Abstract
The study deals with the demand for a new job position known as the “Talent Manager” and best practices in talent management. Organizations need to implement talent management in a competitive market. Intensive development of talent management in the world brings to the fore to need for specialists capable of implementing a talent management system and moving from HRM to Talent Management.The aim of the research is to analyze the vacancies in personnel management in the Russian Federation published on the federal recruitment site Head Hunter (www.hh.ru) and to identify the trend of the development of a new job position based on the best practices. The study was conducted using content analysis. The content selection criterion data was the term "talent" focused on 2 aspects: the job title and job description of the vacancies. Based on the results of the content analysis, the demand for the position of Talent Manager in companies was revealed with the definition of leading. It was found that in some organizations talent management is already the main strategy of Human Resources management, while in others it is only one among other tools for the development of human resources.The development of talent management in the world leads to the emergence of new specialists capable of creating and implementing a talent management system in companies. In turn, this will push for the development of innovative technologies in talent management that can significantly increase business efficiency in all, especially high technology and high-tech industries.
Keywords:
Introduction
Nowadays it is undeniable that human resources are an important factor for the development of any company in market competition. Modern companies are actively changing their approaches to human resources management, e.g. develop and implement human resources management systems. This innovation – Talent Management, in HR Management has been rapidly developing in the last 2-3 years (Neo HR, 2015).
Talent Management is a system of organizational, economic and socio-economic measures aimed at increasing the level of competences in critical activities for business. These measures are carried out by development and implementation of programs on talent attraction, acquisition, development and retention (Shahbazov, & Upravlenie, 2016).
In many companies Talent Management is not only a new tool for development of human resources but a leading strategy of personnel management successfully substituting traditional HRM. Our viewpoint is that talent management is not only a tool or a function of Human Resources Management but HR Management transformed in Talent Management System (TMS). Such a change of paradigm entails the appearance of new job titles in personnel management
Problem Statement
The study deals with the demand for a new job position known as “Talent Manager” and best practices in talent management. Organizations need to implement talent management in a competitive market. Intensive development of talent management in the world brings to the fore the need for specialists capable of implementing a talent management system and moving from HRM to Talent Management.
Research Questions
This study aims to identify the trends of the development of a new job position based on best practices of multinationals and local companies.
Purpose of the Study
An analysis of the vacancies in personnel management in the Russian Federation is considered vital in order to identify the specific competencies and talents that are being sought in this upcoming field. It will enable prospective employees and job-seekers to identify and enhance the skills that are pertinent to the job scope.
Research Methods
The study was conducted using content analysis where vacancies from a professional field “Personnel management, trainings” throughout the territory of the Russian Federation posted on the website hh.ru in January, 2017 were analyzed. Two aspects served as content-criteria for the data selection from all information:
the term “talent” is included in the title of a vacancy;
the term “talent” is found in job description of a vacancy.
Findings and Discussion
Content analysis of the job titles containing the term “talent”
The vacancies included in the first group are mainly offered by the companies from the following market segments:
FMCG (common consumption goods);
services;
agriculture;
banking/insurance;
retail;
medicine;
consulting;
IT.
The demand for the specialists in “talents” is more often found in FMCG, service and agriculture markets (fig.
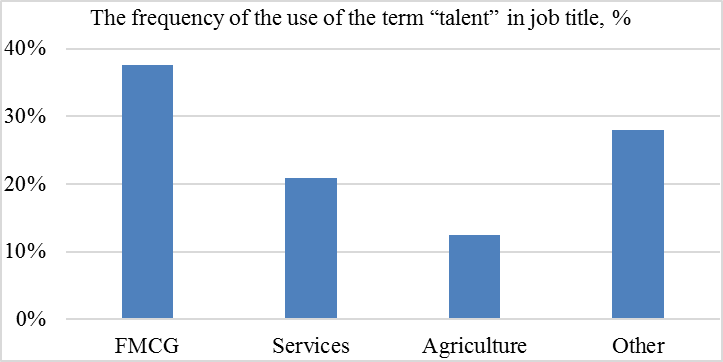
-
Coca-Cola - Talent Development Specialist, Talent Attraction Specialist;
-
Philip Morris International - Talent Acquisition Executive;
-
Nestle - Talent Acquisition Specialist;
-
Coca-Cola- Talent Development Specialist, Talent Attraction Specialist;
-
DuPont - Talent Sourcing Specialist;
-
Align Technology Inc. - Talent Acquisition Lead;
-
SAP - Talent Acquisition Support Intern HR and others.
-
Russian Post - Specialist in the department of personnel selection, assessment and management;
-
Bank Home Credit - Specialist of talent assessment department;
-
Pyaterochka - Talent Manager;
-
Baltica - HR Manager in the department of talent attraction and others.
Content analysis of vacancies with talent management included in job description
In vacancy analysis, the vacancies with job descriptions emphasizing talent management were singled out. However, the job title is formulated traditionally – Human Resources Manager.
Companies offering talent management as a basic function of HR Manager are represented in the following market segments:
FMCG;
services;
agriculture;
banking/insurance;
retail;
medicine;
consulting;
IT;
telecommunications, communications;
development;
fitness;
production company;
furniture;
educational establishment;
advertising;
automobile business.
The specialists with professional duties in the field of talent management are in high demand in the markets of FMCG, production companies, retail, banking/insurance, development (fig.
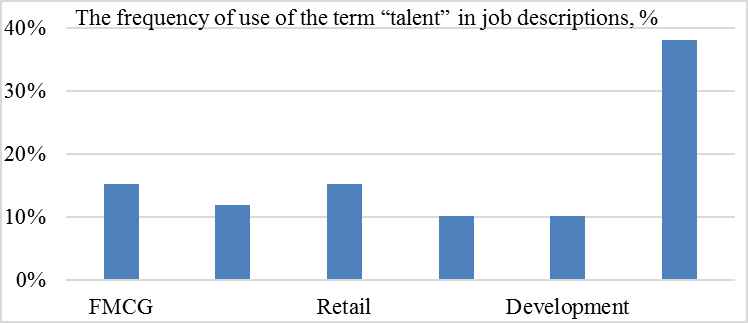
It is important to note that some companies consider talent-management as a function of the HR Department. A vivid example of such an approach is
Meanwhile, the situation in Adidas Group is different. The position of HRM Retail includes “participation in talent management processes and personnel reserve development in the relevant departments” (HeadHunter, 2017c); this proves that the company views talent management as a program of particular employee selection for further promotion.
-
“medium term personnel demand planning (1 year);
-
recruiting and selection of applicants for vacant positions in sales departments;
-
organization of adaptation for new employees;
-
organization and implementation of assessment and development centers;
-
facilitation of talent identification, rotation and development of the employees with high potential;
-
employer's brand development “ (HeadHunter, 2017b)
“Best practices” in talent management
-
application for the chosen position;
-
on-line proficiency testing (mathematical and verbal test);
-
interview with the company's managers;
-
assessment procedure: group and individual tasks during which the candidates are being evaluated by the managers.
life-job balance;
challenging tasks;
fast promotion opportunities;
unlimited internet access;
working in a team of the people of the same age;
close interaction with an immediate manager;
availability of modern gadgets.
Thus, based on the results of the content analysis, the demand for the position of Talent Manager in companies was underscored by the definition of leading. Moreover, in some organizations talent management is already the main strategy of HRM, while in others it is only one among other tools for the development of human resources.
Conclusion
Summing up the results of our research, it should be stated that the rapid development of talent management both in the world in general, and in Russia, specifically, actualizes the demand for the specialists to be able to foreground talent management systems in the innovative development of HRM in order to transition from HRM to TSM.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Act 211 of the Government of the Russian Federation, contract № 02.A03.21.0006.
References
- Direktor po Personalu [HR Director] (2016). How to Attract and Retain the Specialist of Different Generations. Retrieved from http://www.hr-director.ru/article/65953-qqq-16-m9-kak-privlech-i-uderjat-spetsialistov-raznyh-pokoleniy?utm_medium=letter&ustp =F&utm_source=letternews%2cletternews&utm_campaign=letternews_2016_11_10_DPP%2cletternews_2016.11.09_dpp_test_2016_11_10_readers_40754&IdSL=1258890378&IdBatch=2971668. Accessed on 05.11.2016.
- ejer_po_proizvodstvu_liderov/. Accessed on 05.11.2016.
- Gatti, M., & Fedorova, A.E. (2014). Toxic Elements of Corporate Labour Relations: Work Place, Management, and Personnel. Journal of Omsk University. Series 'Economics, 2, 48.
- HeadHunter. (2017a). HR Business Partner in Sales in Siberia and Far East Regions. Retrieved from https://spb.hh.ru/vacancy/19177392. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- HeadHunter. (2017b). HRM Retail. Retrieved from https://hh.ru/vacancy/12833087. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- HeadHunter. (2017c). HR Specialist. Retrieved from https://hh.ru/vacancy/19481988. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- HeadHunter. (2017d). Personnel Manager in a Bank. Retrieved from https://spb.hh.ru /vacancy/19049934. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- HeadHunter. (2017e). Specialist in HR Processes. Retrieved from https://m.hh.ru/ vacancy/19262395. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- HR BP. (2017). Business Partner on Personnel // HeadHunter. Retrieved from https://hh.ru/vacancy/19207529. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- Lysenko E., & Kovaleva I. (2016). Involvement of Personnel in the System of Talent Management: Content-analysis of International, Federal and Regional Companies’ Sites, Having Activities on the Territory of Russian Federation. The 3rd International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference in Social Sciences and Arts. Conference Proceedings. Book 1. Psychology & Psychiatry, Sociology & Healthcare, Education. Vol. III. (pp. 549-556)
- Mars. (2016). The Selection Procedure // Mars. Retrieved from http://www.mars.com/ cis/ru/careers/your-mars/graduates-russia/how-to-apply.aspx. Accessed on 05.11.2016.
- Neo HR. (2015). How the Company Coca-Cola Hellenic Finds and Develops Talents. Retrieved from http://neohr.ru/korporativnaya-kultura/article_post/kak-nakhodit-i-razvivayet-talanty-v-rossii-kompaniya-coca-cola-hellenic. Accessed on 05.11.2016.
- Neo HR. (2016). Global HR Trends in 2016 Retrieved from http://neohr.ru/hr/ article_post/globalnyye-trendy-hr-v-2016-godu-prognozy-hr-direktorov. Accessed on 27.02.2017.
- Shahbazov, A., & Upravlenie, Talantami. (2016). Talent management. Retrieved from http://originaltm.com/upravlenie-talantami-zapadnaya-blazh/. Accessed on 05.11.2016.
- Tokareva Y., & Tokarev A. (2017). The Relationship between Motivation and Efficiency of Professional Sales Managers. The 11th International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague. (рp.1685-1692.)
- Ward Howell. (2016). Procter & Gamble: Conveyor for the Production of Leaders Retrieved from http://www.wardhowell.com/teinstitute/tei_exclusive_2/procter_gamble_konv
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 March 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-036-5
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
37
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-132
Subjects
Politics, government, European Union, European institutions
Cite this article as:
Lysenko, E., & Sereda, E. (2018). The New Job Position In Human Resources Management: The Talent Manager. In V. Regec, Z. Bekirogullari, M. Y. Minas, & R. X. Thambusamy (Eds.), Political Science, International Relations and Sociology - ic-PSIRS 2018, vol 37. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 51-58). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.03.02.5

