Abstract
This article aims to analyze the advantages and disadvantages from the perspective of health care beneficiaries, about public and private hospitals. The research instrument used was the questionnaire in which we effectively managed both independent persons (healthy) and addicts (with milled affections). The main objective of the questionnaire is to identify the reasons why they choose a public or private institute, when they need medical care. Following this analysis it has been found that regardless of age, medical act is a necessity and the choice of an institution to give them medical care, differs according to the status that they have in society and how they are treated / informed by health professionals. Data from the people questioned have led us to identify some positive / negative elements, which we found both in public hospitals and in private hospitals. We emphasize that the Romanian healthcare system can improve its might if it takes into account the opinion of medical professionals and patients. It is important to find a balance between the two institutions, in order for every person requiring hospitalization or treatment to receive medical care.
Keywords: Public hospitalprivate hospitalpatientshealth care beneficiaries
Introduction
Over time the hospital has received numerous approaches, one of the most important is found in the Law no. 95/2006 republished on 2nd September 2016 which defines it as "a health unit with beds, public utility, with legal personality, which provides medical services" (Legea nr. 95, 2006).
Public health system plays an important role in helping the creation and development of new medical staff. Also this is the first option for providing emergency medical services. In the public services patients receive free care, funds that are not reimbursable for the medical institutions (Fraze et al., 2010).
The Hospital has to take into consideration the opinion of the experts in the field over the organizational and functional modes and to analyse all of the medical care accomplishment links. Also they have to take into consideration to standardize and simplify these actions, to analyse the patient/clients flux, resources and information, and also the optimization of them in order to be able to handle in case of situations that might intervene in the normal activity (Ciurea et al.,2007). It is of great importance to have all the organizational topics analysed and compared with expert’s ideologies in order to establish an optimized healthcare system.
Even if public hospitals and private hospitals offer different conditions, by their choice the patient relies strictly either on quality of services or, on meeting the personal needs of the beneficiaries of the health care. We notice that updating healthcare systems can be achieved by stimulating the establishment of privatization or increasing the private health units, but also by stimulating the health insurance in the private system - bringing additional funds and increase transparency (Ciurea &-Husti, 2013).
Despite the fact that our country receives the lowest funding from the European Union it is observed that the number of hospitals is growing, mainly due to private hospitals being built. It requires a balance between public and private hospitals to provide medical services for all social classes.
Thus, whatever type of organization is necessary to trigger a major change, possible only by the management staff reports of “opportunities to improve the business overall, a department or group of persons from that organization, or by the appearance of a problem, which could affect the development of the organization " (Verboncu et al., 2011).
Problem Statement
Nowadays people are more attracted towards the private healthcare system, as the services provided are more secure, inspite of the free state healthcare system. This represents an issue and a balance between the two and a more equilibrated way needs to be discovered for providing the services and to take care of the people in need of the healthcare services. These parts have to be developed in order to cover all the needs and to provide the highest quality services to the patients.
Research Questions
The research responds to the questions: Which healthcare do you prefer? And why? But the study also responds to the question: How do we improve the system?
Purpose of the Study
This research aims to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of public hospitals / private health care from the perspective of beneficiaries (patients).
The research was conducted over two months. People surveyed were chosen randomly so could independent people and dependent people both could express their opinion.
Recipients of care were receptive and participated with interest in this investigation endeavor. They have provided over a research tool the advantages and disadvantages of public hospitals / private. In this way, the paticipants were motivating also the choice they make before opting for certain medical care.
Research Methods
The research instrument used to conduct this research was the questionnaire. It was anonymous and contains 14 questions with reference to the research theme.
The questionnaire had two major impact goals, namely:
Investigating the motivation on which the patients choose public or private hospitals;
Identify the advantages and disadvantages in terms of public hospitals and private health care beneficiaries.
Completing the research tool by the participating people in the study lasted on average 10 minutes. Lot of people surveyed was comprised of:
Women and men with different statuses in society;
Aged from 18 years and over 45 years;
Married / unmarried;
Background: urban / rural;
Findings
The research was conducted during June-August 2016. Questionnaires were sent both to independent persons (healthy) and addicts (hospitalized with mild disease).
Beneficiaries of care have shown interest in this study because they offered clear and accurate information and have not omitted questions in the questionnaire.
Characteristics of the sample
Investigative approach was done according to the following features:
age;
gender;
background;
profession.
Analyzing Table
Private hospitals are visited more often by younger patients (pupils, students, employees, etc.) the percentage is approximately 70%, with the predominant age ranges between 20-25 years and 26-35 years. A percentage of approximately 50% of the above percentage, make that choice because operating companies provide to them free services in private institutions at certain time intervals or whenever they need medical care. The rest consider private hospitals reliable institutions that offer more security in terms of the medical services.
People surveyed were equally men and women (about 50% each). Among those 67% who opted for private hospital and 52% of those who chose public hospital, are from urban areas. Whilst those who chose public hospitals (48%) in spite of private ones (33%) came from rural areas.
Choice motivation of public / private hospital
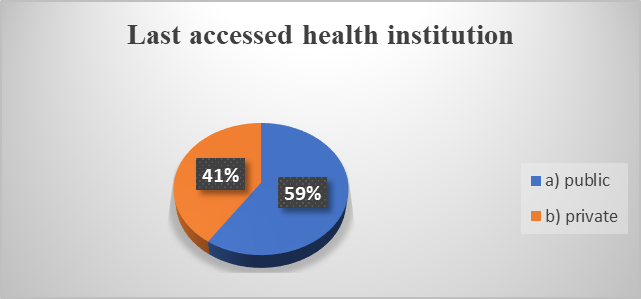
In Figure
Also in the above figure we see that a significant percentage of about 40%, chooses the private health institutions. First of all the respondents do this because they believe that the private sector provides more certainty in terms of medical services quality. Secondly the participants are satisfied with the way in which information is transmitted and, not least, are pleased that their appointments are respected.
Interest areas for recipients of medical care
We see in Table
A 18% believe that medical staff in public institutions was less helpful, because of the large number of the patients whom they had under supervision. We mention that from the respondents who received care in the public system, not all have opted voluntarily to that institution.
The table above shows that patients who received care in private hospitals have made this option considering that it is compliant with all quality standards, demonstrated also by the percentage of 100%.
Advantages and disadvantages public hospital & private hospital
Information obtained from recipients of the health care have led us to achieve results that can be seen in table.
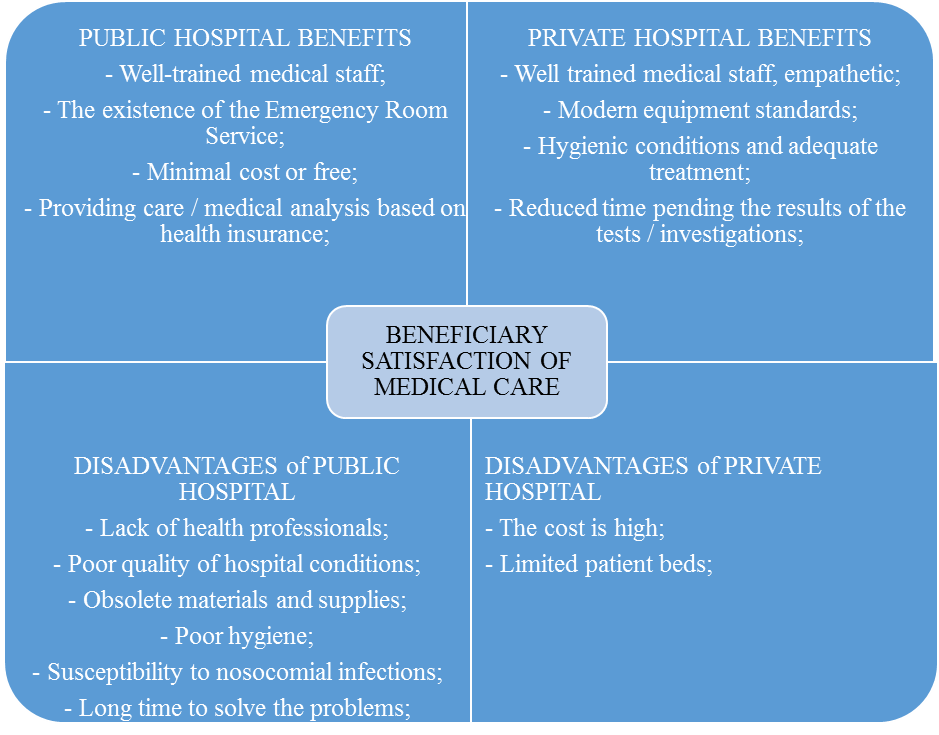
In Table
Public hospital advantages are that the costs are minimal, existing emergency service packages receiving and granting free medical care to the insured persons.
A number of advantages recounted in the table. 3 for private hospitals, namely: high technology equipment according to the current standards, optimum microclimate, hygiene and treatment and last but not least is the reduced time to obtain the results of the analyses and investigations due to progress information.
Unfortunately respondents are not statisfied of public hospitals because the medical staff is reduced, which leads to delay in delivery of healthcare and problem solving. Also they argue that the hygiene, materials and tools used, are not up to the expected level and believe that all these hospitalization conditions attract major risks to their health and people requiring medical care.
In Table 03. two major disadvantages for private hospitals are seen. The first is given by the high costs of hospitalization and the second by the limited number of beds and / or nonexistent emergency service.
Conclusion
Whatever health institution type - public or private, it is necessary to pay special attention to the circumstances in which the medical act is done.
Evaluating the information obtained we can see that the Romanian health system might improve by strict adherence to quality standards and through the active involvement of foreign investors. Also you need to supplement the number of health professionals by attracting them and by giving them very good working conditions.
As an improvement, it is recommended that public hospitals to consider provision of sanitary materials and instrumentation adapted to the new applicable regulations, and, also to turn their efforts towards compliance with the rules of hygiene.
Regarding the private hospitals in order to reduce the costs it is necessary the involvement of specialized authorities and / or the home state healthcare insurance, to subsidize a certain percentage of the total cost of the package of healthcare.
Although there are problems in the Romanian health system and a number of improvements are required, the level of service is ensuring minimum decent healthcare.
References
- Ciurea, A.V. & Luca-Husti, I. F. (2013, August 28). Servicii de Sănătate: spitalul public versus spitalul privat [Healthcare Services: public hospital versus private hospital]. Viata medicala [Medical Life Magazine], 33. Retrieved from: http://www.viata-medicala.ro/Servicii-de-Sănătate-spitalul-public-versus-spitalul-privat.html*articleID_7362-dArt.html
- Ciurea, A.V., Ciubotaru, V. Gh., Avram, E. (2007). Dezvoltarea managementului în organizațiile sănătății [Management development in healthcare organizations]. Bucharest: Universitară.
- Fraze, T., Elixhauser, A., Holmquist, L. & Johann, J. (2010). Public Hospitals in the United States. Statistical Brief #95. Retrieved from https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb95.pdf
- Legea nr. 95 din 14 aprilie 2006, republicată până la data de 2 septembrie 2016 [Law no. 95/2006, republished at 2nd September, 2016]. Retrieved from http://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/71139
- Verboncu, I., Nicolescu, O., Popa, I., Ceptureanu, E. & Ceptureanu, S. (2011). Schimbarea organizațională prin reengineering [Organizational changing through reengineering]. Bucharest: ASE.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-026-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
27
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-893
Subjects
Teacher training, teaching, teaching skills, teaching techniques,moral purpose of education, social purpose of education, counselling psychology
Cite this article as:
Iorga, C., & Șerban, A. (2017). Public Hospital Vs Private Hospital. In A. Sandu, T. Ciulei, & A. Frunza (Eds.), Multidimensional Education and Professional Development: Ethical Values, vol 27. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 283-289). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.03.36

