Competitiveness Management Mechanism Of Industrial Enterprise Under Conditions Of Import Substitution Policy
Abstract
In this paper, the method of assessment of economic entity competitiveness in modern conditions of applying the import substitution policy by the Russian leadership is considered. Foreign experience of using the import substitution policy and its influence on the country’s national economy are also analysed. The authors of the paper suggest a mechanism of competitive recovery of an industrial enterprise as an economic entity under condition of import substitution. In addition, the authors consider in detail the method of assessing competitiveness, based on researching the works of greatest scholars in the economy field. The main purpose of the paper is to preserve competitive sides of the economic entity, and in some cases, to increase competitiveness of the enterprise. The examples of application of the import substitution policy, which, during the long-term use, leads to the competitiveness reduction in the home market, are given. The authors consider the application of import substitution by the leadership of Belgorod region. An extensive literature review on the problem of assessing the competitiveness of industrial enterprises in modern conditions, as well as on the problem of realisation of the import substitution policy, is conducted. In addition, during development of the mechanism of competitive recovery of industrial enterprises under conditions of realisation of import substitution policy, the authors have taken into account the foreign experience, during analysis of which it has been revealed that long-term application of import substitution leads to the reduction of internal competitiveness and national security.
Keywords: Competitiveness assessment; import substitution policycompetitiveness of industrial enterprise; economic entity competitiveness; food embargo; national economy
Introduction
The issues related to the management of competitiveness of an economic entity is presently well studied and explored; therefore, it is becoming increasingly difficult to develop any method or concept ensuring competitiveness management. However, currently one is facing the conditions under which the development of methods and concepts designed to manage the competitiveness of an economic entity is necessary. One of such conditions would be the changes introduced to trade policy, particularly, the introduction of food import embargo against European and Western countries that have imposed economic sanctions on the Russian Federation. In this regard, the Government of the Russian Federation is placing greater emphasis on the import substitution of goods.
The purpose of this article is to make a diagnostic description of current situation and problems, as well as to provide an approach aimed at the development of the mechanism ensuring competitiveness improvement of the economic entity, taking into account environmental factor changes.
To achieve this goal, it was necessary to solve a number of tasks:
To analyze economic situation in the country.
To identify external risk factors and new opportunities.
To calculate import substitution evaluation in the country.
To develop principles and tools used for the mechanism development ensuring the increase of competitiveness of an enterprise (company) as an economic entity, taking into account changes in the foreign trade environment.
To solve the above mentioned tasks, the authors used information from the database of the Federal State Statistics Service.
Due to the introduction of the continuing sanctions against Russia and “fall” of the ruble, the issues related to the development and implementation of the import substitution policy were studied in this article. Besides, the current situation in the country determined the following needs:
To develop the production facilities for food item manufacturing on which a food import embargo was imposed as a response to sanctions (the list of food categories that have to be substituted is increasing).
To invest into development and production capacity increase of raw materials that were previously imported (including import of Ukrainian goods).
To increase the competitiveness of existing Russian companies to meet the needs of new “market windows”.
For the reason of consistency, let us begin these studies of the mentioned-above issues with the definition of import substitution.
Several domestic researchers as well as international ones have studied the term “import substitution” and, therefore, the issue itself: A.I. Altukhov, V.R. Boev, V.A. Klukach, N.A. Borkhunov, I.N. Buzdalov, E.N. Krylatykh, A.A. Vodyanov, A.B. Gordeev, V.D. Goncharov, S.V. Kiselev, V.P. Korovkin, A.F. Serkov, V.I. Tarasov, I.G. Ushachev, Yu.I.Agirbov, I.P. Faminsky, E.B. Khlebutin, G.I..Shmelev, D. Lindsay, E. Dolan and others (Chekmeneva, Anokhin, & Lachinsky, 2009).
Basing on the studies of the researchers mentioned above, one may come to the conclusion that some mechanisms were developed to ensure food security as well as methods increasing the competitiveness of industrial domestic enterprises, which led to an improvement of the situation with food supply in Russia. Having analyzed the standpoints of the above-mentioned researchers, the authors concluded that import substitution is a mechanism which enhances the competitiveness of the economic entities by means of developing the economy for the account of the country’s domestic resources.
Some researchers provide data on the import component content (calculated throughout the supply chain) in the selected food items supplied to the Russian market: potatoes, carrots, cabbage - 75%, pork - 40%, milk - 33%, poultry - 22%, chicken eggs - 15%, packed vermicelli - 10%, butter - 3.5%, bread - 3%, rice - 3%, packed salt - 34%. Hence, under the conditions of the growing exchange rate, the import substitution policy becomes socially important.
Due to insufficient supply of the domestic products and goods, the issue of national food security has been discussed in Russia for a long time (Table
The experience of import substitution policy implementation in such countries as the USA, Brazil, some Asian countries and Latin America has demonstrated an effective application of such tools as raising of taxes and customs duties on the imported products, artificial inflation of the exchange rate of the domestic currency and introduction of food ban. The reason for choosing the protectionist practices is connected with the difficulty to achieve cost-effectiveness due to the economies of scale when directing business activities only to the domestic market. Strengthening of the domestic market is the basis for further development of exports. Western Europe and the USA were the first to use this strategy in 1850 to support their own industry [Why are the prices on the domestic food are still growing and will continue to grow?]. Thus, the import substitution policy started being implemented in the middle of the XIX century; however, it became more widespread in the middle of the XX century in the developing countries. The advantages of the import substitution policy lie in the reduction of unemployment, an increase in the level of economy industrialization, development of infrastructure, an increase of competitiveness of national producers.
Problem Statement
In the middle of the XX century, leaders of developed and developing countries raised the question about bridging the economic gap between their countries. As a result, the following decision had been made: those countries with the developing economies take a number of measures to reduce prices on domestic products and to spend the retained money on the industry modernization. After applying this method, namely the import substitution policy and rapid economic growth of the country, one may introduce an open economy. The main thing about import substitution policy is to avoid long-term application of the policy; otherwise, it would lead to the efficiency decrease of national economy.
Research Questions
To achieve the goal set in this paper, it is necessary to have a clear understanding of such terms as competitiveness, import substitution and competitiveness of the entity. These three terms are combined, which makes it possible to understand the main issue, i.e. what is the effect of import substitution on the economic entity competitiveness?
Let us consider how the production enterprise affects the economic entity.
Let us begin with the term competitiveness. This term has a long history; that is why, having analyzed the studies of various researchers, the authors came to the conclusion that competitiveness is a competitive position of a company or an enterprise compared to other similar companies or enterprises operating in the same area.
According to many researchers studying the term competitiveness, the main problem would be constantly changing external factors of economy which make a great influence on the shift in competitiveness of the company. The formula used in this paper to calculate competitiveness is as follows:
(1)
where, К is the total competitive advantage of the company;
– competitiveness index by commodity weight;
– relative efficiency index.
Each index is calculated using the following formulae:
(2)
(3)
where n is the number of consumer parameters,
m is the number of economic parameters.
K is an integral numerical characteristic of company’s competitiveness. If K<1, then the company is less competitive compared to another company; if K>1, then it is more competitive; K = 1 when the competitiveness is equal.
Under the conditions of import substitution, Russian companies must not only increase the volume of production, but also improve the quality of products and goods which can be achieved by the improved manufacturing and management processes, introduction of marketing methods when creating and promoting brands into the business processes of Russian companies. Logistics is also the tool used to improve competitiveness; however, due to infrastructure and transportation problems the implementation of optimal solutions becomes rather difficult. In other words, the objective aimed at competitiveness improvement among Russian food production companies is the issue relating not only to companies themselves but also to the government support.
The use of domestic raw materials for the production of goods leads to a reduction in the production costs and to the improvement of the quality of goods.
The first factor determining the competitiveness of products is its quality, i.e. a set of properties and products that determine its ability to meet certain needs under specific conditions of consumption and operation.
The second factor is a cost which is determined by the purchase price, including the price of consumption. The latter includes all the operating costs that can arise from the consumer: delivery, installation, maintenance and repair, spare parts, insurance and training of personnel, etc.
Generally the competitiveness level of goods depends on both the consumer performance and the price. The higher the consumer performance per price unit, including the price of consumption, the higher the marketing opportunity and the number of consumers.
On 20 March 2014, the USA extended the list of Russian high-ranking officials against whom they imposed sanctions; besides, the sanctions were imposed against the Bank of Russia and some Russian businessmen who they thought had some business relations with the President of the Russian Federation V.V. Putin (G.N. Timchenko, brothers A.R. and B.R. Rotenberg, Yu.V. Kovalchuk). Later, on March 27, the United States of America suspended cooperation with Russia in the field of drug control. Moreover, they stopped issuing export licenses to American companies exporting potentially unsafe products to Russia (Schetinina, Starikova, Borzenkova, Chizhova, & Androsova, 2014).
Domestic companies are aimed at the import policy which leads to the deterioration of competitiveness of a company and consequently to the decrease in quality of the produced goods. All these may have a bad influence on the competitiveness of goods.
Having studied global experience of the import substitution policy, it can be concluded that application of the policy may result in the following issues:
Products are marketed domestically.
Companies become less competitive. It is only monopoly companies that stay afloat; small and medium-sized businesses are disappearing.
National economy is becoming less efficient.
This work is aimed at studying the issue of import substitution of sweet goods in Belgorod region as well as making proposal for the mechanism development to increase performance of an industrial company under current economic conditions.
Several domestic researchers as well as international ones have studied the issue of import substitution. Among them: A.I. Altukhov, V.R. Boev, V.A. Klukach, N.A. Borkhunov, I.N. Buzdalov, E.N. Krylatykh , A.A. Vodyanov, A.B. Gordeev, V.D. Goncharov, S.V. Kiselev, V.P. Korovkin, A.F. Serkov, V.I. Tarasov, I.G. Ushachev, Yu.I.Agirbov, I.P. Faminsky, E.B. Khlebutin, G.I..Shmelev, D. Lindsay, E. Dolan and others (Rubtsova & Gabdrakhmanov, 2012).
Having studied the works of these researchers, one may conclude that they developed a mechanism ensuring food security. Moreover, they developed the methods to advance competitiveness of industrial domestic companies, which improved the situation with food supply in Russia. (Shchetinina & Dubrovina, 2015)
Import substitution can be considered as one of the mechanisms to increase competitiveness of industrial domestic companies (Bagautdinova, Gafurov, Kalenskaya, & Novenkova, 2012).
Business environment of Russian companies, especially those connected with the international economic activities, has the attributes of growing uncertainty and turbulence. When filling the emerging market niches, the domestic companies are more actively using the production capacities, which lead to the import substitution of goods. On the one hand, such situation contributes to the improvement of the economic security of the country and results in an increase of the number of work places within companies, as well as the economic growth. On the other hand, a decrease of the competition level from the international companies (largely due to their move to the premium segment) reduces the need for product competitiveness. However, in the authors’ opinion, Russian companies should use the emerging market opportunities and pursue a policy of increasing competitiveness (Russian banks began lending to import-substituting branches of food industry and agriculture).
Purpose of the Study
The goal of the article is as follows. Company’s competitiveness depends on both external and internal environments. Some elements of the external environment can be partially controlled by the company itself and depend on goals and strategies of the company. While other (internal) elements do not depend on any activity of the company; therefore, it is necessary to adjust to them. The external environment can be divided into national, regional and sectoral factors.
Research Methods
Materials and methods of research. The ability of an industrial company to correspond to the competitors’ activities can be estimated using the economic magnitudes. The key elements of managing company’s competitiveness could be the attraction of new investors and resources as well as satisfaction of customer’s needs among which is social and economic need in the form of company’s products. Provided that the above-mentioned conditions are fulfilled, it becomes possible to assess the organizational and economic basis of an industrial company.
Findings
Having analysed various information sources, it was found out that the market competitiveness of a company is the resulting parameter of company’s operation which characterizes the degree of comparative rationality of available resources application. Competition can also be considered as the action of two or more market participants aimed at mastering the unique and limited factors of production available to all competing companies when making certain efforts. The authors E.I. Mazilkina and G.G. Panichkina, in their book Management of Competitiveness, state that the competitiveness of companies is a relative indicator that shows company’s performance activities in comparison with similar companies (competitors) according to certain characteristics. The indicators that determine company’s competitiveness are as follows: market capacity, position of competitors in specific market, quality of produced goods, ability to enter the selected market, etc. (Kucheryavenko & Stenyushkina, 2016). The study of measuring competitiveness requires in-depth analysis of the factors affecting the final estimates.
To have better understanding of how import substitution can enhance the competitiveness of an industrial company, a mechanism can be designed. This mechanism ensures the competitiveness enhancement of an industrial company under the conditions of introduction of retaliatory sanctions. To design such mechanism, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies during which the issues will be revealed. The solutions of these issues are presented in the form of measures described in the mechanism presented (Kupriyanov, Dadalova, & Dubrovina, 2015).
It should be kept in mind that social competitiveness has to be taken into account as this is an ability of a company to demonstrate a better degree of need satisfaction of not only buyers but also employees, suppliers, shareholders, and local communities compared to its competitors (Kotler, 2006). An example of the company’s social competitiveness can be an effective cooperation with trade unions, moral support of employees, charitable actions and events that ultimately lead to an improvement of social and economic situation in the region where the company is located (see figure
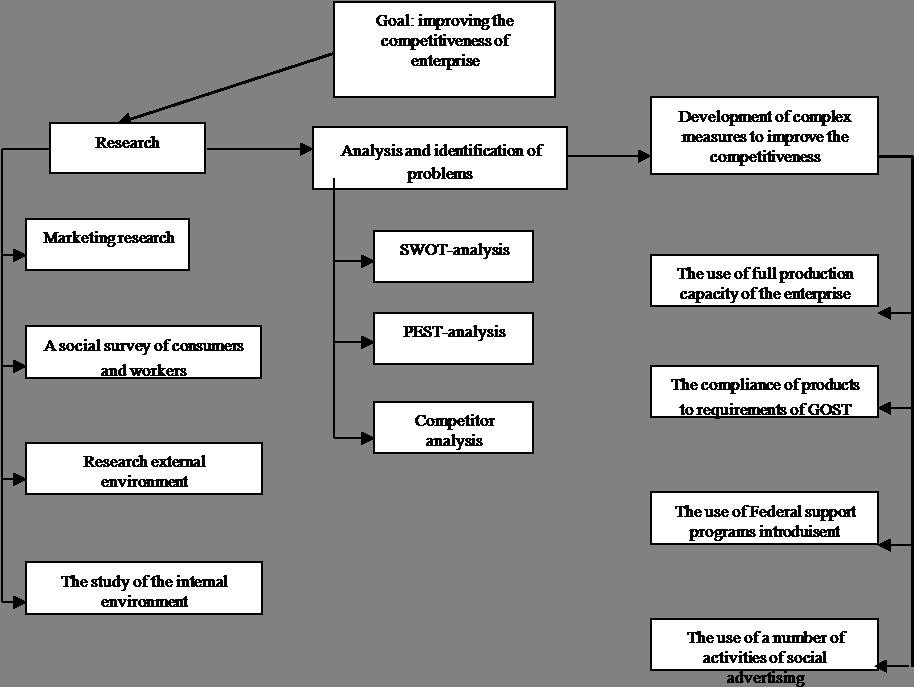
It is worth mentioning that competition as a social process is also studied in the framework of economic sociology specifically in the area of market sociology developed by Radaev (Rudychev, Nikitina, Gavrilovskaya, 2013). One may assume that in the near future, the competitiveness of the company will be evaluated against one indicator, i.e. the degree of social importance of a company.
Basing on the above-mentioned considerations, the authors propose calculating an integrated competitiveness index (KSP) with the included social performance component (SE):
where IKSPj is the index of company’s comparative advantage on the basis of market parameter j.
The following formula is used to calculate the coefficient of social performance:
,(5)
where NP is the number of work places created by the company during the evaluation period, people;
NR is the number of work places created in the municipal structure where the company is operating, people;
WP is the pay level in the company during the evaluation period, rubles;
WR is the pay level in the municipal structure where the company is operating, rubles;
СP is the amount of funds allocated by the company for the solution of social problems during the evaluation period, rubles;
СR is the amount of funds allocated in the municipal structure where the company is operating;
n is the number of indicators of the comparative social performance of the company (Belykh, 2011).
Application of the proposed approach will ensure an unbiased assessment of company’s competitiveness and will make it possible to consider the role it plays in the society.
The outcomes of the study and their discussion. Upon introduction of sanctions initiated by Western countries against Russia, which, in its turn, resulted in the retaliatory sanctions such as food import ban, many Russian banks switched to the lending policy of import substituting industries; among them are food and agriculture. However, there are also some industries, to which Russian banks are now paying less attention than they did in the past. These industries include the tourism and automotive sectors. Hence, one may conclude that the landing policy was crossed over to other sectors due to the changes introduced in the external economy. ITAR TASS has provided data related to the changes in priority industries which were obtained in the course of the marketing research during which the bankers were surveyed and the reports on the international standards of 50 largest banks of the Russian Federation were studied. For several years banks have been placing a priority on the oil industry, metallurgy, financial sector and telecommunications; however, after the food import ban and sanctions have been introduced the priorities were changed.
When analyzing the situation on Belgorod market, some insignificant changes were identified. Long before the economic sanctions were introduced by Western countries, the government of Belgorod region made a decision to start implementing the policy of import substitution. Due to the political acumen of the deputies of Belgorod, the food market of Belgorod region is saturated with a wide range of domestic products.
In the framework of the Economic Council, there was a meeting devoted to issues of the investment activities in the region and import substitution of products and goods with the products made by Belgorod commodity producers. The key participants of the meeting were Vitaly Chikhuanov, Deputy Mayor, Head of the Economic Development Department and representatives of Belgorod business community.
Since sweet goods are an integral part of customers’ product portfolio, it is necessary for the product to meet not only the certification requirements of management systems (TU, GOST, ISO 9001) but also social aspects of the society (Glagolev & Moiseev, 2014).
Such concept combines social and economic goals, including subsidiarity and collective initiative, as well as responsibility and social partnership, i.e. economic, environmental and social regulation by means of competition and coordinated plans. This concept encompasses such constituents as public and private partnership, innovative integration, cluster theory and other organizational innovations (Maksimchuk & Suvorova, 2014).
Conclusion
This article deals with such matter as a provision of the competitiveness management of a company. Besides, this article describes current management methods and evaluation of this economic category. Basing on the analysis of the principles, approaches and factors of company’s competitiveness, it is evident that nowadays the social competitiveness is the front and center evaluation criterion of businessman activity. In case, when at least some principles and approaches of social competitiveness are implemented, the reputation of a company is improved. In the authors’ view, this is the main criterion for measuring the competitive advantage.
Acknowledgments
The article was prepared in the framework of the Strategic Development Program of BSTU named after V.G. Shukhov, 2012-2016 (grant: Development of Mechanism to Increase Competitiveness of Enterprise in the Context of Import Substitution).
References
- Bagautdinova, N., Gafurov, I., Kalenskaya, N., Novenkova, A. (2012). The regional development strategybased on territorial marketing (the case of Russia), World Applied Sciences Journal, 18, 179-184.
- Belykh, V. I. (2011). Principles for the formation of competitiveness of automotive companies, Polymatic network online scientific journal of Kuban State Agrarian University, 71, 414-424.
- Chekmeneva, L., Anokhin A. Lachinsky S. (2009). Geodemographic situation: the concept and approaches to study, 312 p.
- Glagolev, S.N., Moiseev, V.V. (2014). Essence and the main content of anti-Russian sanctions of the West, High technology and innovation: Book of reports of the Jubilee International Scientific and Practical conference dedicated to the 60th anniversary of BSTU. V.G. Shukhova, pp. 81-95.
- Kotler, F. (2006). Marketing bases, Prentice Hall, p. 813.
- Kucheryavenko, S. A., Stenyushkina, S.G. (2016). Formation of the system of risk management in small and medium business, Research Result. Series: Economic Studies vol. 2. 2(6), 52-57.
- Kulik, G. (2015). New economic policy for the village, The Russian Federation today 1-2: Retrieved from: http://www.russia-today.ru/article.php?i=1273.
- Kupriyanov, S. V., Dadalova, M. V., Dubrovina, T. A. (2015). Assessment of the industrial enterprises competitiveness in terms of import placement, Research Result. Series: Economic Studies, vol. 1, 4 (6), 20-26.
- Maksimchuk, E.V., Suvorova, A. A. (2014). Some Economic Aspects of Import Substitution, Bulletin of the Belgorod State Technological University named after. V.G. Shukhova, 6, 109-112.
- Rubtsova, V., Gabdrakhmanov, N. (2012). Demographic potential of the Republic of Tatarstan: analysis, assessment, territorial differences, Vestnik of Udmurtia university. Biology. Sciences about Earth, 1, 145-155.
- Rudychev, A. A., Nikitina, E. A., Gavrilovskaya, S. P. (2013). The main aspects of the preparation and development of a model for assessing the competitiveness of a company, Bulletin of the Belgorod State Technological University. V.G. Shukhova, 6, 137-140.
- Russian banks began lending to import-substituting branches of food industry and agriculture, Reference date: 24.09.2015 http://www.zol.ru/znews/showlinks.
- Schetinina, E. D., Starikova, M. S., Borzenkova, K. S, Chizhova, E. N., Androsova, G. A. (2014). The development of the business strategy based on the commercialization of innovations International, Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 9(22), 16881-16890.
- Shchetinina, E. D., Dubrovina, Т. А. (2015). Developing a strategy for import substitution of food products using the example of the confectionery industry in Belgorod Region, Vestnik of the Irkutsk State Technical University, 1 (96), 190-195.
- Why are the prices growing and will continue groving on the domestic food (in one picture). (2016, May 15). Retrieved from: http://www.informdetox.com/?p=17234.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
19 February 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-034-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
35
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1452
Subjects
Business, business innovation, science, technology, society, organizational behaviour, behaviour behaviour
Cite this article as:
Shchetinina, E. D., Ponomareva, T. N., Dubino, N. I., & Dubrovin, T. A. (2018). Competitiveness Management Mechanism Of Industrial Enterprise Under Conditions Of Import Substitution Policy. In I. B. Ardashkin, N. V. Martyushev, S. V. Klyagin, E. V. Barkova, A. R. Massalimova, & V. N. Syrov (Eds.), Research Paradigms Transformation in Social Sciences, vol 35. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1163-1172). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.02.137

