Abstract
The article provides the analysis of the most general characteristics of the «successful» and «non-successful» ones during the intensive and traditional foreign language teaching forms. The individual differences have been examined on the different levels of activity: а) on the behavioural characteristics level manifested as a type of the foreign language mastering; б) on the level of the determination of certain abilities in the cognitive processes directly relating to the foreign language mastering type; в) on the level of the neurodynamical characteristics. The types of the abilities and native and foreign language mastering types discovered on the experimental model of the intensive teaching turned out to be universal enough: they can be found in other, less rough conditions. This idea concerning the foreign language mastering types as stable individual and typical characteristics of the students, which form rather independently on the teaching method, has got the experimental confirmation in several our papers and papers implemented under our guidance. The results of studies of the junior, teenage and adolescent schoolchildren have confirmed the existence of three foreign language mastering types –‘communication and speech’, ‘cognitive and linguistic’and‘mixed’ ones, which tend to survive from one age to another. These foreign language mastering types have a different psychophysiological and psychological nature including the communication and speech and cognitive and linguistic aspects. The favorable condition for maximal development of the schoolchildren’s language abilities is a correspondence of the teaching type, content of the education technology and individual and typological schoolchildren’s particularities.
Keywords: Language abilitiesforeign language mastering typesinterhemispheric brain asymmetryeducation technologies
Introduction
On the contemporary stage of scientific studies, the education’s individualization and differentiation at the general education school and higher education institution supposes the account taken in the foreign language mastering process of the schoolchildren’s individual and typical particularities stipulated by interhemispheric brain asymmetry. The psychological exploration of the individual foreign language mastering strategies manifested in the adolescent age permits to deepen essentially the explanation of the individual activity strategies.
The psychological particularities of the brain hemispheres’ functioning manifest themselves in the personality’s cognitive style, thus, the interhemispheric asymmetry can serve the ground of the personality’s individual and psychological particularities manifested in the cognitive activity (Kolb & Whishaw, 2009).
The types of the abilities and native and foreign language mastering types discovered on the experimental model of the intensive teaching turned out to be universal enough: they can be found in other, less rough conditions.
This idea concerning the native and foreign language mastering types as stable individual and typical characteristics (individual mastering style) of the students, which form rather independently on the teaching method, has got the experimental confirmation in several papers implemented under our guidance or using the language abilities typology and their detection methods offered by us (Kabardov, 2013).
Problem Statement
It is well-known that the foreign language teaching is activity teaching and communication teaching at the same time. Here the problem of the individual and typical in the foreign language mastering process and the problem of the influence of the studied language’s peculiarities on the functional specialization of the human brain’s hemispheres are of big importance (Bishop, 2013; Purves et al., 2008).
This idea concerning the native and foreign language mastering types as stable individual and typical characteristics (individual mastering style) of the students, which form rather independently on the teaching method, has got the experimental confirmation in several papers implemented under our guidance or using the language abilities typology and their detection methods offered by us (Kabardov, 2013).
The teaching methods taking the age into account influence essentially on the forming of these types, but do not overlap them. The favorable condition for maximal development of the schoolchildren’s language abilities is a correspondence («valence») of the teaching type, content of the education technology and individual and typological schoolchildren’s particularities. The different combinations of these free factors create the following situations: а) favorable correspondence of the abilities to the education technologies and б) unfavorable combination of these abilities with education technologies. One should pursue the analysis of the teaching methods types (innovation, active, communication, traditional (supporting), analytic and others) for such situations.
Research Questions
We had an opportunity to examine all these problems in the age aspect (1-9th classes; students and middle age) taking the education system into consideration. In all, 250 general school pupils and 120 students of linguistic faculties from Moscow have taken part in our study. The study was conducted in the traditions of Teplovs school.
On all the age phases of the exploration the existence of the speech and language abilities types has been established. The experiments have demonstrated persuasively that the language mastering strategy (both native and foreign ones) depends on the individual configuration of the abilities components including the memory (aural and visual, arbitrary and non-arbitrary one); speech and thinking activity including both the thinking lability and verbality-non-verbality, analyticity-synthetical character; activity’s tempo characteristics relating to the whole structure of individuality; communicative components providing the interpersonal interaction quality (which depend not only on the individual’s experience, but also on the natural predilection; and, finally, the natural conditioning of the communicative and speech and cognitive and linguistic language mastering strategies.
The characteristics of the speech and language competency and abilities are presented in the form of the dichotomy (‘language competency’ and‘ speech competency’) corresponding to the cognitive and linguistic and communicative and speech foreign language mastering types (Kabardov, Artsishevskaya, Bauer 2017).
It is demonstrated that the language mastering efficiency depends on the correspondence degree of the main education technology and stable foreign language mastering strategy (activity’s style, mastering type).
-
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of our exploration was to determine the favorable conditions for maximal development of language abilities of the foreign language students. We have conducted the research of the foreign language mastering peculiarities by general school pupils and students of linguistic faculties in order to retrace the interaction of the language mastering individual strategies of students and the applied teaching method (Smirnova-Bauer, 2007). The junior and senior schoolchildren, as well as the students of the linguistic faculty of the Moscow Pedagogical University aged 17-20 took part in this experiment (250 general school pupils and 120 students of linguistic faculties from Moscow).
Research Methods
The complex study included the psychodiagnostic examination of schoolchildren and students with the subsequent estimation of foreign language mastering peculiarities as well the levels and components of the foreign language mastering success. The data collection organization was built on the ground of the comparative method in its two forms – in the form of the «transversal» (comparative) and «longitudinal» (dynamic) cuts.
In order to study and diagnose the schoolchildren-adolescents’ cognitive sphere the following methods have been used -observation, laboratory experiment, experimental and genetic method, method of independent experts.
The results obtained during the study were have passed the mathematic and statistical processing using the calculation of the sign variation parameters, Student’s t-criterion; MANOVA two-factor multidimensional dispersion analysis. The correlation analysis was also pursued to specify the connection between parameters.
Findings
The results of the exploration of the junior, teenage and adolescent schoolchildren have confirmed the existence of three types of the foreign language mastering –‘communication and speech’, cognitive and linguistic’and‘mixed’ ones, which survive from one age to another. These foreign language mastering types have a different psychophysiological and psychological nature including the communication and speech and cognitive and linguistic aspects.
In Fig.
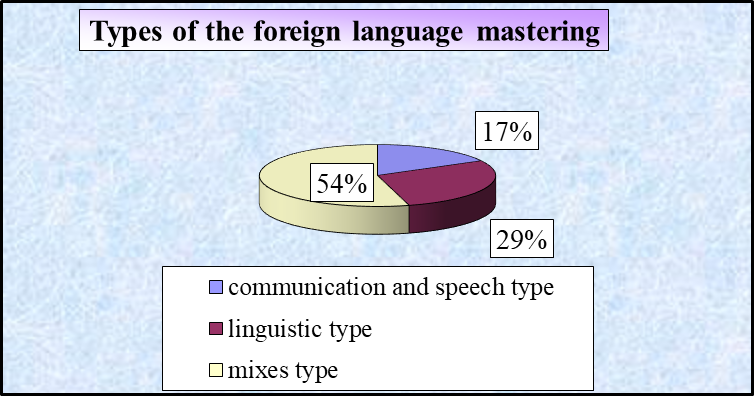
Thus, on the ground of our data and the data obtained by different explorers who checked the individual and typological conditioning of the language abilities types one can build the scheme of the interaction and mutual conditioning of the teaching types, language abilities types (or mastering types).
In the conditions of the traditional methodology the psychophysiological analysis has established other correlations: the combination of the inertia and inactivation of the nervous system turned out to be a favorable prerequisite of the foreign language mastering success. Such a combination of the typological properties is more typical for the cognitive and linguistic type, which is distinguished by left hemisphere’s dominance as well.
The foreign language mastering types found in the adult contingent of the tested people have been manifested by junior schoolchildren in the process of the Russian (native) language as well (on the ground of the orthographic literacy’s forming):
– optional control, high degree of the orthographic problem’s awareness are adequate conditions for orthographic command’s forming for schoolchildren of thinking type and are inadequate for schoolchildren of artistic type;
– non-arbitrary control, unclear orthographic problem’s awareness are adequate conditions for orthographic command’s forming for schoolchildren of artistic type and are inadequate for schoolchildren of thinking type;
– orthographic rules and orthographic vigilance formed on their ground contribute to form the literal writing for the schoolchildren of thinking type, but make it more difficult for schoolchildren of artistic type de-automating the orthographic command appearing on the ground of the ‘orthographic feeling’;
– traditional method realizing the grammatical method creates the unequal learning conditions for the schoolchildren of difficult typological groups: the rational and logical orthographic command formed in the type of education and typical of ‘thinkers’ provides more success for them. The same conditions are less favorable for ‘artists’ both in comfort and success;
– the same tested people have demonstrated the individual differences in correlation of the verbal-non-verbal thinking components, arbitrary–non-arbitrary regulation of actions in the cognitive sphere, image and verbal, aural and visual memory.
The conducted forming work has resulted in the fixation of the changes in the school results of the teenagers of the experimental group comparing with the control one. The data obtained are expounded in Fig.
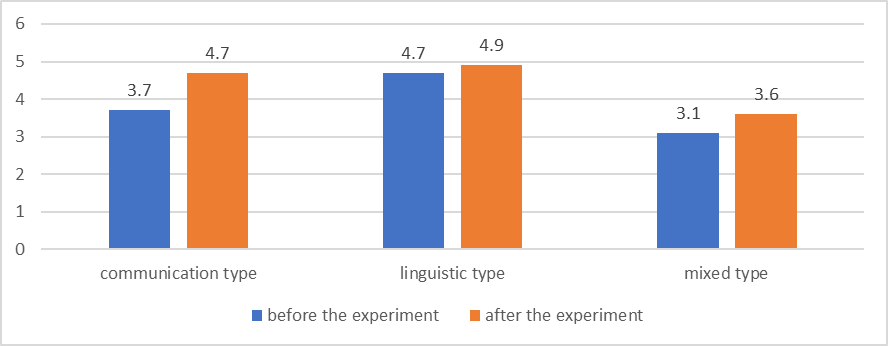
Pursuant to the data obtained, as a result of the new method of the foreign language teaching, which takes the foreign language mastering type into account, the statistically significant increase of the foreign language school results among the representatives of the communication and speech and mixed foreign language mastering types. As for the representatives of the cognitive and linguistic type, their school results being high enough even before the experiment, have increased too (Kаbаrdоv, 2013).
Conclusions
The results of studies of the junior, teenage and adolescent schoolchildren have confirmed the existence of three foreign language mastering types –‘communication and speech’, ‘cognitive and linguistic’ and ‘mixed’ ones, which tend to survive from one age to another. These foreign language mastering types have a different psychophysiological and psychological nature including the communication and speech and cognitive and linguistic aspects. The favorable condition for maximal development of the schoolchildren’s language abilities is a correspondence of the teaching type, content of the education technology and individual and typological schoolchildren’s particularities.
We have elaborated the conception of the new method of the foreign language teaching, which takes the foreign language mastering type into account. The conducted forming work has resulted in the fixation of the statistically significant increase of the foreign language school results among the representatives of the communication and speech and mixed foreign language mastering types.
References
- Bishop, D. V. (2013). Cerebral asymmetry and language development: cause, correlate, or consequence? Science, 340(6138), 1230531. DOI:
- Каbаrdov М.К. (2013). Language Abilities: Psychology, Psychophysiology, Pedagogy. Мoscow, Smysl, (in Russian).
- Kabardov M.K., Artsishevskaya E.V., Bauer E.A. (2017). Communicative and cognitive aspects in the foreign language mastering process, International Congress - Neuroscience for Medicine and Psychology‖, Sudak, Crimea, Russia, May 30-June 10, 2017. P..184.
- Kolb, B., Whishaw, I. Q. (2009). Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology, 6th edition. Worth Publishers: USA.
- Purves, D., Augustine, G. J., Fitzpatrick, D., Hall, W. C., La Mantia, A., McNamara, J. O., White, L. E. (2008). Neuroscience, 4th edition. Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Massachusetts, USA.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
13 December 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-032-7
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
33
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-481
Subjects
Cognitive theory, educational equipment, educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), psycholinguistics
Cite this article as:
Kаbаrdov, M., Artsishevskaya, E., & Bauer, E. (2017). Types Of Language Abilities: Differential And Psychological Attitude. In S. B. Malykh, & E. V. Nikulchev (Eds.), Psychology and Education - ICPE 2017, vol 33. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 149-155). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.12.15

