Abstract
An organization can use risk assumption, risk avoidance, risk retention, risk transfer or any other strategy in order to properly manage the future events - based on (
Keywords: Riskmanagementtools
1.Introduction
Like any other effective business activity, risk management requires:
=a process with a clear purpose,
=reliable inputs,
=well-designed activities and value-added outputs.
The risk management process typically includes activities such as the identification, sourcing,
measurement, evaluation, mitigation and monitoring of risk. A well-articulated process view of risk
management provides a benchmark for companies to help them formulate their proprietary view of their
process that best fits their needs (Corporate Compliance Insights, 2017).
Risk management means an establishment of a balance between risk and results (Meghea et all,
2008). There are many other definitions of risk management, one of the most used is a five-step theory:
1. Identify – the identification and categorizing the risks;
2. Analyze – the assessment of risks according to their importance / what-if scenarios, the
evaluation of the risks impact;
3. Evaluate – the prioritization of the risks according to a set of criterions;
4. Treatment – methods of treatment: avoid, transfer, accept, reduce etc
5. Audit - monitor and review the risk management plan.
2.Problem Statement
Some tools and methodologies used during the various phases of the risk management are
presented below (Clarizen Inc., 2017):
-Tools and Techniques for Risk Identification
�=Brainstorming / Delphi method
�=Assumption analysis / Diagramming techniques / Cause and effect diagrams / System or process
flow charts
�Influence diagrams / SWOT analysis
-Tools and Techniques for Qualitative Risk Analysis
�=�The assessment based on risk probability and risk impact
�=�The matrix of probability and impact / The categorization of risks
�=Risk urgency assessment / Expert judgment
-Tools and Techniques for Quantities Risk Analysis
�=Data gathering & representation techniques
�=Interviewing / Probability distributions
�=Sensitivity analysis
�=Modelling & simulation
�=Schedule risk analysis
There are
below there is an analysis of some of them.
3.Research Questions
1.Are there software tools for risk management?
2.Which are the most commonly used software tools in a company to manage the risks?
3.What are the risk management method phases supported by each analyzed software tool?
4.Taking into account the criterions such as: tool architecture, interoperability with other tools,
geographical dispersion, skills that are compulsory to install, compliance to IT standards, the
technologies used in the tool - is there an appropriate software tool to manage the risks in a
company?
4.Purpose of the Study
The paper is an exploratory research, a comparative view of some certain software tools used to
manage the risks in an organization represents the core of the article.
The core objectives of this paper are:
To describe some software tools for the management of risks: Risk Watch, Riscare, Risk Management Studio, Krio, MEHARI 2010 basic tool To comparatively describe some certain risk management software tools – which is the
essence - of the article based on some criterions such as: tool architecture,
interoperability with other tools, geographical dispersion, skills compulsory to install,
compliance to IT standards, the technologies used in the tool, etc.
To outline the final aspects based on the results of the study.
5.Research Methods
In this article the tools and methods used for research are:
�=Descriptive analysis;
�=Exploratory research;
�=Bibliographic study;
�=Analysis in a comparative manner.
Every software tool was described using criterions such as: tool architecture, interoperability with
other tools, geographical dispersion, skills compulsory to install, compliance to IT standards, the
technologies used in the tool, etc.
The descriptive analysis of every tool consists of the tool presentation and also the risk
management method phases supported.
6.Findings
6.1. The software tools – a descriptive analysis
In the next chapters a descriptive analysis about some software tools used to manage the risks in an
organization is presented. Based on some representative sources (E.N.I.S.A. Inventory of Risk
Management, 2017) (ENISA Technical Department, 2006) and the authors experience, five tools have
been analyzed in a non- exhaustive manner.
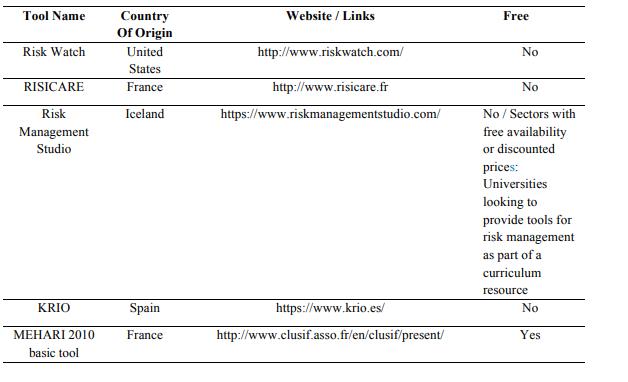
6.1.1.Risk Watch - analysis based on (ENISA Risk Watch, 2017)
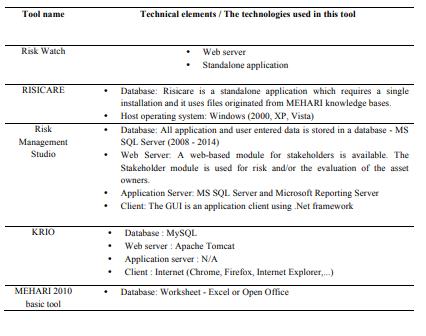
Risk Watch is the Risk Watch company' solution for information security risk management. The
software instrument makes automated risk analysis and vulnerability assessments of the information
systems. Other functionalities:
=The databases that are used in the software tool are completely customizable by the user – it is
possible to create new assets, threats, vulnerabilities, safeguards, etc;
=There is an online demo available for the product;
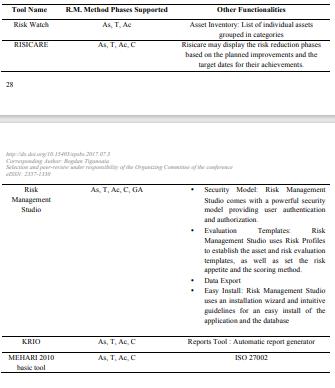
=Risk management method phases supported:
- Risk assessment
- Risk treatment: Phase III : Define safeguard details
- Risk acceptance: Phase III : "what-if" scenarios.
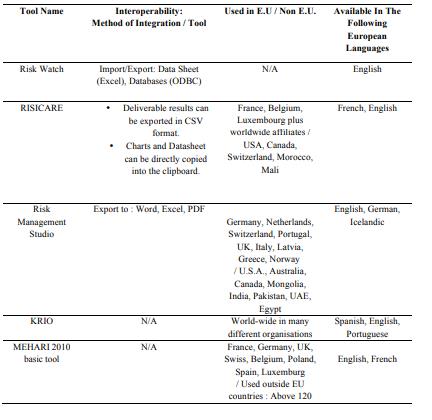
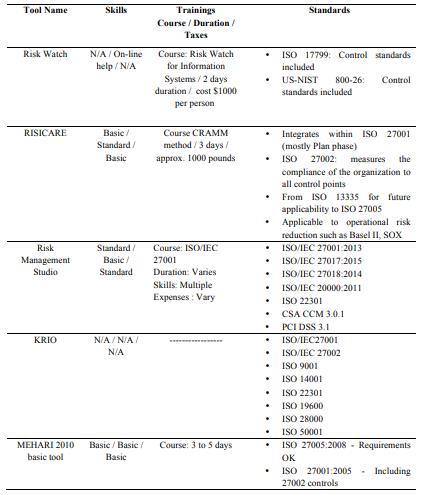
An analysis of the software tool can be found in the Tables from 1 to 6.
6.1.2.Risicare
Risicare assists the information risk analysis and management actions in support of MEHARI Risk
Model, options and formulas developed by CLUSIF (E.N.I.S.A. Risicare, 2017).
IS
- R= The tool make real-world conditions simulations and test multiple "what if" sc
The tool can be viewed as a risk modelling software;
O 27002 (E.N.I.S.A. Risicare, 2017).
Risk management method phases supported:
- Risk assessment: the tool analyses multiple threat situations (scenarios);
=
The tool allows the management of an ISMS and uses a set of control points which includes those of
- Risk treatment: simulations and optimizations in order to provide suitable security measures for each
unacceptable risk;
- Risk acceptance;
- Risk communication.
An analysis of the software tool can be found in the Tables from 1 to 6.
6.1.3.Risk management studio
Risk Management Studio is an efficient risk management software tool. It brings holistic approach
by combining the Assessment module with the Business Continuity module.
Features of the software tool (ENISA RM Studio, 2017):
=Existing data for the organization (asset lists, policies, stakeholders) can be imported;
=Diverse Risk libraries (IT, operational, project, environmental, strategic) are included;
=ISO/IEC 27001 and Annex A, Security Controls, along with the Implementation Guidelines from
ISO/IEC 27002 ready for immediate deployment
=The certification process is facilitated by a stage-by-stage approach
=The tool provides Gap Analysis, Risk Assessment, Control Effectiveness Assessment;
=A turn-key solution or customizable to meet the individual needs of each organization – ready for
deployment.
=Risk management method phases supported:
- Risk assessment;
- Risk treatment;
- Risk acceptance;
- Risk Communication
=Gap Analysis: GAP Analysis/Compliance check against a standard such as ISO/IEC 27001 or other
deployed standards (9001, 14001, 20000, 22000, 22301, PCI DSS, WLA-SCS, CSA CCM).
More info about the software tool in tables 1-6.
6.1.4.Krio
KRiO is a tool for risk management based on the ISO 31000 standard. The tool allows you to
manage, identify, analyze and treat multiple scenarios of:
-Regulatory risk
-Technological risk;
-Financial and operational risk;
-Environmental risk;
-Reputational risk.
KRIO is used to manage the process of identification, evaluation and treatment of risk, in accordance
with 31010 ISO standards. It enables compliance with 100% of the processof analysis and management
of risks set forth in the rules of high level (HLS) (ENISA Krio, 2017).
Risk management method phases supported (ENISA Krio, 2017):
-Risk assessment: Identification, analysis and assessment.
-Risk treatment: Threat definition and vulnerability valuating system scenarios
-Risk acceptance: Define, select and justify of ISO specific Controls
-Risk communication: Report
More information about this tool can be found in the tables from 1 to 6.
6.1.5.Mehari 2010 basic tool
The vendor name of the software tool is CLUSIF and the country of origin is France. MEHARI has
the following features:
=The results of the Risk Assessment and Risk Management activities can be viewed step-by-step;
=Additional controls for risk reduction are available;
=The worksheet of the method contains multiple formulas.
=Risk management method processes supported (ENISA Mehari, 2017):
-Risk assessment: The likelihood-impact analysis determines the level of risk scenarios;
-Risk treatment: Security measures are proposed to reduce the risk level;
-Risk acceptance: Options to accept or transfer risk;
-Risk communication: The worksheet can be completed with communication elements.
More information about this software tool can be found in the tables from 1 to 6.
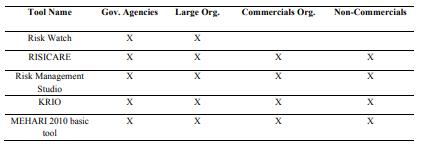
6.2. The Software Tools - A Comparative Analysis
The tables from 1 to 6 show a comparative analysis of risk management tools, based on common
criterions. Using the template below (tables 1-6), based on the data from (E.N.I.S.A. Inventory of Risk
Management, 2017) and (ENISA Technical Department, 2006), each tool is described and compared to the
others.
7.Conclusion
The constant evolution of information technology requires the usage of new tools during the risk
management process. This paper is a comparative study on tools which are being used by companies to
manage risks. Every tool has both advantages and disadvantages, for example: some of them are not free
to use. The most important criterions when choosing a good software tool for risk management are:
method phases supported, tool architecture and interoperability with other software platforms or
packages. The future tools for risk management must have a more efficient interoperability and also they
should integrate the risk management process other processes within the organizations.
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by University Politehnica of Bucharest, through the “Excellence Research Grants” Program, UPB – GEX. Identifier: UPB–EXCELENȚĂ–2016, Contract number 11/30.09.2016.
References
- Clarizen Inc. (2017). Risk Management - Useful Tools and Techniques,. Retrieved from https://success.clarizen.com/hc/en-us/community/posts/203996208-Risk-Management-Useful-Tools-and-Techniques Corporate Compliance Insights (2017), Key Elements Of The Risk Management Process, http://www.corporatecomplianceinsights.com/key-elements-of-the-risk-management-process/ E.N.I.S.A Technical Department. (2006), Risk Management: Implementation principles and Inventories
- for =Risk =Management/Risk =Assessment =methods =and =tools, =Retrieved =from
- http://www.enisa.europa.eu
- E.N.I.S.A.(2017). Inventory of Risk Management / Risk Assessment Methods, Retrieved fromhttps://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/riskmanagement-inventory/rm-ra-methods E.N.I.S.A.(2017). Risk Watch, Retrieved from https://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-ratools/t_riskwatch.html, accessed in (2017); E.N.I.S.A.(2017). Risicare, Retrieved from https://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-ra-tools/t_risicare.html E.N.I.S.A.(2017). RM Studio, Retrieved fromhttps://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-ratools/t_rm_studio.html E.N.I.S.A.(2017). Krio, Retrieved fromhttps://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-ra-tools/t_gxsgsi.html E.N.I.S.A.(2017). Mehari, Retrieved fromhttps://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-ra-tools/t_mehari.html Meghea, A., Ionescu, S., Diulescu, D., Grecu, I., Ghita,I., Badea, N., Partsch, C., Dietrich, M., Necşoiu, T. (2008).Riscurile micilor afaceri, Politehnica Press.
- Web =Finance =Inc. =(2017). =Business =Dictionary, =Retrieved =from
- http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/risk-management.html
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-024-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
25
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-74
Subjects
Education, design learning, educational technology
Cite this article as:
Tiganoaia, B., Cercel, C., & Pavlícek, A. (2017). Some Risk Management Software Tools – An Exploratory Study. In Z. Bekirogullari, M. Y. Minas, & R. X. Thambusamy (Eds.), Living the Future: Technology, Engineering, Education & Computer, vol 25. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 23-32). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.3

