Abstract
Due to its accessibility, physical education and sports are practiced in many different forms throughout life, having her formative strategies and methods for implementing the objectives for each age category. The purpose of the research is a study on assessing the level of effort capacity of students and providing a basis for reporting and subsequent revaluation to estimate the effectiveness of measures to be taken. Hypothesis of the research. It is assumed that involvement in a regular program of physical activity can have a beneficial impact on the body, stressed the effects on functional levels and can improve significantly the effort capacity. The research methods used were: bibliographic study method, observation method, method of registration results on separate sheets for each student. Ruffier – Dickson test - was described in 1920 and named for its author "assessment test of fitness (fitness)". It is a functional sample cardio-vascular valuable especially for children, untrained people and the elderly, but less valuable for athletes, especially those who practice dynamic efforts. The research was conducted on a total of 81 students from the specialty of kinesiology and special motricity in the Faculty of Physical Education and Sports of the Ecological University of Bucharest. The research aimed to aware the students about the effects of systematic practice of physical exercise within some programs aimed at maintaining and improving health to prevent premature degradation of the body and its functions in general.
Keywords: FitnessdistancehealthHettinger testlevel
Introduction
Physical education is accessible to all, regardless of age, gender, religion, occupation, etc. Due to its accessibility, physical education and sports are practiced in many different forms throughout life, having her formative strategies and methods for implementing the objectives for each age category.
Education in the Olympic spirit can establish a necessary transition between generations, a philosophy of life and sports, is a game of all generations is a universal language and a huge social role. Education is a process that forms, grows and matures fundamental human sides: physical, mental, moral, aesthetic cognitive, emotional, and volitional (Urichianu-Toma, Urichianu, & Enache, 2016).
As a self-employed person, physical education takes place only during leisure time of subjects and in the absence of the teacher. This activity was independent of physical education should be prepared within the framework of bilateral educational process (Cârstea, 1997, p. 25). Carrying out physical exercises causes a series of stimulus that cause changes and structural and functional adaptations, and forms the basis on which to draw up a better capacity of the subject.
Physical activity as a self-employed person contributes, besides physical education carried out in school, further action to enhance the health of the body, hardening, improving the resistance to physical capacity and improving the process, continual adaptation to effort of major functions, but also to improve the General level of physical training.
According to Teodorescu (1973), physical capacity is the totality of natural acquired motor possibilities, by which one can realize varied efforts from the point of view of the structure and dosing.
Muscle activity is one of the factors that are related to the processes of adaptation of the body. Each exercise causes immediate processes necessary for adapting and adjusting the body functions at the level of the corresponding increase in energy metabolism (Atko, 1995, p. 33).
The continuous growth of sports results and the need to increase training efforts involve a high level of morphologic potential, the guarantee of higher performance achievement (Urichianu-Toma, & Urichianu, 2011, p. 97).
Problem Statement
Lately, we see a significant drop in the number of students who practice exercise in their free time, eloquent example being, on the one hand the decrease in the number of athletes, but also of those who practice any kind of movement in their spare time, while on the other hand the increase in the number of people overweight nationwide.
Currently, physical education is addressed to all categories of the population, adapting the objectives, resources, methods and forms of organization to the specificity of each of them (Neder, 2015, p. 12). Physical education and sport of prophylactic or curative can be carried out to maintaining bio-psychical condition of adult generations.
Physical education and sport of prophylactic or curative contributes to increase the body's resistance to physical and intellectual effort to enjoy and relax having a pivotal role in the formation of the people, of rest which they determine a character actively.
Exercise is used as a means of physical education both in the classroom and in extracurricular activities of the individual. The choice of exercises in the physical activities of independent sports must be arranged within a certain period of time. Exercises can be dispensed as necessary throughout the space and increase the time by modifying the weight and volume of objects used, by changing the period of recovery after exercise.
In order to increase the capacity of effort jogging may be performed in any form, as the most affordable exercise and because of this, they have acquired a large spread among the masses. Running mission work muscle groups, causing an intense cardio-vascular systems and respiratory systems, as well as of the whole body. Running is one of the fundamental means of physical development of multilateral agreements.
Development of resistance may be made by exercises performed in the series, with the rest breaks between them, through prolonged action or movement. The determination must be made in years by age, sex and level of physical training of the practitioner.
Research Questions
Hypothesis of the research. It is assumed that involvement in a regular program of physical activity can have a beneficial impact on the body, stressed the effects on functional levels and can improves significantly the effort capacity.
Objective of the study: The establishment of the study group and the research methods; To evaluate the fitness levels of students deadlock specialization; Interpretation of the results and the formulation of conclusions; Creation of data bases as support for information and training of a healthy lifestyle.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the research is to develop a study on the evaluation of the level of effort capability of students and to provide a basis for reporting and subsequent reassessment in order to estimate the effectiveness of the measures to be taken.
Research has sought to bring into the attention of students, the effects of the systematic practice of physical exercises in the framework of programmes intended to ensure the maintenance and improvement of health, prevent premature degradation of the body and its functions in general.
Research Methods
The research methods used were:
Findings
The research was conducted on a total of 81 students from the specialty of kinesiology and special motricity in the Faculty of Physical Education and Sports of the Ecological University of Bucharest in January 2015.
The efficiency of cardiovascular system is possible to evaluate optimally by making use of the functional tests. One of them is The Ruffier test, which in simple way and with sufficient rate of reliability sets the functional state of the cardiovascular system (http://www.aos.sk). Dickson-Ruffier Test has been described in 1920 and named after its author the "test capacity assessment (fitness)". It is a sample of the cardio-vascular, functional, valuable especially for children, the elderly and the illiterate, but less valuable for athletes, especially those who practice efforts.
The sample consisted in the execution of 30 squats with outstretched hands, in 45 seconds. Before the execution was measured pulse rate at rest, then immediately after the end of the accounting period and at 1 minute after exercise. The calculation was made by the formula:
Ruffier-Dickson test:
Where:
P = pulse rate resting
P1=pulse rate at the end of pulse effort
P2 = pulse a minute from the end of the effort
Appreciation index: 0-5 = excellent adaptation
5-10 = good adaptation
10-15 = average adaptation
15-20 = poor adaptation
As a result of the study conducted there were obtained the following results, which have been listed in table
As a result of testing sample-whole Ruffier Dickson batch, it was observed that the percent of students 12.25 had good adaptation, 44.9% adaptation was average and 42.86% registered a poor adaptation. No subjects have been recorded with a great adaptation.
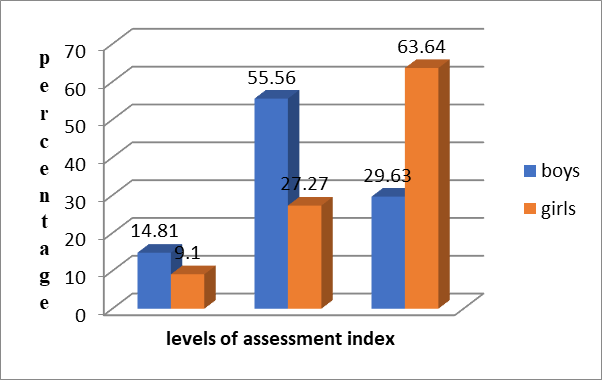
Analysing the results depending on the sex of the participants shall observe the following situation: In terms of the capacity of effort of girls, having obtained a good adaptation 9.1% of them, a 27.27% had average adaptation and poor 63.64%. There have been no results with excellent adaptations.
For boys, 14.81% of students gained a good adaptation, 55.56% average adjustment and for 29.63% adaptation was poor. There have been no recorded excellent results with any adjustments for boys.
The sample of study subjects, have a poor ability to effortlessly. They can perform in their spare time, if they want to maintain a good body health, exercises for the development of all skills, in particular resistance. However, it is well known that the development of an automated motor qualities lead to the improvement of others.
Each exercise corresponds to a dominant quality. When athletes increase load exercise is to force, when you increase the rapidity or frequency in an exercise the effort is speed, and when increased distance, duration or the number of repetitions, the athlete performs an exercise in stamina.
At the end of the research it will be possible to designed kinetoprophylactic programs to increase endurance of the students.
In order to improve the physical condition we recommend subjects study: for the force, to perform exercises that require a large, muscular strain, such as those for overcoming its own weight: jumping, pushups, squats, leg raises in the arms, abdomen and back exercises, exercises with medicine ball or with the dumbbell, the speed develops through rapid execution of movements of body segments that permit running game: with ankles and knees up, the place and on the go, running, while mobility develops through drills with a large amplitude and voltage: outlets, bends, twists, tension etc. If drills are repeated multiple times within the same lessons and attract major functions supported in the task, they acquire orientation in the direction of the development of resistance.
In Romania, the physical activity of independent sports shall not be given special attention for young people and not only. In 2015 we conducted research concerning participation in physical activities outside of school hours, at the level of children 4-14 years, out of which came as their interest but also of parents for practicing physical exercise decreases as the child grows. In this paper, we tried to see what the situation at the level of the students is.
The reduced level of effort capability of youth from age educational practice is a result of no practice sports physical activities over time. Not all people want to practice sports, it's true. But the small number of hours of physical education from schools in Romania, lack of interest in conjunction with the movement of people, leading in the end to a sick population, unable to carry out professional activities and not only.
The results obtained when testing the capacity of effort of the students of this work, can form the basis of departure in kinetoprophylactic programs to increase the endurance level of the students, to not miss the bodily activities practiced regularly.
Conclusion
The conclusions reached in the study performed are:
1. The result of the testing capacity of the effort, 12.25% of students had a good adaptation, 44.9% adaptation was average and 42.86% registered a poor adaptation. No subjects have been recorded with a great adaptation.
2. We found significant differences concerning the capacity of effort of participants on the basis of the sex of the participants. For girls, have achieved a good adaptation of 9.1% of the respondents, 27.27%, an average amount of adaptation, and 63.64% registered a poor adaptation. For boys, 14.81% of students achieved a good adaptation mean 55.56% %, an average amount of adaptation and 29.63% registered a poor adaptation. There have been no recorded excellent results with adaptations for either girls or boys.
3. By comparing the results obtained it is observed that the boys have seen better values than girls.
4. Both girls and boys need physical exercises programs to increase endurance of the students. The development of resistance can be done at the expense of predominantly aerobic efforts.
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the research plan of the Faculty of Physical Education and Sports of the Ecological University of Bucharest in collaboration with the University of Bucharest, Physical Education and Sports Department.
References
- Akademia Ozbrojenych Sil. (2017, November 24). The Ruffier functional. Retrieved from testhttp://www.aos.sk/struktura/katedry/utv/ruffierang.html
- Atko, V. (1995). Mecanismul adaptării antrenamentului în Sportul de performanță. CCPS, (359-361), 31-35.
- Cârstea, Gh. (1997). Educația fizică, Teoria și bazele metodicii. București: ANEFS Publishing.
- Neder, P.F. (2015). Atletism, teorie si practica. Iasi: PIM Publishing.
- Teodorescu, L. (1973). Terminologia educației fizice și sportului. Bucuresti: Editura Stadion.
- Urichianu-Toma, S. & Urichianu, B. (2011, June). Characteristics of beginner rowers’ selection and initial stage of training. Paper presented at The Internatiional Congress of Physiical Education, Sports and Kinetotherapy, Romania: Bucharest.
- Urichianu-Toma, S., Urichianu, A., & Enache C. (2016), Olimpismul şi rolul sportului în educaţia moralǎ şi socială, Congresul Stiintific International: “Sport. Sanatate. Olimpism”. USEFS, 1, 109-113.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-026-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
27
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-893
Subjects
Teacher training, teaching, teaching skills, teaching techniques,moral purpose of education, social purpose of education, counselling psychology
Cite this article as:
Paraschita, F. L. (2017). Independent Physical Activity- Efficient Mean Of Good Health. In A. Sandu, T. Ciulei, & A. Frunza (Eds.), Multidimensional Education and Professional Development: Ethical Values, vol 27. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 537-543). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.03.63

