Abstract
Healthcare systems in every country are facing considerable challenges in providing high-quality, safe and universally-accessible care. Some countries are undertaking a major overhaul of their health systems, while others are striving to be more responsive to the needs of the public. This research focus on the impact of online newspaper in Ivory Coast or Cote d’Ivoire namely, Abijan.net in distributing health information using public health campaign towards the public. A total of related 50 news were content analysed for one year in 2016. Instruments via coding sheet and coding instructions were developed to answer the research questions using the Agenda-Setting concept and information sharing and social marketing framework. Holsti reliability and validity test revealed 0.87 consistencies. The Ivory Coast government with the help of NGOs has been very pro-active for the past few years promoting health campaign to the public. An effective smart partnership between government of Ivory Coast and NGO was important modus operandi to run this policy via health campaign. One of the PDNS campaign is collaboration with Galenicum and NGO ADESC. The research result revealed that Abidjan.net as online newspaper gave attention to women and children, high infant mortality and maternal mortality rate. Health campaign news also gave attention to basic health, hygiene and nutrition. Information on health care services which were being carried out through consultations at the community clinic, medical visits to primary schools, vaccination and medical examinations for children were also noticeable in the Abidjan.net.
Keywords: Healthcare ToolsE-HealthHealthcare SystemNews CoverageHealth PolicyCote d’Ivoire
Introduction
In public healthcare and facilities are significant in the health policymaking, where the media is an underutilized as a tool in health communication strategies in mobilizing and supporting, the policymakers that can contribute significantly to health and community mobilization around health issues. Therefore, health policy maker initiative for public healthcare, for instance, conducting training community members to report on VIH/AIDS through an SMS helpline, web-based platforms to link pregnant women, and creating digital data for health reporters and medias. However, the partnerships between health services providers and media to create effective and integrated methods of two-way communication. On the other hand, the traditional media remains one of the methods of communication, in the context of local language, using media of state-run radio and television services to nationwide.
In terms of e-health services, Cote d’Ivoire is practically still in its infancy, from related studies, de Morais and Stückelberger (2014) argues that in Cote d’Ivoire, the number of mobile phones surpasses that of fixed lines, e-Health and m-Health seem to be a favorable network for medical communication and healthcare. Currently, however, only limited applications are accessible. One of the most successful is the Duty Chemist application, launched by Orange Healthcare, which identifies the closest pharmacies to patients via mobile, supporting local communities by leveraging technical innovations to advance areas, such as public healthcare systems, e-health and m-payment, see figure

Health communication can help people adopt positive health behaviors and create for preventive, this field was inspired by the AIDS epidemic starting in 1985 when there was no antiretroviral treatment and the only tool for prevention was social and behaviour change (Goldstein, MacDonald & Guirguis, 2015).
Problem Statement
In the contemporary world, media plays a key role (Abdoulaye & Zanuddin, 2017; Mudjirin & Zanuddin, 2017; Rung & Zanuddin, 2017; Yasir et al., 2016; Zanuddin & Abdoulaye, 2017; Zanuddin & Alyousef, 2017; Zanuddin & Mudjirin, 2017). Healthcare professionals, policy makers and implementers are challenging mainstream ideas to take public health to a new level, as public health policy and health-related attitudes are greatly influenced by local media coverage. However, the mass media play a role in health information that can support and save lives of the individual and community. In addition, the accountable and true media coverage has a positive impact in informing people on the possibilities and preventive of diseases. Therefore, the study shows that media interventions can contribute to policy making changes to mobilize communities towards improved health effects.
It is interesting to point out the scope and the nature of media content analysis coverage of health issues delivery system. The coverage was more about personalities like film stars endorsing health issues, a minister making a statement etc., mostly in the nature of ‘who’ and ‘what’ coverage. The lifestyle health issues like tension, stress, obesity and back pain etc. had been covered more than other serious health issues such as policy issues, preventive aspects, epidemic or social practice. It suggests that, in some cases, the coverage peaked around certain dates or events, such as the World Health Day, and launch of a programme by the government, and few items covered had people perspective towards better issues.
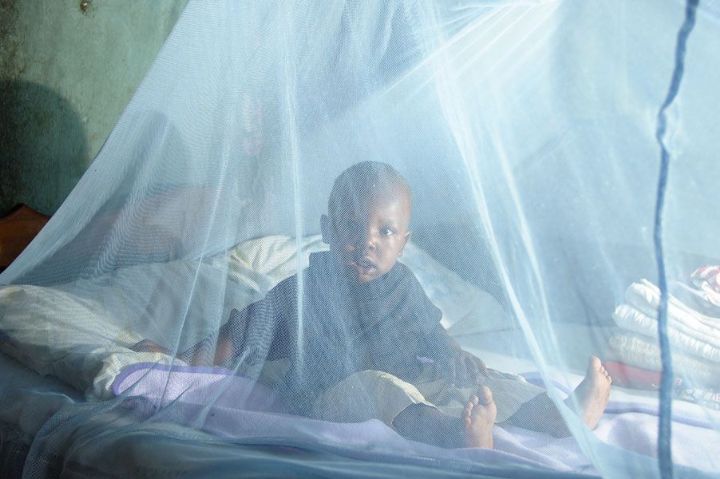
Among the samples of online news coverage, a Non-Government Organization; the Ivorian Association for Progress and main actors, the community leaders, politicians and media men in the fight against malaria, poverty and disease in the health regions of country. They can effectively contribute to the fight against malaria, to send awareness messages and methods of malaria control to populations. However, Malaria remains the leading cause of death in Côte d'Ivoire, despite numerous measures taken by the government to eradicate it. Figure

Research Questions
-
What is the effectiveness of public relations and online news in delivering public health messages?
-
Are online media outlets able to reach people and improve their health information in an effective way?
-
What are the actions and programs of major actors towards public healthcare issues in Cote d’Ivoire?
Purpose of the Study
Purpose of this study is;
To examine interaction with news media and medical communities to meet the information needs
To examine the impact of online newspaper in delivering public health message to support national welfare, and save lives of the people
To explain agenda-setting of media influence and public relations, to disseminate healthcare awareness
To determine the coordination and resource mobilization for the effective implementation of impact interventions.
Literature Review
Healthcare facilities in Cote d’Ivoire
In Côte d’Ivoire, healthcare facilities, which are dominated by the public sector delivery health care and services in the primary level, which is constituted of sanitary institutions of first contact, and the secondary level is constituted of health facilities used for first referrals, while the private sector , which plays a role, including non-profit, for-profit, and traditional treatment providers.
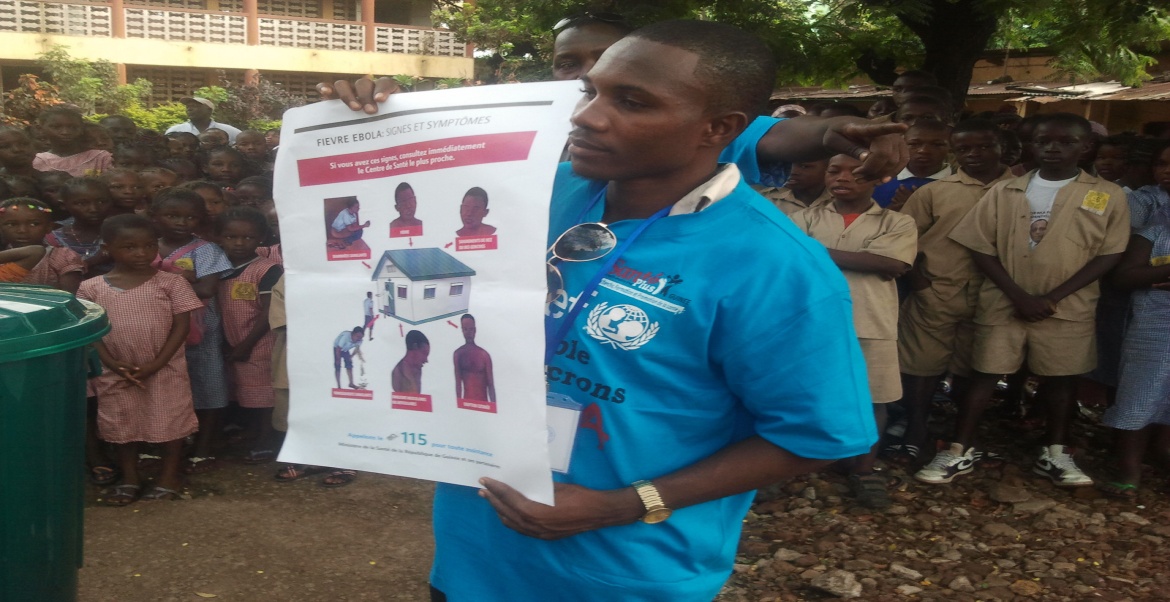
As a consequence of health issue, seeing the geographical location of Cote d’Ivoire, Cisse (2011) point out that it is susceptible to certain common sicknesses such as malaria and meningitis, which are among the main causes of people death. While the mortality which declined progressively over the 1958-1994 and then rose until 1998. In fact, the proportion of mortality fell from difference phases, 28% in 1965 to 17% in 1975 as well as 13% in 1988 then reached 14.2% in 1998. Moreover, in the context of Ebola virus disease in West Africa, particularly in two countries that share a border with Côte d'Ivoire, the risk of epidemics and other emergency situations remains high, therefore; that justifies the strengthening of national health policies in the areas of prevention, awareness and response to improving public healthcare.
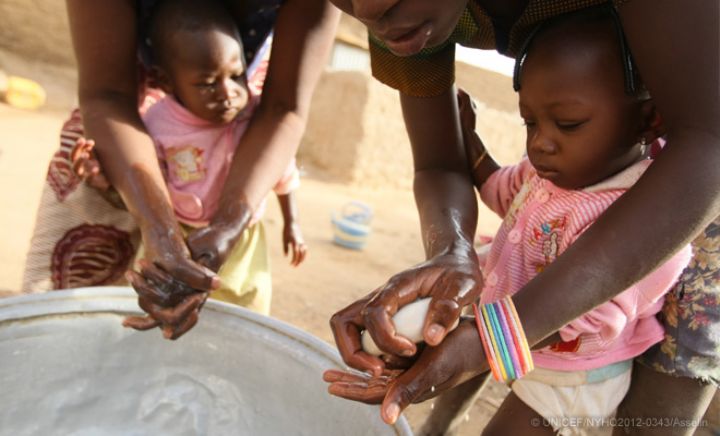
The Government Information and Communication Center (CICG) in collaboration with several organization, such as the National Program for Mother-Child Health (PNSME) in collaboration and UNICEF launch health campaign in Abidjan to raise awareness about

Public Health Policy
In terms of public health system, in May 2011, a policy of free public health services and medicines was performed. Although the government’s social welfare intentions, the policy suffered from insufficient planning, and increased service utilization soon strained providers and equipment in a system weakened by a decade of poor governance and under-funding. Moreover, in early 2012, the Government of Côte d’Ivoire shifted toward a program of “targeted free services” for pregnant women, children, and medical emergencies. Implementation is being planned now, and will be included within the National Plan for Health Development (PNDS).
To strengthen health policy and provide health facilities to all people, WHO provided the Ministry of Health with the necessary support to develop policies, strategies and plans and to strengthen the health system, including in specific areas such as maternal and child health and disease control programs. The country thus has a number of strategic documents that need to be updated, as well as The National Health Development Plan (PNDS) envisions a performing, comprehensive, responsible and efficient health system that guarantees the best possible standard of health for all people living in Côte d'Ivoire, especially the most vulnerable.
As part of Cote d’Ivoire’s public health policy
In addition, to respond to stop Ebola to spread, the ivory coast government banned the sale and consumption of bushmeat to limit the spread of the Ebola virus, in line with Theresa, Christian, and Nandi, (2014) that WHO has observed that there is no animal vaccine against RESTV that is available, the culling of infected animals, with close supervision of burial or incineration of carcasses, may be necessary to reduce the risk of animal-to-human transmission”. It suggested that this should be banned the movement of animals from infected farms to other areas to reduce the spread of the disease (Theresa, Christian, & Nnadi, 2014)
Hypothesis
In view of the concept of Agenda-Setting, in determining the correlations between variables, it can be hypothesized that:
H1.The public relations and online newspaper play a significant role in delivering public health message.
H2.The effective implementation of health policy has significantly supported the people of Cote d’Ivoire for disease prevention and awareness and health promotion
H3.The online media coverage could positively influence people of Cote d’Ivoire, for the public health campaign and advertisements
Theoretical Framework
Applying the concept of Agenda-Setting, which have been found within previous studies, in order to explain the impact and influence between the variables and how the level of influence, considering online news coverage and health campaign influence health policy and public’s perception. In general, the considerable of the media’s influence, as in 2008 paper of Agenda-setting, Douglas Van Belle argues that while during the Cold War the media had an important effect on responses to aid, around 1990 media influence declined and the so-called ‘CNN effect’ was only ever illusory. For instance, the ‘CNN effect’ came about due to the US intervention in Somalia, where media coverage was a huge factor in decision making because it was no longer limited by the constraint imposed by likely or potential Soviet reaction (Cooper et al., 2015). The different categories of media towards impact of political agenda-settings to the consumers, Sayre, Bode, Shah, Wilcox and Shah, (2010) point out that the ascendance of digital media has the potential to alter this function in three distinct ways. The mainstream media significantly diminish traditional media’s ability to set the nation’s political agenda. Seeing that even though most people consuming digital media, but they are continuing to use more traditional media sources as well.
On the other hand, Social Marketing Orientation aims to improve the public health promotion as Nowak, Gellin, MacDonald and Butler, (2015) point out that it represents the extension of thinking to the “selling” of ideas, attitudes and behaviors, usually ones characterized as “pro-social” or focused on improving the health and well-being of both the targeted individuals and the broader community or society (e.g. preventing or promoting physical activity, and sharing nutrition recommendations). The journalists and editors took part in a workshop on “

Methodology
Data Collection
Data was collated through a quantitative content analysis of exiting literature, WHO reports and Health Account News Release, which consists of subject, related to the public health policy and health information coverage. Cote d’Ivoire online newspaper has been explored as well, which covered the public health that took place from 1st January 2016 to 31st December 2016 about (such as HIV/AIDS, Yellow Fever, Dengue and Malaria and many others). The online newspaper was then translated from French into English; they serve to analyse healthcare and awareness of the people of Cote d’Ivoire.
An initial set total of related 50 news articles were examined and content analysed. Instruments via coding sheet and coding instructions were developed to answer the research questions. Therefore, Holsti reliability and validity test revealed 0.87 consistencies. It is analysed using as well the Statistical Package of Social Sciences (SPSS) and non-parametric analysis, such as Chi Square to answer the hypothesis
Reliability and Validity
Intercoder reliability was deployed to test the validity and reliability of the content analysis instrument, a method of summarizing the substance of a set of mediated messages. The Holsti reliability and validity test, revealed .87 (87%), which showed strongly reliable instrument. The inter-coder reliability testing will be calculated by using Holsti Test Format as follow:
Findings
The paper analyzes Abidjan.net news article publication, to identify what is being covered per each month. It focuses on a primary variable-the topic of Health Programs and Campaign Coverage and the main actors are involved. (See Table

The result shows that from 1st January 2016 to 31st December 2016, the month of December achieved a highest distribution of news article coverage related to health campaign and awareness, which 10 of news article, followed by October 6 of news articles, July, September and number 2 of news articles, while March and August 1 of news articles (See Table
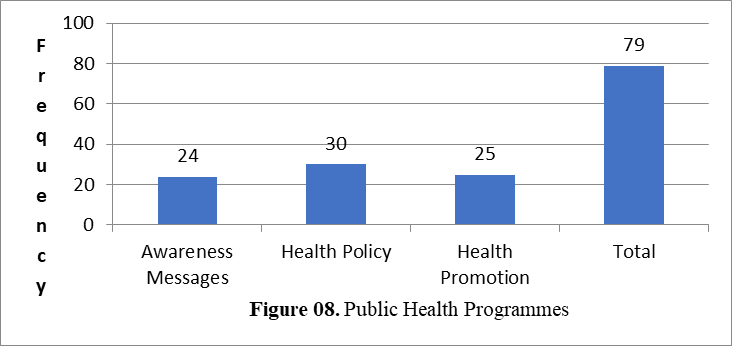
The study notes that it is undeniable fact that the media is a tool in public health intervention; supporting, and enhancing information can contribute to health and community around health issues. In terms of health policy initiative, as in Cote d’Ivoire, in line with PNDS policy to encourage prevention of diseases caused by an unbalanced diet, the absence of preventive measures against childhood diseases and by poor hygiene. But many existing constraints delay results and scale-up of health programs, directly or indirectly, from limited political will, weak health systems and little leverage to improve access to quality treatment. We suggest that, the health policy makers do more to fully engage new media in efforts to improve the public’s health. Regarding the online and traditional media agenda-setting, it shows that, even though the ability of the mainstream media to shape issues to the public perceptions, but also the ascendance of digital media has the potential and ability to set the nation’s political agenda. As in the current trend, most people are using digital media more than traditional media as a source of their health information.
Table
While public health programmes in (Table

There is a significant association between article perceptions and public healthcare program as covered by online newspaper, chi-square χ2 = 17.914, df =1, sig. = .000. Therefore, the public perceptions and healthcare program played a significant role in influencing health policymaker and government health officers of Ivory Coast. This hypothesis showed a significant association between the two variables (Table
Specific “Content” in (Table
Conclusion
The paper discussed the healthcare issue services and online news media coverage towards influencing public health policy and people heath issue, in responding to the research questions, therefore, it sought to meet the research objectives, the public healthcare is a priority in the health policy, where the media intervention is a tool in delivering public health message and health information to the community for health issues. Health policy maker initiative for public health strategy, for instance, community will be to report on the health issues through online new media as well as web-based platforms, therefore that can create the collaborations between health providers and media. In fact, journalists must be able to tell a story, entertain and engage the people. In terms of theoretical framework, the paper adopts information sharing, health belief models as well as Agenda-setting influence for health policy and online media coverage, it is suggested that public health policy and people health concern are influenced by media coverage, seeing that the media coverage has a critical role in informing people about health issue and how to take action. We conclude that the media interventions can influence and contribute to policy changes to support and mobilize communities towards better healthcare, and save lives.
Lastly, the paper indicated some samples of online news coverage, which was noticed in the Abidjan.net, the online newspaper about health campaign and information on healthcare services, it brings attention to basic health, hygiene and nutrition, such as medical visits to primary schools, vaccination and medical examinations for children, in addition, administrators and media men in the fight against malaria, poverty and disease in the health regions of some areas in Cote d’Ivoire, mobilizing community, political, administrative and media leaders to contribute in fighting against malaria through their influence. We suggest that, improving access to and equity within health systems will require multispectral interventions, and engaging the cooperation and participation of all stakeholders, including national and provincial governments, the private sector, and local communities have a role to play in assisting to build the capacity of national health systems.
References
- Abdoulaye, O. K., and Zanuddin, H. (2017). Online Media's Role in Public Health Information and Communication Sharing in Cote d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast). Information-an International Interdisciplinary Journal(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
- Abidjan.net (2016), Côte d’Ivoire: 3 millions d’électeurs supplémentaires pourraient voter pour la présidentielle, http://news.abidjan.net/h/523892.html.
- Cisse, A. (2011). Analysis of health care utilization in Côte d'Ivoire. Nairobi, Kenya: The African Economic Research Consortium.
- Cooper, C. P., Gelb, C. A., & Chu, J. (2015). Life cycle of television public service announcements disseminated through donated airtime. Preventive medicine reports, 2, 202-205.
- de Morais, J.-C. B., & Stückelberger, C. (2014). Innovation Ethics. African and Global Perspectives.
- Goldstein, S., MacDonald, N. E., & Guirguis, S. (2015). Health communication and vaccine hesitancy. Vaccine, 33(34), 4212-4214.
- Mudjirin, A. C., and Zanuddin, H. (2017). Political Information Sharing Pattern and Trend Among Students in the Islamic Boarding School in Madura, Indonesia: A Non-Digital Choice? Advance Science Letters(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
- Nowak, G. J., Gellin, B. G., MacDonald, N. E., & Butler, R. (2015). Addressing vaccine hesitancy: the potential value of commercial and social marketing principles and practices. Vaccine, 33(34), 4204-4211.
- Rung, C. J., and Zanuddin, H. (2017). Media Attention for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in Malaysia: A Comparative Analysis of Malaysia Chinese Newspapers Coverage. Information-an International Interdisciplinary Journal(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
- Sayre, B., Bode, L., Shah, D., Wilcox, D., & Shah, C. (2010). Agenda setting in a digital age: Tracking attention to California Proposition 8 in social media, online news and conventional news. Policy & Internet, 2(2), 7-32.
- Theresa, N.C., Christian, N.G., and Nnadi, F. (2014). ‘The Pervasiveness of Ebola Virus Disease in Africa: Implication for Economy, Ecology and Socio-Religious Dynamics’. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 19, 69-77.
- Yasir, M., Batool, S., Khan, F., Imran, A., & Qureshi, M. I. (2016). Social Media, Technostress and Workplace Deviance: An Evidence from The Software Houses in Pakistan. Abasyn Journal of Social Sciences, 559-571.
- Zanuddin, H., and Abdoulaye, O. K. (2017). Health Public Relations Campaign and Online News Coverage Focus: Does it help Public Health Policy and the People of Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast)? European Proceedings of Social and Behavioral Science(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
- Zanuddin, H., and Alyousef, Y. (2017). Social Media Grooming: The Relationship of Social Media, Youth and Terrorism in Saudi Arabia. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioral Science(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
- Zanuddin, H., and Mudjirin, A. C. (2017). Fostering Political Participation among Students of Pesantren through New Media in Madura. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioral Science(AIMC 2017 Special Issue & Paper presented at the Asia International Multidisciplinary Conference, UTM Johor, Malaysia, May 1-2).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 May 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-039-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
40
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1231
Subjects
Business, innovation, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Zanuddin, H., & Abdoulaye, O. K. (2018). Health Public Relations Campaign And Online News Coverage Focus. In M. Imran Qureshi (Ed.), Technology & Society: A Multidisciplinary Pathway for Sustainable Development, vol 40. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 869-882). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.05.71

