Abstract
Young people must have a healthy physical and mental state and must be prepared to cope with changes in the modern world to obtain harmonious physical development and socialize well with others. We believe that poor health can affect the ability of young people to be physically active, discourages the ability to cope with various situations, and prevents participation in group and community activities; including participation in sports. The purpose of this paper is to run a study based on a questionnaire, to determine social factors that influence the quality of life and wellbeing in order to improve physical, mental, and social status. The questionnaire was applied to a total of 300 students, from I to III years of study from the Ecological University of Bucharest. Methods used were review of literature by theoretical analysis, observation, and sociological test. The study aims to evaluate the effects of physical exercise and other factors on the young students’ lives.
Keywords: Fitnessquality of lifestudentpsychomotorhealth
Introduction
A study by the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) called "Programme on Ageing" shows that in order to be happy, people should focus on health, simple pleasures, and live a balanced life (Semnele timpului, 2012). Psychologists believe that wellbeing influences the quality of life and does not rely solely on the number of personal achievements, but rather on the ratio of positive versus negative events in our lives.
From this statement we can say that our purpose in life is to be successful in many areas, and to try to tilt the balance to have more positive experiences than negative ones. Marcu A. (2002) structured some factors that influence quality of life, namely: reducing disease symptoms, minimizing anxiety, and encouraging inflows of wellbeing and optimism. Practicing regular fitness exercises leads to weight loss, increased chest and arm circumference, as well as pectoral muscle tone and strength development (Potop, Triboi, & Ulareanu, 2016). Maintaining a network of positive social interactions and adopting positive skills enhances the ability to work and to maintain a healthy standard of living (Marcu, 2002).
Practicing physical activities is effective in the maintenance and/or the recovery of health, the quality of life, and the active presence in social and economic settings. There is a wide range of advantages of athletics, including the strengthening of the body, development of motor skills, and other physical abilities (Neder, 2010, p. 23).
World Health Organization adds to the definition of health the social component, stating that health is not merely the absence of disease or disability, but a state of physical, mental and social wholeness. The same source reports that health is imperative to everyday life, and enhances social, personal, and physical capabilities (Pop, 2010).
We know from Iamandescu (2002) that the most important factors for maintaining good health are exercise and balance between work, rest, and recreation.
Problem Statement
There is much research on quality of life that can be found in the medical world, and it is useful in assessing the effects of physical, psychological, and social effects on the everyday lives of people. The wide interest in the study of this topic is evident in the multitude of articles that have been published in prestigious journals and presented in the PUBMED database of the National Library of Medicine, US. Quality of life is embodied in physical well-being, physical mobility, adequate diet, sufficient leisure time, appropriate health insurance, hobbies and passions, optimum physical fitness. These are reflected in the four S factors of fitness: Strength - physical force; Stamina- endurance; Suppleness – flexibility; and Speed – quick performance; (Mărginean & Precupețu, 2010). Schulte and Vainio (2010) covers the concept of Wellbeing At Work (WAW) stating that wealth, and physical and mental wellbeing, is "an additive concept that characterizes the quality of life, including workplace safety and health issues (SSM)".
Health manifests itself throughout life and it is important to know and appreciate, from a young age, the factors that result in good health. Well-being is a component of health and is a result of a balance between personal and professional life. Regular exercise improves wellbeing and energy levels every day. Physical inactivity is a major risk factor associated with a large number of lifestyle diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes and obesity.
Research Questions
To complete the study, the following questionnaire was done and found appropriate solutions for youth awareness of the benefits of leisure through physical activity:
Which are the leisure time and prophylactic sport activities for ensuring good quality of life in young people?
Which are the most important factors which directly and indirectly affect health and wellbeing?
Do practising leisure time activities matter in enhancing health and quality of life at 19-25 group age?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this paper is to run a study based on a questionnaire, to determine social factors that influence the quality of life and wellbeing in order to improve physical, mental, and social status at 19-25 age group.
Research Methods
The research was conducted from September 2015 - February 2016, and a total of 300 students from Years I-III of the Ecological University of Bucharest were assessed.
At the same time, the study aims to highlight the quality of life of the disadvantaged, and the negative results that can be avoided or mitigated through physical exercise and preventive and ameliorative habits of young students.
Research methods consisted of a study of references, sociological tests, direct observation of some aspects of urban sports, direct talks with practitioners and enthusiasts of sports and leisure areas, and processing and interpretation of data collected – mathematical, statistical, and graphical methods. Research methods and techniques used are compliant with the rigors of high-level scientific research, respecting the choice of subjects under investigation, harvesting and data recording, etc. The questionnaire consists of 13 questions with 2-5 possible answers, and the subjects are anonymous and answered questions voluntarily after receiving information regarding the study.
Research methods consist of a study of references and sociological tests, direct observation of some aspects of urban sports, direct talks with practitioners and enthusiasts of sports and leisure areas, and methods of processing and interpretation of data collected - mathematical statistical method and graphical method. Research methods and techniques used are compliant with the rigors of high-level scientific research, respecting the decisions of subjects under investigation and the data collected, etc.
Findings
In an attempt to identify and discuss the favoured factors as well as the underprivileged, a table was compiled of the possible factors that may have a decisive role in the quality of health, and thus on overall wellness.
It was concluded that to achieve physical development and a harmonious lifestyle, including the ability to relate to other individuals, young students must have a state of optimal health, both physically and mentally, and must be prepared to face the changes of the modern and changing world. Ill health is an unfavourable character when trying to relate and communicate with other members of a group or community to which he belongs, even in terms of practicing exercise.
Motivation and desire to practice physical exercise in order to achieve peace of mind is another contributing factor to the possibility of practicing sport and socializing during and after training sessions. People who are constantly attracted to the practice of physical exercise through various means, are emotionally stable due to emotional balance created by chemical and physical processes that occur in the human body. Lastly, relationships with people practicing physical exercise can create favourable conditions for entry into the large family of sports practitioners for a better understanding of psychomotor resources of the body. The present statistical situation in the group of students polled illustrates social involvement, communication, and regular practice of a sport.
Based on responses presented in Table
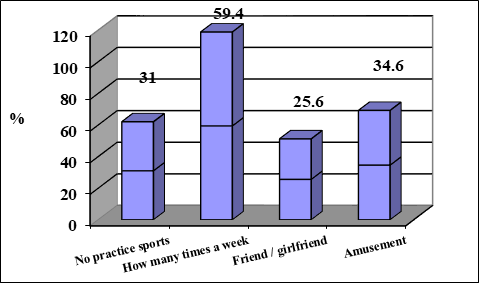
We see in Figure
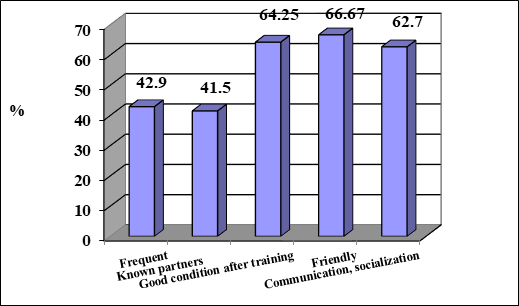
In Figure
Physical education practiced systematically contributes to the development of all physical, cognitive, emotional, and volitional processes (Neder, 2015).
From the analysis of the questionnaires it is concluded that practicing sports activities during free time can be a factor of social integration and can contribute to restoration of social equality of individuals in the community, as well as act as a catalyst for human relations in groups and functions of the body, whereas daily stress, especially vocational training, represents a serious threat to health. All this can create conditions for developing the factors favouring or disfavouring wellness.
Conclusion
Study findings provide a set of concrete habits, represented by common factors that secure the quality of life and welfare of the young students with high predictive power and adequate osmosis based on Romanian and European values.
Habitual and systematic practice of any form of physical activity with a leisurely nature,, is a way to prevent the risk of disease such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, osteoporosis, stress, anxiety, depression, etc.
Motivation and the desire to practice physical exercise in order to achieve a state of good psychological comfort is a contributing factor to the possibility of practicing sports and socializing during and after training sessions.
Acknowledgments
We thank the students who responded to the questionnaire and also for their involvement in organizing the study.
References
- Iamandescu, I. B. (2002). Medical Psychology. Bucharest: Infomedica Publishing.
- Marcu, A. (2002). Metode utilizate în monitorizarea stării de sănătate [Methods used in public health monitoring]. Bucharest: Institute of Public Health Publishing.
- Mărginean, I. & Precupețu, I. (2010). Calitatea vieții în România [Quality of life in Romania]. Bucharest: Expert Publishing House.
- Neder, P. F. (2010). Methodology athletic disciplines. Bucharest: Printech Publishing House.
- Neder, P. F. (2015). Athletics - theory and practice. Iasi: PIM Publishing House.
- Pop, C. E. (2010). The health of the population of Romania in the European context. An approach in terms of quality of life. Quality of Life, XXI (3–4), 274–305. Retrieved from http://www.revistacalitateavietii.ro/2010/CV-3-4-2010/04.pdf
- Potop, V., Triboi, V. & Ulăreanu, M. (2016). Pectoral muscles toning by means of fitness. International scientific session Aplications of kinetotherapy and sports medicine in motor activities. Bucharest: Ecological University of Bucharest.
- Schulte, P. & Vainio, H. (2010). Welfare at work. Overview and Future. Scandinavian Journal of WorkEnvironment and Health, 36 (5), 422-429.
- Semnele timpului. (2012, June 5). 8 -factori-cheie-pentru-starea-de-bine [8 th key-factor-for-well-being]. Retrived from https://semneletimpului.ro/social/psihologie/fericire/8-factori-cheie-pentru-starea-de-bine.html
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-026-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
27
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-893
Subjects
Teacher training, teaching, teaching skills, teaching techniques,moral purpose of education, social purpose of education, counselling psychology
Cite this article as:
Toma, S. U., & Urichianu, B. A. (2017). Profiling Factors Which Act Upon Wellbeing Of Young Students Aged 18-25 Years. In A. Sandu, T. Ciulei, & A. Frunza (Eds.), Multidimensional Education and Professional Development: Ethical Values, vol 27. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 837-842). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.03.99

