Abstract
Keywords: Cloud SimulatorsCloudSimGreenCloudCloud AnalystEMUSIMGroudSim
Introduction
Although cloud computing started to be used in production more than a decade ago, we still have
many challenging situations that requires a significant amount of research to be done. A physical cloud
for conducting research it is not practical for medium to small sized educational institutions. A physical cloud requires a considerable investment in necessary equipment (servers, networking
devices, air conditioning). A solution for this situation is to use cloud simulators which can create a
virtual cloud infrastructure without the considerable investments of a real cloud.
A cloud simulator assists at creating various model of cloud applications by making data centers,
virtual machines and other utilities that can be configured appropriately, thus making it easier to analyze.
Until today many cloud simulators had been developed and have been actively used to conduct cloud
research. These simulators have different features like GUI, base programming languages, extensibility
through plugins or modules, etc.
The academic websites and journals includes now many articles comparing different cloud
solutions. This article takes a deeper approach on cloud simulators. In this article I present a
comprehensive study of multiple cloud simulators by highlighting their features and analyzing advantages
and disadvantages. A conclusion with the best cloud simulator for a certain project is provided at the end
of the article.
A comparative analysis of various cloud simulators is presented on table
Benefits of using cloud simulators over physical cloud are as follows:
-Low
simulators are available free of charge this making cloud simulators more convenient. Free cloud
simulators are usually also open source. This opens the possibility of developing custom features
that haven’t been designed in the original software.
-
developing of the desired model without any other variables involved. The model can be tested
as many times we want, until we get the desirable output.
-
Cloud Simulators
This section takes in consideration various cloud simulators that are mostly used to conduct cloud
research simulations. We have described in this section 6 cloud simulators.
CloudSim is one the most popular simulation tool available for cloud computing environment.
CloudSim it is a library for simulation of Cloud computing environments. Software has been developed at
the Computer Science and Engineering Department of the University of Melbourne, Australia at
CLOUDS Laboratory. The classes provided within library permits describing data centers, virtual
machines (VM), applications, computational resources, and policies necessary for management of
different parts of the system. The simulation tool can be adapted to our requirements by simply extending
or replacing the classes built in. As we have mentioned before, CloudSim is not a ready to use solution
where we set parameters and gather results necessary to use for our project. Being a library, CloudSim requires that we write a Java application using its components following our desired scenario and then
collect the obtained results for the analysing the performance of Cloud applications. (“CloudSim
Simulation Framework - Superwits Academy”, 2016) (Umang, S. & Ayushi ,S. 2016).
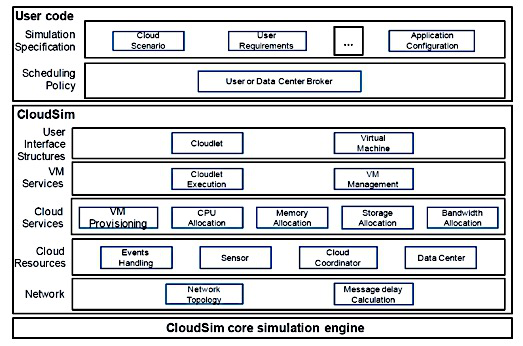
The layered architecture of CloudSim is outlined on Fig.
Cloudsim contains the following features:
Support for modelling and simulation of large scale Cloud computing systems
Permits modelling and simulation of virtualized server hosts
Support for simulation of network connections together with the simulated system components
Support for simulation of federated cloud environment that includes also inter-network resources
for both private and public domains
Permits user-defined policies for allocation of hosts to virtual machines and policies for
allocation of host resources to virtual machines
Support for user-defined policies at allocation of hosts and host resources to virtual machines
Permits simulation of electric energy consumption for desired model
Support for modelling and simulation of application modules
permits insertion of simulation elements and also stop and resume of simulation
Open source
2.2 Green Cloud
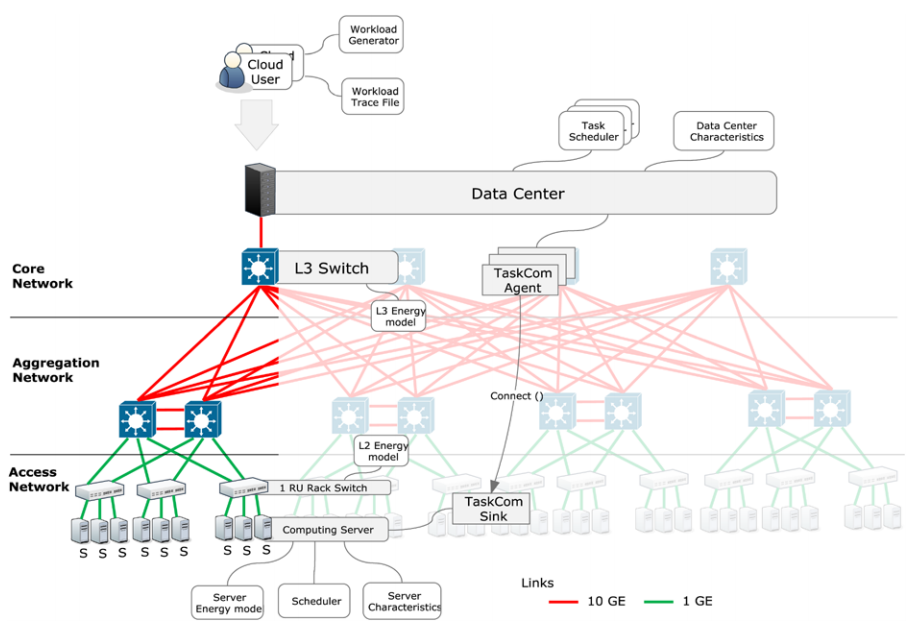
GreenCloud is a packet level simulator that has been created as an extension to well-known
network simulator NS2. GreenCloud has been developed in the context of ECO‑CLOUD and GreenIT
projects. This simulator is specially made for energy-aware environment. GreenCloud permits calculation
of energy consumption for any particular cloud computing component such as servers, network switches
and communication links. (Boru, D. & Kliazovich, D. & Granelli, F. & Bouvry, P. & Zomaya,
A.Y.,2015)
GreenCloud features:
Permits simulation of electric energy consumption for desired model
Defining of energy models for each type of cloud component
Simulation of CPU, memory, storage and networking resources with special attention to
networking component
Supports virtualization
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Full support for TCP/IP protocol
Open source
GreenCloud is suitable mostly for calculating energy consumption when designing cloud
computing structures. About 80 percent of GreenCloud code is implemented in C++, and the remaining
20 percent is in the form of Tool Command Language (TCL) scripts. To develop new features to
GreeenCloud user supposed to know both of mentioned languages. (“Greencloud - The green cloud
simulator”, 2016).
The architecture of GreenCloud is represented on Fig.
the the performance of large-scale distributed cloud applications with high user workload that are
geographically distributed over several data centers. Cloud Analyst has been built as an extension of
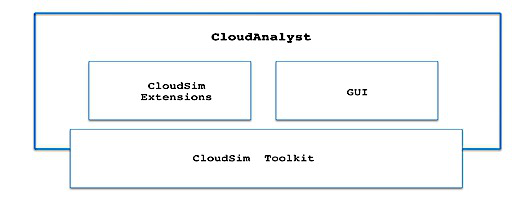
Features of CloudAnalyst:
Intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI)
High degree of configurability and flexibility
Repeat experiments with slight modifications
Results are represented also graphically in the form of charts and tables
Ease of extension – permits extending its capabilities to improve the simulation
The architecture of Cloud Analyst is represented on Fig.
2.4 EMUSIM
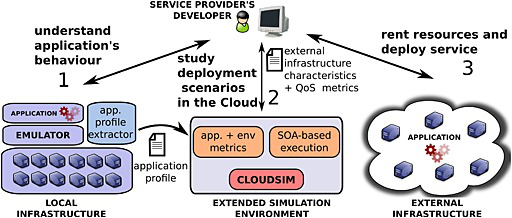
EMUSIM has been developed at the Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems (CLOUDS)
Laboratory, University of Melbourne. EMUSIM provides both capabilities of an emulator and as well of
a simulator of a cloud environment. The simulator is built up on CloudSim and Automated Emulation
Framework (AEF). On EMUSIM, the simulation model is generated with extracted information from
application behaviour via emulation. (“EMUSIM“,2016)
With EMUSIM, cloud service providers, are able now to know now how many resources are
required to have a given response time considering a specific arrival time and the effects of the changes
on the mentioned arrival rate. (Al-Sakib K. P.& Muhammad M. M. & Shafiullah K.,2015)
Features of EMUSIM:
Includes all features of CloudSim
Improved simulation by combining emulation and simulation of cloud computing
EMUSIM does not include a GUI. Cluster configuration is done by editing cluster.xml file. Files
aef.properties and emusim.properties are used to define information about the specific emulation to be
performed
Permits extending its capabilities to improve the simulation by working with CloudSim modules.
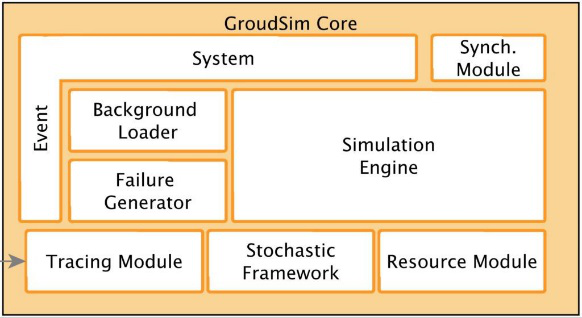
2.5 GroudSim
GroudSim (Gr-Grid and oud-Cloud Simulator) is an event simulation platform for both cloud and
grid computing environments. Main programming language for GroudSim is Java. (Kecskemeti, G &
Ostermann, S & Prodan, R., 2014) (”What are cloud simulators and it's applications”, 2016)
GroudSim features:
It can be extended easily by using probability distribution packages.
GroundEntity module from GroudSim has its own definition for error behaviors. With this
module user can change the configuration during each error occurrence.
The simulation parameters are entered through configuration files in XML format. The
application has no GUI interface
Introduces background load functionality
2.6 DCSim
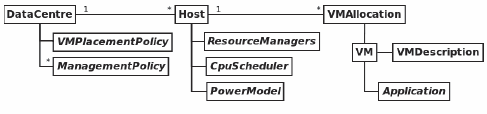
DCSim (Data Center Simulator) simulates a virtualized data center providing IaaS service for the
cloud. DCSim is an event-driven simulator designed for transactional and continuous workloads such as a web server. The simulator is developed in Java. The main component of DCSim is the DataCenter, which
contains hosts, VMs, and different management components and policies. The data center is composed of
interconnected hosts that are managed by a set of management policies. Each host it’s composed of a set
of resource managers that manage local resource allocation, a CPU scheduler to decide when to run VMs,
and a power model that decides how much power is being consumed by the host at any point in time. (Al-
Sakib K. P.& Muhammad M. M. & Shafiullah K.,2015) (Tighe, M. & Keller, D. & Shamy, J. & Bauer, M
& Lutfiyya, H.,2013)
Figure
DCSim features:
VM live migration and replication
Simulation tasks can be load balanced between multiple application instances running on
different VMs
DCSim generates a log containing the simulation results. This log can be used to generate
graphs, statistics in order to understand the behavior of simulated data center. Simulator includes also a
visualization tool that generates the necessary graphs using as input the generated log file.
Sharing of workload between multiple VM
Introduces SLA Violation parameter to monitor when a VM requires more resources than are
available to it. The percentage of CPU resource required and not available is recorded.
Calculates power consumption for each host
Conclusion
Each cloud simulator presented covers a certain domain of interest. Unfortunately, on the market
there is no cloud simulator to cover all possible cloud architectures. The user looking to simulate a
specific feature that cannot be found on any cloud simulator can develop his own module with the help of
a certain programming language.
CloudSim seems to be the most used cloud simulator to develop new features. CloudAnalyst and
EMUSIM simulator took advantage of CloudSim toolkit to develop their own cloud computing features.
Cloud Analyst analyses the performance of large-scale distributed cloud applications with high user
workload that are geographically distributed over multiple data centers. EMUSIM combines the AEF
emulator with CloudSim to optimize the simulation results obtained with CloudSim. Java is the most used
programming language among cloud simulators. One benefit of using java programming is portability
between operating systems or even perform mobile simulations (OpenMobster).
Analysing the synthetized results of table
cloud simulator solution.
Future work will concentrate on extending the research to other cloud simulators and to structure
them by the ability of extending their features beyond their standard features. Programming language and
ease of adding new features will be taken in consideration.
References
- Al-Sakib K. P.& Muhammad M. M. & Shafiullah K..(2015). Simulation Technologies in Networking and
- Communications EMUSIM,DCSIM p338,340
- CloudSim Simulation Framework - Superwits Academy (2016, August 1). Retrieved from
- http://www.superwits.com/library/cloudsim-simulation-framework
- Umang, S. & Ayushi ,S. (2016). CloudSim Simulator Used for Load balancing in Cloud Computing -
- International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering. Volume 6 Issue 4
- Greencloud - The green cloud simulator (2016, August 3). Retrieved from
- https://greencloud.gforge.uni.lu/index.html
- Boru, D. & Kliazovich, D. & Granelli, F. & Bouvry, P. & Zomaya, A.Y. - Energy-efficient data replication in cloud computing datacenters, Springer Cluster Computing, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 385-402, 2015. (2016, September 1). Retrieved from https://greencloud.gforge.uni.lu/ftp/energyrep.pdf.
- EMUSIM: Integrated Emulation And Simulation For Evaluation Of Cloud Computing Applications (2016, August 5). Retrieved from http://www.cloudbus.org/cloudsim/emusim/
- What are cloud simulators and it's applications - (2016, August 23). Retrieved from https://codingsec.net/2016/08/cloud-simulators-applications/
- Tighe, M. & Keller, D. & Shamy, J. & Bauer, M & Lutfiyya, H. (2013)- Towards an Improved Data Centre Simulation with DCSim, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM 2013), P364 – 372
- Kecskemeti, G & Ostermann, S & Prodan, R. (2014) - Fostering Energy-Awareness in Simulations Behind Scientific Workflow Management Systems, 2014 IEEE/ACM 7th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, P29 - 38
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 May 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-022-8
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
23
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2032
Subjects
Educational strategies, educational policy, organization of education, management of education, teacher, teacher training
Cite this article as:
Gordin, I. (2017). Energy Aware Of Cloud Computing Development Using Cloud Simulators. In E. Soare, & C. Langa (Eds.), Education Facing Contemporary World Issues, vol 23. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1298-1305). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.05.02.159

