Abstract
Slacklining (walking on slackline) as a sport activity is a specialized motor skill with great demands on variability, anticipation and responding to external conditions. The research study works on an assumption that motor learning progress in slacklining is influenced by the level of coordination skills. The purpose of the study was to investigate how the level of coordination abilities affects progress in slacklining. The research question relates to coordination abilities being a performance precondition for motor tasks with similar coordination demands. 40 university students (19-24) participated in the study. Indicators of the level of coordination abilities were standardised 1-leg standing balance test and Iowa-Brace battery. The participants trained slacklining within 8 sessions (10 attempts once a week). Motor learning progress was recorded. Statistical significance of difference across the sample was evaluated by Mann-Whitney test (p < 0.05). The progress in acquiring slacklining was recorded in terms of the best performance and the total number of attempts on slackline. A significant difference (p < 0.05) was found out across the sample in both selected indicators of coordination abilities, which suggests that the progress in slacklining of the participants with higher level of coordination abilities was faster. In conclusion, the level of coordination abilities, especially balance, can help the progress of motor learning in slacklining. However, slacklining is a complex and concentration-demanding skill and the progress can also be influenced by other factors, such as external conditions, personality and motivation.
Keywords: Slackliningcoordination abilitiesbalancemotor learning
Introduction
Slacklining was originally developed as a leisure activity of Yosemite climbers. Later on it was recognized as a good method for improving postural stability and strength. Slacklining can be characterized as balancing on a narrow flat nylon ribbon fixed between two anchor points. The activity itself is a specialized open motor skill, with demands on muscle coordination and postural stabilization with respect to variable external conditions and their anticipation. It involves neuromechanical response of a whole body, and active strengthening of body segments against the effects of external force. The ability to control our body’s position in space emerges from complex interaction of musculoskeletal and neural systems (Shumway-Cook, A., Woollacott, M. H., 2007).
Most of the previous research focused on slacklining as a technique developing balance and strength skills, coming to the conclusion that whether slackline training (balancing over a narrow nylon ribbons) serves as an appropriate training strategy to improve static and dynamic balance performance is as yet unclear (Donath et al., 2016). Very large task-specific balance training adaptations have been observed in individuals taking part in slackline training. Slackline training induced moderate to large improvements of slackline-specific and dynamic balance performance. Static balance performance only marginally benefited with small effects from slackline training alone (Donath et al., 2016). Research carried out by Serrien et al. (2016), confirms that balance on slackline is specifically bound to an instable base. The main findings from this analysis are that subjects learned to increase their postural control on the slackline (significantly longer standing time) by adopting a strategy consisting of higher range-of-motion and lower velocity and frequency of most degrees-of-freedom. A second important conclusion concerns the lack of transfer to balance on the flamingo task, indicating that the strategy that is being learned is strongly dependent on the external stimulus from the slackline (Serrien et al., 2016). Similarly next studies that evaluated postural control on the slackline itself and transfer to other tasks have reported mostly limited muscular or kinematic responses (Donath et al., 2015; Gabel, Osborne and Burkett, 2015). The influence on balance, in terms of its physiological causes, was studied more deeply by the latest research of Dordevic et al. (2017). Their results indicate that one month of intensive slackline training is a novel approach for enhancing clinically relevant balancing abilities in conditions with closed eyes as well as for improving the vestibular-dependent spatial orientation capability; both of the benefits are likely caused by positive influence of slackline-training on the vestibular system function.
Other studies focus on the effects of slackline training on human health as postural control under dynamic or unexpected perturbations is essential for reducing injury risks in sport (Granacher et al., 2010), and prevention of falls in general (Mansfield et al., 2015). Strejcová (2012) came to the same conclusions, her results indicate that the activity on slackline could be used as the prevention of injuries, ankle rehabilitation program and the postural stability exercise.
Problem Statement
Definition of slacklining and training methodology
A slackline is basically a small nylon rope, 2.5 cm wide, stretched between two anchor points upon which people try to maintain their balance on one or two feet or try to walk, turn, jump or perform other functional exercises. By adjusting the length and tension in the slackline, the exercises can be made easier or harder. When people make their first attempts on a slackline, the standing leg and rope swing uncontrollably and assistance is almost always necessary (Keller et at. 2012). The perturbations caused by this fast and frequently moving base of support provide a strong impulse for which the neuromuscular system must provide an appropriate response in order to stay on the slackline (Serrien et al., 2016).
Two training methods have been described currently. The first method is based on training without methodological aids while slackline walking is trained through repeated attempts. The second method uses various aids and preliminary exercises (Thoman, 2013). A methodology involving a 4-stage protocol that consists of 20 steps for progression of slackline training in a clinical setting was developed by Gabel and Mendoza (2013) in order to achieve standardization of the methods used to support the motor learning process, which can promote the safe and effective use of slacklining as a rehabilitation activity. Research carried out by Kroiss (2007) did not prove any significant differences in the learning progress. The second method is preferred due to greater motivation during the learning process.
The technique of slacklining, which is important for the motor learning process, was described by Horáková (2015), Kroiss (2007) and Balcom (2005).
Factors influencing motor performance on slackline
In this research the focus is on an importance of coordination abilities as complex performance pre-conditions. Měkota and Novosad (2005) defined the importance in the following aspects: facilitation and accelerating of the process of learning new motor skills, contribution to stabilisation and refining the already adopted skills, participation in the determination of the level of condition abilities utilization, influence on aesthetic feelings, joy and satisfaction from the exercise.
This research studied also the progress of motor learning, which takes place in three phases. The cognitive phase involves the rejection of ineffective strategies and adoption of effective strategies, which usually leads to rapid improvement. The associative phase lasts for weeks to months, during which skills are acquired and consolidated, and performance consistency improves. The autonomous phase lasts for months to years, during which skills can be executed without conscious effort. This motor learning process leads to improved control of the natural oscillations that occur when standing on an instable suspended strap (Gabel and Mendoza, 2013).
Factors influencing the progress of motor learning and therefore the rate of learning were described by Horáková (2015). She differentiates somatic, technical, mental, tactical, and fitness factors. Balance skills represent a key factor for walking on a slackline. A good level of postural stability is required to master the slackline (Granacher et al. 2010, Balcom, 2005). Postural stability can be defined as the ability of maintaining such posture that prevents an uncontrolled fall. Stabilisation is understood as a constant process of maintaining optimum posture. It is an active and dynamic process, that is characterised by motoric coordination that supports the spine during all the motions (deep spine-stabilising system). Postural stability belongs to those skills, that are influenced by visual control, the vestibular apparatus, and by proprioreception at the same time (Giagazoglou et al., 2009). The ability to maintain and control the balance is the basis for the design and construction of more complex motor skills in the context of sport performance (Altavilla, Tafuri, and Raiola, 2014).
Another factor influencing the rate of learning slackline walking is the level of condition abilities – when standing and balancing on one leg the muscles of the foot, shank, or calf must actively regulate the motions. The neuromechanical dynamics of the body is coupled with the external dynamics of the rope which itself moves in response to body swaying. (Paoletti and Mahadevan, 2012).
The mental factors include fatigue, which impairs performance. Fatigue impairs sensorimotor performance, reduces spinal reflexes and affects the interaction of antagonistic muscles in complex motor tasks. The study evaluated response to postural perturbation during a fatiguing balance task. The number of failed attempts significantly increased with fatigue (Ritzmann et al., 2016). Motivation also influences slackline learning, which may negatively impact the performance testing. Relatively high motivation is presumed in slackline learning, as slacklining appeals to young people as a new, innovative, and attractive sport discipline.
Research Questions
The research questions work on an assumption that coordination skills and balance are a performance precondition to motor learning progress in slacklining. We suggested that better participants have better developed coordination and balance.
In this research it was investigated whether the progress of slacklining relates to the level of coordination skills?
For learning slacklining, balance, as one of the components of coordination skills, seems to be the key factor. We therefore defined the research question as to
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study was to investigate how the level of coordination abilities and static balance affects progress in slacklining. The secondary aim was to survey the progress made by walking on slackline and to observe influence of the motivation on performance.
Research Methods
Research sample
40 university students participated in the research (age 19-24, 28 men and 12 women). They studied Economics and Management programmes, all of them attending voluntary classes of indoor climbing. The classes were offered to students of University of Hradec Kralove, as a part of a complex system of voluntary physical activities. The volume and frequency of physical activity is 1.5 hour once a week and the aim is to compensate for sedentary study demands, to prevent from muscle imbalances, and to motivate students to regular and targeted physical activity. The key selection criterion for inclusion in the research sample was no preceding slackline experience and no sport on professional level.
Intervention
Slackline was trained within 8 weeks, with a regular frequency once a week. In every session the participants had maximum of 10 attempts to walk. The line width was 2.5 cm and the length was 8 meters, divided in 8 equal sections. Learning progress was recorded in every lesson, with regard to a best performance (number of section) achieved and the number of attempts. Training was preceded by individualized instruction and demonstration how to walk on slackline. The method used was based on practice by repeated attempts, without additional aids (see Introduction). Running and non-controlled walking was forbidden.
Methods
The level of acquisition of the specific skill – walking on slackline – was evaluated by an individual performance in slacklining as a sport discipline. The test is a locomotive-type and individual performance represents an objective score for evaluation. Both the motor content and conditions of evaluation and sport performance correspond for logical validity, in agreement with Měkota and Novosad (2007).
Motor performance of participants was diagnosed in input testing by the selected standardised indicators of coordination: 1-leg standing balance test and Iowa-Brace battery. Monopedal static balance was tested on 2 cm wide balance beam. The tested subjects stood with the foot of their dominant leg on the balance beam, arms akimbo, and upon command they lifted the supporting leg from the ground and tried to maintain balance for as long as they could. Every subject had two attempts, and the better of the results was recorded (Měkota and Blahuš, 1983). The level of coordination abilities we diagnosed by Iowa-Brace battery, which is also used to measure the motor educability – the ability to learn a variety of motor skills. This test includes track and field items. This test developed Brace in 1927 involving 20 stunts (Morrow, 2000) and in the Czech Republic it was first used by Štěpnička (1976). The test originally involved 21 tasks, but Štěpnička modified and standardized it to the currently used 10 tasks. The test battery includes coordination-demanding motions, balance and skill testing physical exercises. Completion (performance without fail) on the first attempt means two-point gain, completion on the second attempt means one-point gain. The maximum gain is 20 points (Havel, 2010).
Analysis
The statistical significance of differences among groups was tested by Mann-Whitney (p<0.05). The analysis was done by IBM SPSS Statistics 24. The data were changed to ranks, disregarding whether the scores were for group A or group B. The evaluation was based on mutual comparison of all the measurements from group A to all the measurements from group B and testing in favour of which group the results gave evidence. The groups were divided according to the results achieved in slacklining. The criterion for inclusion to group A (better performance) was to achieve at least section
Findings
Normality was disproved (K-S, p<0.05) and the scores were analysed by non-parametric test of statistical significance of difference (Mann-Whitney, p<0.05). The selected indicators of motor coordination abilities to verify the hypothesis were 1-leg standing test and Iowa-Brace test battery. The sample was divided as to the motoric performance (best result in sectors and attempts on slackline) and the distribution across the groups was tested. A statistically significant difference across the groups (A/B) was found out both in 1-leg standing balance test and Iowa-Brace test (Figure
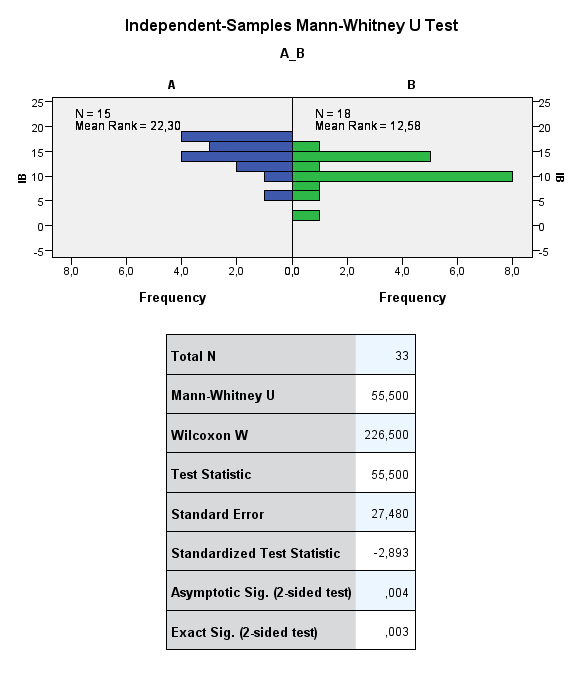
The comparison of A and B group statistics shows a significant difference in the static balance test, where the median of group B was only 7 seconds while of group A 27 seconds. The maximum performance of the entire group of tested subjects was 121 seconds (Table
Upon the observation during the testing we came to other interesting topics to be studied in further slacklining research. We assume that group B failed to master the technique, even roughly, whereas group A mastered the technique of slackline walking on the level of the 2nd phase of motor learning (associative). If a participant already reached sector 4 then he mastered the technique on the level of 1st phase of motor learning (cognitive) and their further progress in training was much faster. None of the tested persons reached the 3rd phase of motor learning, as a much longer process of learning is required for reaching the autonomous phase. The motivation factor was significant as well. We can assume that the degree of motivation increased the level of concentration on the learning process, which, as a result, was much more efficient. Motivation also influenced the coordination skills tests, which are sensitive to external influences that may easily distort the results.
In future studies it would be interesting to extend the test portfolio by motor function examination with special focus on the function of the deep stabilising system in accordance with the findings of Hrušová (2014). Effective involvement of the deep stabilization system is essential for stabilization of spine and major joints and for effective movement. To improve stabilizing function specific exercises, such as slacklining, can be used.
Conclusion
The progress in acquiring slacklining was recorded in terms of the best performance and the total number of attempts on slackline. A significant difference was found out across the sample in the selected indicators of coordination abilities, which suggests that the progress in slacklining of the participants with higher level of coordination abilities and static balance was faster. The research survey verified the predictive value of balance, coordination and precision, which can help the progress of motor learning in slacklining as a specialized motor skill. However, slacklining is a complex and concentration-demanding skill and the progress can also be influenced by other factors, such as external conditions, personality and motivation.
References
- Altavilla, G., Tafuri, D., Raiola, G. (2013). Journal of Physical Education and Sport. 14(3), pp.351-354.
- Button, C. et al. (2013). Variability in Neurobiological Systems and Training. Complex System Sports. pp. 277-292.
- Balcom, S. (2005). Walk the line: the art of balance and the craft of slackline. Ashland, Oregon: SlackDaddy Press
- Di Cango, A. et al. (2014). Motor Learning as Young Gymnast’s Talent Indicator. Journal of Sport Science and Medicine. 13(4), pp.767-773.
- Donath L., Roth R., Zahner L., Faude O. (2015). Slackline training and neuromuscular performance in seniors: a randomized controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, pp. 275–283.
- Donath L., Roth R., Zahner L., Faude O. (2016). Slackline training (Balancing Over Narrow Nylon Ribbons) and balance performance: a meta-analytical review. Sports Med. [Epub ahead of print].
- Dordevic, M., Hökelmann, A., Müller, P., Rehfeld, K., Müller, N. G. (2017). Improvements in Orientation and Balancing Abilities in Response to One Month of Intensive Slackline-Training. A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 55.
- Gabel C. p., Mendoza S. (2013). Slacklining for Lower Extremity Rehabilitation and Injury Prevention, International Journal of Athletic Therapy and Training,Volume 18 (4).
- Gabel C.P., Osborne J, Burkett B. (2015). The influence of ‘Slacklining’ on quadriceps rehabilitation, activation and intensity. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.18(1): pp. 62–66.
- Giagazoglou, P., Amiridis, I. G., Zafeiridis, A., Thimara, M., Kouvelioti, V., Kellis, E. (2009). Static balance control and lower limb strength in blind and sighted women. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(5).
- Granacher, U., Iten, N., Roth, R., Gollhofer, A. (2010). Slackline training for balance and strength promotion. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 31(10), pp. 717–723.
- Havel, Z., Hnízdil, J. (2010). Rozvoj a diagnostika koordinačních a pohyblivostních schopností. Banská Bystrica: Univerzita Mateja Bela, Pedagogická fakulta. pp. 6-44.
- Horáková, P. (2015). Vliv krátkodobého programu slackline na rychlost osvojování specifických dovedností a svalové síly hlezenního kloubu. Diplomová práce.
- Hrusova, D. (2014). Effect of a modified pilates programme on stabilization and muscle coordination at women with a sedentary job. In: Kinesiology: fundamental and applied kinesiology - steps forward: 7th international scientific conference. Zagreb: University Zagreb, pp. 36-39.
- Kellis, E. (2009). Static balance control and lower limb strength in blind and sighted women. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(5), pp. 571–579.
- Keller, M., Pfusterschmied, J., Buchecker, M., Müller, E., Taube, W. (2012). Improved postural control after slackline training is accompanied by reduced H-reflexes. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, 22(4), pp. 471–7.
- Kroiss, A. (2007). Der Trendsport Slacklinen und seine Anwendbarkeit im Schulsport. Schriftliche Hausarbeit zur Ersten Staatsprüfung für das Lehramt an Gymnasien, TU München.
- Mansfield A, Wong JS, Bryce J, Knorr S, Patterson KK. (2015). Does perturbation-based balance training prevent falls? A review and meta-analysis of preliminary randomized controlled trials. Physical Therapy. 95(5): pp. 700–709.
- Měkota, K. a Blahuš, P. (1983). Motorické testy v tělesné výchově. Praha: Státní pedagogické nakladatelství.
- Měkota, K., Novosad, J. (2007). Motorické schopnosti. Olomouc: Univerzita Palackého, 55-107.
- Morrow, J., R. (2000). Measurement and evaluation in human performance. 2nd ed. Champaign: Human Kinetics.
- Orth, D., Davids, K., Seifert, L. (2016). Coordination in Climbing: Effect on Skill, Practices and Constrains Manipulation. Sports Medicine, 46(2), pp. 255-268.
- Paoletti, P. and Mahadevan, L. (2012). Balancing on tightropes and slacklines. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 2012, 9, pp. 2097-2108.
- Pfusterschmied, J., Buchecker, M., Keller, M., Wagner, H., Taube, W., & Muller, E. (2013). Supervised slackline training improves postural stability. European Journal of Sport Science, 13(1), pp. 49–57.
- Ritzmann, R., Freyler, K., Werkhausen, A., & Gollhofer, A. (2016). Changes in Balance Strategy and Neuromuscular Control during a Fatiguing Balance Task—A Study in Perturbed Unilateral Stance. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 289.
- Qu, X., Nussbaum, M. A. (2009). Evaluation of the roles of passive and active control of balance using a balance control model. Journal of Biomechanics, 42, pp. 1850–1855.
- Serrien, B., Hohenauer, E., Clijsen, R., Baeyens, J., Küng, U. (2016). Balance coordination strategies on slacklines: analysis by means of self-organizing maps, in Current research in motor control V. AWF Katowice, pp. 239-245.
- Shumway-Cook, A., Woollacott, M. H. (2007). Motor control: Translating research into clinical practice. Philadelphia: Williams & Wilkins, 158.
- Strejcová, B., Šimková, L., Baláš, J. (2012). Ankle isokinetic strength and postural stability in “slackliners”. Česká kinantropologie, 16, (3), pp. 93–100.
- Štěpnička, J. (1976). Somatotyp, držení těla, motorika a pohybové aktivity mládeže. Acta Universitatis Carolinae. Gymnica, 12 (2), pp.11-93.
- Thomann, A. (2013). Methodik im Slacklinesport - Wie geht guter Slacklineunterricht? Technische Universität München.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
14 September 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-029-7
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
30
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-376
Subjects
Health, public health, preventive healthcare, preventive care, preventive medicine
Cite this article as:
Chaloupská, P., & Hrušová, D. (2017). Effect Of Level Of Coordination Abilities On Motor Learning Progress In Slacklining. In Z. Bekirogullari, M. Y. Minas, & R. X. Thambusamy (Eds.), Health and Health Psychology - icH&Hpsy 2017, vol 30. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 337-345). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.09.33

