between interest rate and GDP towards housing loan. For unemployment rate, the probability value is more than a significant value of 1%. It indicates that do not significant and have a negative impact toward housing loan. (Ni, Shuen Shi, & Wen, 2011)
Table
The result also indicates that in the correlation result, there are few variables only does have a relationship, in overall the significant level in regression shows the total impact of the variables, which make the total housing loan, is strongly affected.
In the Table
The correlation results show the inflation rate, interest rate, and GDP are having a strong relationship with total of housing loan. The mean square of the regression is 1.454 and the F-value showing at 6.261 percent. This both value showing the relatively a strong significant among the variables.
Conclusion
Based on this research, there is some recommendation that could be made for the use for future. As the result which inflation rate, interest rate and GDP have a significant relationship towards total housing loans, the company can use this study to make their business plan and activities.
Other than that, the government also perhaps can use this study to help government making decision process. It might work as references for the government and it might work as the key indicator for the construction sector. Malaysian government needs to interrupt and give advice to the construction company in their business activities
References
- Chong, H. A. (2007). Substitution effects: Do inflation and Deflation Affect Islamic Home Financing? Labuan e-Journal of Muamalat and Society, 41-51.
- Guo, M., & Wu, Q. (2013). The Empical Analysis of Affecting Factors of Shanghai Housing Prices. International Journal of Business and Social Sciences, 219-223.
- Ni, J.-S., Shuen Shi, H., & Wen, Y. (2011). Interest Rate, Unemployment Rate and House Market in US. International Conference on Social Science and Humanity, 413-417.
- Oliver, L. (2010). Is there a Link between Home Ownership and Unemployment Level? Evidence from German Regional Data. CAWM Discussion Paper, 1-29.
- Ong, T. S. (2013). Macroeconomics Determinants of malaysian Housing Market. Human and Social Research, 119-127.
- Rizvi, W., Malik, M., & Khan, S. (2015). The Impact of Inflation on LOan Default: A Study on Pakistan. Australian Journal of Business and Economics, 87-92.
- Sabri, B. (2005). Dynamics Relationship between Houses Prices and Macroeconomics Aggregates. Research Report in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for the Degree of Master Business Administration, 1-36.
- Theodore, P. (2015). On the Macroeconomics determinants of the housing Market in Greece: AVECM Approach. Hellenic Observatory Papers on Greece and Southeast Europe, 1-31.
- Yuval, K., Peter, N., & Jan, R. (2012). Homeownership, Unemployment and Counting Distances. Tinbergen Institute Discussion Paper, 1-27.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 July 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-043-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
44
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-989
Subjects
Business, innovation, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues, industry, industrial studies
Cite this article as:
Ramlan, H., Hashim, S. L. M., & Saleh, N. E. (2018). Macroeconomic Determinants Of Housing Loan In Malaysia. In N. Nadiah Ahmad, N. Raida Abd Rahman, E. Esa, F. Hanim Abdul Rauf, & W. Farhah (Eds.), Interdisciplinary Sustainability Perspectives: Engaging Enviromental, Cultural, Economic and Social Concerns, vol 44. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 644-649). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.07.02.69

