Abstract
Teaching - Learning – Evaluation Process of the study program Kinesiology and Special Drivability Faculty of Physical Education and Mountain Sports Brasov's main objective is training physiotherapists’ specialists, who are able to satisfy the needs of citizens from different social and economic areas of the country, with different body disorders. Therefore, educational curriculum after which this learning process is conducted has a wide range of disciplines, aiming at acquiring the necessary skills in the field, but also to provide individual theoretical and practical training for the student and to the future specialist in the art of movement, prevention, physical and functional recovery of the body. These disciplines harmoniously combine theoretical and methodological contents and practical training with the ultimate aim of developing multiple sports skills, but also to increase physical condition and overall enrichment of sports skills. Thus, disciplines like athletics, gymnastics, soccer, swimming, skiing, Pilates, aqua gym and not least the game of handball meet the solving of these goals by requiring continuum physical efforts and varied beneficial effects on the body and health. In this study, I will present the contribution of the discipline “Prevention and wellness through handball “in educating the driving ability and increase physical condition indices of freshmen students during an academic year. Through this research I am trying to prove that we can achieve a high level of physical condition as a basis for acquisition of vocational skills through systematic, methodical and rigorously planned training and specific to handball game.
Keywords: Physical therapy and special motor skillshandballphysical conditionevaluation
1.Introduction
The reasons I chose the subject of the research regarding ways to stimulate student interest from
KMS to perform physical activity in order to increase physical condition are multiple. Firstly the degree
of specific culture held by them concerning future profession is very low. The vast majority has no
knowledge about the field which they chose and content / subject discipline will have the route of
specialization nor the importance or role of physical exercise in the chosen profession.
A further reason is related to the low preparation of theirs physical skills and insufficient technical
and tactical motor acquisitions in sport branches (due to reduced number of hours of physical education in
undergraduate cycles).
Going forward with arguments, the chosen profession - physiotherapist – is linked to the necessity
of maintaining a static positions for implementing the procedures in patients. These positions have
negative repercussions on their body systems and devices: trunk twisting, tension and pressure on the
chest, limb isometric action, lifting and supporting people with different locomotors disorders and
keeping a working positions longer. By practicing systematic physical exercise these shortcomings can be
prevented or mitigated.
Not least was the methodology chosen and the forms for the subjects that participated in the
acquisition of sports skills. Even though the handball discipline is rich in content and intense physically
and mentally solicitation, I was able to arouse the interest and participation of students by alternating the
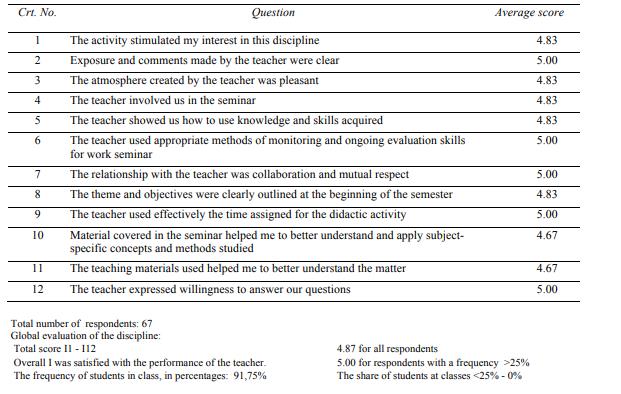
standard exercises with motion games. The frequency in practical classes was in proportion of 91.75%
and the cases of effective and affective outs were of a medical nature (physical indisposition, mild injury
etc.). Analysis of student satisfaction at handball lessons was conducted by questionnaire evaluation of
teaching submitted by the specialist and statistically analyzed.
Human motor behavior (Famose, J.P, 1993, Neagu N, 2010, 2012,) develops as a complex
combination of movements, attitudes or postures used to adapt to the different, constantly changing
environmental conditions. The motor skills of the body materialize in the harmony and easiness of motor
expression upon the occasion of exercise, leisure, sports or expressive activities, by performing various
movements involving one or several parts of the body or a combination of body parts, which require the
intervention and coordination of the important muscle groups. Thus, the more multilaterally the body is
trained, the better it integrates with the environment, being able to properly respond to stressful factors
with a minimum level of effort. Adaptation (Dragnea A.C. Mate-Teodorescu, 2002) is the level that
allows us to become acquainted to the environment. It is the dynamic balance between the assimilation of
the external environment and the accommodation – the integration of the internal body structure
information with the environmental requirements. The physical condition also is responsible for the level
of people's integration with the environment and their adaptation to its requirements. The health condition
comprises the way in which the body responds to either mechanical or mental strain pursuant to their
favorable or more favorable effects.
The proper and systematic performance of motor activities triggers the increase of the physical,
mental and social performance capacity, which, in the end, leads to good health and, implicitly, a high
quality of life. Physical exercise, physical condition and health are interrelated. Thus, in the opinion of the
reputed Mitra A, Mogos (quoted by Danila DM, 2011, p. 23) "physical exercise represents the voluntary,
deliberately and systematically repeated movement within an educational process organized for the
purpose of the achievement of concrete training and educational goals meant to develop and refine motor
skills, abilities and qualities, with the multilateral education of personality"
Physical condition (Hales, D. Lauzon, L. 2004) could be defined as the capacity of the body to
respond to environmental strain, with a proper cardiovascular, respiratory, muscular strength level
underpinned by the high motor and especially will qualities.
Health does not only mean the absence of the illness but, instead, in the vision of WHO, 1896,
health is the status of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, which fosters personal growth and
development, the capacity to cope with problems and attain complete comfort.
2.Methodology
2.1.Participants
The experiment included 66 subjects (32 girls and 34 boys), 1st year Kinetotherapy and Special
Motility students at the Faculty of Physical Education and Mountain Sports from Brasov, and took place
during years 2015-2016. The students covered a motility content specific to basic handball, adapted to
their main field of study, so as to acquire practical and methodical knowledge, while also enhancing their
motor capacity (The 2015-2016 curriculum for the Kinetotherapy and Special Motility Education
Program).
2.2.Measurement
Pedagogic observation meant to collect information on the researched phenomenon, pedagogic
experiment required in the elucidation of unknown facts through research, analysis of the training and
education process, of the relation between the planning and achievement of the content, the method of the
tests revealing the efficacy of the training efforts.
2.3.Procedure
The development of basic sports skills has been sought, through the initiation into the basic
techniques – catching and passing, dribbling, goal-throw, feints, necessary tactical knowledge, providing
an optimum framework for the performance of the bilateral game, while stimulating interest and
emulation towards the formally organized motor activity, as well as towards the enhancement of physical
fitness. Apart from the above, the general back, abdominal, arm muscle strengthening, coordination and
leg muscular force and resistance exercises have been used ("Prevention and Physical Condition through
Handball" Discipline Sheet for 2015-2016).
2.4.Statistical Analysis
The statistical data processing (Tudosi S, 1990) used were the following: arithmetic mean,
dispersion, standard deviation and relevance coefficient, correlated samples.
2.5.Research hypothesis
This study starts from the premises that a high level of physical fitness may be attained through
systematic, methodic and rigorously planned training, with the general and specific means in the handball
game - a field discipline of Kinetotherapy. The research aimed at systematizing certain training elements
in the Kinetotherapy (KMS) curriculum, meant to develop professional skills, but which, through their
physical strain level, also lead to the increase of the physical fitness level. Thus, (Neagu N, 2012) the
objectives of the research have materialized in: the study of the sports training sources with regards to the
factors that help attain a high motor output; the identification of the measurable parameters in the subsequent specialty training; the registration of the motor indicators achieved pursuant to the physical fitness tests; the result processing and study completion.
3. Results
3.1 The quantitative side
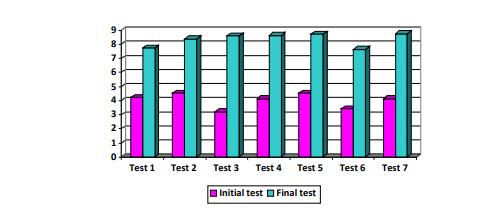
the students' endeavour to enhance their effort resistance - assessed through muscular strength tests (upper body raises while lying back/30sec., upper body raises while lying frontally/30sec, press-ups (no. of repetitions), jump-rope (no. of repetitions without rest time) and small marathon (450m/time). The initial tests were organized at the beginning of the first semester, during 10-20.10 2015, and they were completed during 25.05-3.06 2016. The results were added to the theoretical admission examination grade (see tables 1 and 2). The criteria list established the quantity of physical exercise each student had to make at the end of the practical lesson basics, while educating their segment and general body strength and the aerobic/specific resistance.
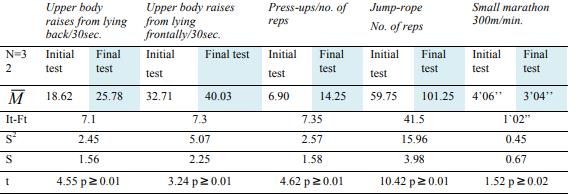
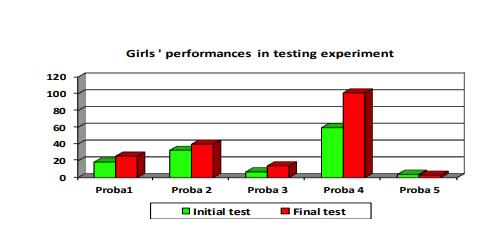
A careful look at table 1 and figure
The results of the arm strength test through front support press-ups were much more obvious. Girls do not have high muscular strength in the arms, but exercise can bring relevant improvement. Thus, if at It, girls had an average of 6.9 repetitions, after 10 months of training, the results for this test increased to 14.25. The statically calculated T is 4.62, much higher than in Fisher's table (2.57) for limit p ≥0.01.
For the girls, jump-rope should not raise any coordination or smooth performance issues, it being a known fact that they very often do this exercise – during first and secondary school years. However, It registered a value of 59.75 reps without interruptions, whereas the final test value was of 101.25 reps, 41.5 more than upon the initial testing. The calculated T is 10.42, higher than the table value for p ≥0.01.
The last test, the small marathon brings to the forefront the resistance to speed, because distances are shorter, with direction and body movement shifts, stop-start-acceleration. If upon the first test the time covered was of 4.06 minutes, upon the final test the results were spectacular, reaching 3.04 minutes. This shows that resistance and strength can be educated with very good results as long as the principle of continuity is observed. The calculation of the t has confirmed our work hypothesis up to 99.8%, since the obtained value was of 1.52, much higher than in Fisher's table at p ≥0.02.
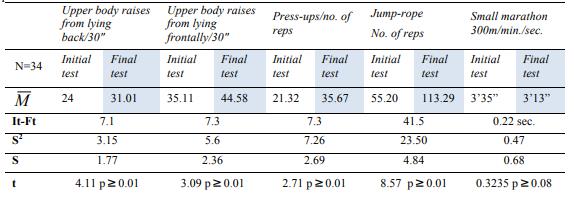
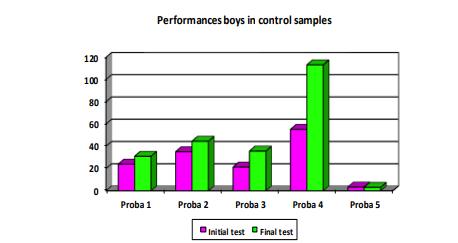
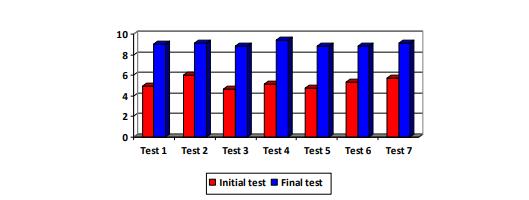
If girls managed to improve their performance by 25% to 35%, the results obtained by the boys are just as promising. In the two muscular resistance tests (table 2 and figure
For test 3, press-ups, the boys had an average of 21.32 reps for the initial test and, upon the final test, they have achieved average performance of 35.67. The statically calculated T is higher (2.71) as compared to the one in Fisher's table (2.57) for p ≥0.01
In test 4, they have faced quite a lot of difficulties, being unable to synchronize movements. If at It 30%
of the subjects were unable to connect several consecutive rounds, some being actually unable to
jump two consecutive times and obtaining an average result of 55.2, upon the final test, the
average number of rope jumps has increased to 113.29. This performance was widely spread, the
lowest value being of 3 reps, and the highest of 103. At the end of the training stage, the
differences between the motor action performance capacity and its quality has considerably
decreased. The calculated T was of 8.57, higher than in Fisher's tables (2.57) at p≥ 0.01.
For the small marathon test, the initial performance was of 3.35 minutes reaching 3.13 upon the final
testing. The calculated t reached 0.3235, more than the table t for p≥ 0.08.
3.2. The qualitative level of the handball-specific technical and tactical knowledge achieved expressed
through grades. The discipline-specific technical content has been included in the didactic
process for 10 months, a period during which field displacement procedures, ball catching and
passing, dribbling, goal-throws, basic game and full effect bilateral game notions have been
practiced. The objective was related to the achievement of professional and cross
competencies, as well as the increase of the body capacity to withstand effort. The results
expressed in grades are presented in table 3 and figure
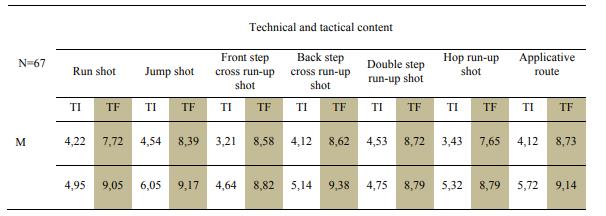
4.Discussions and Conclusion
The review of the practical competency acquisitions should start from the fact that all subjects were
initially tested in order to check the individual progress level. The test results show that 84.6% of
the subjects were unable to respond to the minimum test requirements (grade 5), because they
had not covered the handball curriculum during the pre-university physical education and sports
classes. Thus, during the hours dedicated to the subject-matter, the teaching-learning level
methods, the global training for more accessible processes, as well as the segmented or
analytical methods for the more complex ones have been used, in order to achieve tactical
learning. The final tests have revealed a good performance level for all technical disciplines,
with higher average individual progress results of approximately 7.72 for run shooting (girls)
and 9.38 for back cross leg shooting for boys.
Good and very good performance was registered for the applicative route - pass - running across a
ranging pole - catching the ball thrown by the team mate - dribbling - jump pass to the pivot
player - regaining - 6m penetration shot at the goal. The assessment of the performance capacity
and of the implementation of the technical procedures and tactical actions focused on: the
subjects' dexterity in handling and controlling the ball, confident passing, and the choice of the
best technical alternatives for the tactical situation. The performance ranged between mean
values of 8.73 for girls and 9.14 for boys.
Based on the data obtained pursuant to the experimental research and on the didactic observations
concerning the education of the motor capacity and of the physical condition by covering the
handball curriculum, it may be concluded that their acquisition:
- enhances the sports skills required for the performance of leisure activities
- enhances the quality of the technical process and bilateral game performance
- develops the accurate coordination of movements, of the locomotor system, and leads to the
establishment of complex and unitary movement structures;
- fosters confidence and ease of performance;
- improves physical condition through the isolated repetition of technical processes and tactical actions, as
well as through bilateral game;
- educates motor qualities: force, displacement and execution speed, coordination, spatial and temporal
orientation, as well as general and specific resistance.
- educates the effort capacity, while optimizing the physical condition and the quality of motor
executions.
Concerning the statistically processed results, we conclude that the level of physical effort systematically
made during the specialty classes, based on the joint curriculum structure, has multiple
influences on the education of the capacity and, especially, the optimization of the physical
condition of the future kinetotherapy specialist. The superior performance registered by both
boys and girls in the physical capacity and, implicitly, physical condition, tests have reflected in
the accuracy of handball-specific executions. If motor capacity indexes are educated in terms of
the capacity to withstand effort, the level of specific motor acquisition also is higher. All
subjects registered significant progress in terms of the motor capacity and physical condition optimization.
Considering the experimental results obtained, we believe that the future kinetotherapy specialist needs a
proper psychomotor education in order to be a reliable role model for his peers, hold sound
knowledge on the personal and public health protection or recovery methods.
References
- Danila, M, D. (2011). Bazele teoretico-metodice ale exerciţiului fizic, Bacau.
- Dragnea A.C. Mate-Teodorescu (2002). Teoria Sportului, FEST, Bucuresti, Famose, J.P. (1993). Performance motrice: un essai de definition.In cognition et performance. INSEP
- Publication, Paris.
- Hales, D., Lauzon, L. (2004). An invitation to health, Nelson Education, Toronto.
- Neagu N. (2010). Teoria și practica activității motrice umane, University Press Printing House, Tirgu Mures.
- Neagu, N. (2012). Motricitatea umană, fundamente psihopedagogice,University Press Printing House, Tirgu Mures.
- Tudosi, S. (1990). Statistică aplicată în educaţie fizică, Bucuresti.
- *** The 2015-2016 curriculum for the Kinetotherapy and Special Motility Education Program *** "Prevention and Physical Condition through Handball" Discipline Sheet for 2015-2016
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 May 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-022-8
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
23
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2032
Subjects
Educational strategies, educational policy, organization of education, management of education, teacher, teacher training
Cite this article as:
Balint, E. (2017). Increasing The Physical Condition Of Students By Playing Handball. In E. Soare, & C. Langa (Eds.), Education Facing Contemporary World Issues, vol 23. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 282-290). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.05.02.36

