Abstract
The research is focused on the preparation of undergraduate students enrolled in the quality management program in Tomsk Polytechnic University. The subject of the research is organizational and pedagogical conditions necessary for the formation of social competencies and socially responsible thinking in future undergraduate students enrolled in the quality management program. The research aims to identify and present the theoretical basis for organizational and pedagogical conditions to form social competencies in students enrolled in the quality management program. The methods and means utilized in the present research are as follows: analysis of information sources, peer review, interviewing of students and teachers, a passive experiment, and statistical methods of data processing. The organizational and pedagogical conditions for the development of social competencies in undergraduate students enrolled in the quality management program are to be identified, and the model of the social competency development in students with due regard to the principles of social responsibility of an individual is to be developed. This research contributes to the scientific evidence base and confirms that the formation of social competencies of students is an important psychological and pedagogical problem.
Keywords: Corporate social responsibilitysocial competenciespedagogical conditionsa college educationquality management
Introduction
The project "for the " specifies the purpose and principles of the state policy related to young people for the medium- to long-term perspective, that is, the formation of the competitive younger generation of Russians able to achieve economic, social and cultural competitiveness of the Russian youth (Russian Federation Youth Development Strategy for the Period until 2025, 2016).
The document emphasizes that the social competitiveness of young people can be achieved through positive reproduction of social-cultural models; through the formation of social responsibility and social competencies; through the priority of family values and the development of patriotism and citizenship.
This project considers the youth as an active subject of social transformation, a valuable resource for the economic growth and well-being of generations, driver of the development and leadership of the country. The key priority of the youth policy is the formation of positive outlook and popular social competencies in independent young citizens. The project states that the social and political position of young people and their responsibility for the future affect the pace of the state’s progress in the field of innovations.
It is also noted that young students should be prepared to build efficient and responsible relationships with the participants of the labor market, to lead active social life, and to become responsible parents. Thus, social responsibility and social competencies are important characteristics of the Russian youth, and the formation of these characteristics is an important pedagogical task.
Relevance
Relevance of the study is determined by the contradictions between:
the state order for the formation of social competencies in students under the conditions of modernization of the Russian education and insufficient development of educational technologies to solve this strategic problem;
teachers’ understanding of the importance of the formation of social competencies in students enrolled in the quality management program and lack of conditions for the process activation;
motivation of the youth to develop socially responsible thinking, self-determination, free personal choice, and unpreparedness to implement these rights.
The analysis of these contradictions revealed that the problem of search and selection of organizational and pedagogical conditions for the formation of social competence in the students of the Physical Methods and Instruments of Quality Control department is relevant and needs to be addressed at the level of an individual educational program.
Methods and discussion
In recent years, the problems of the formation of social competencies in future undergraduate students, meaningful pedagogical conditions, and the resources and technologies of their development have been actively developed. The key directions of the problem investigation are as follows:
basic principles of pedagogical understanding of social responsibility as a major component of social competencies considered in the works by A.S. Makarenko, V.A. Sukhomlinsky, and S.T. Shatsky;
at the present stage, the theory of social education as a theoretical and methodological basis for understanding the process of the formation of socially significant qualities and conditions (social competencies) (A.V. Mudrik, T.A. Romm, T.V. Furyaeva, and others);
the issues of social and professional maturity and responsibility as important components of the formation of social competencies considered in the works by L.A. Baranovskaya, I.A. Gladyshev, and A.F. Gulevskaya.
The research is focused on the organizational and pedagogical conditions for the formation of social competencies in undergraduate students of the Department of Quality Control Physical Methods and Equipment.
The research method is chosen due to the purpose and content of the study.
In the current research, we utilized theoretical (study, comparison, analysis, systematization, generalization of psychological and educational literature, educational and methodical documentation, teaching experience) and empirical methods (survey, questionnaire, investigation of the outcomes).
The theoretical and empirical research methods were utilized to identify organizational and pedagogical conditions for the formation of social competencies in undergraduate students enrolled in the quality management program at the Department of Quality Control Physical Methods and Equipment, National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University.
The first phase of the research (July–September, 2015) included the study of the problem elaboration in the Russian and foreign theory and practice; definition of the research objectives; study and analysis of the specific character of social competencies in future undergraduate students of the department.
The second phase (October–December, 2015) provided an expert assessment, surveys of the first- to fourth-year students and interviewing of the staff, the model design, and implementation of social and creative projects. The obtained results were processed and the appropriate conclusions were made.
Results
The analysis of the survey results and expert assessment revealed the following organizational and pedagogical conditions for the formation of social competencies and socially responsible thinking in future undergraduate students of the department:
Motivation of students to the formation of social competencies.
Organization of subject-subject relationship between a teacher and a student.
Preliminary modelling and planning of the formation of social competencies.
Current level of students' independence.
Project-based learning environment.
The first condition is considered to be the most important. The problems of students' motivation to the formation of social competencies require special attention. The study revealed that 78% of students (1 to 4 year students) understand the importance and significance of these competencies in the course of training in a higher educational institution and show a positive attitude toward this kind of competency. At the same time, only 28% of the first-year students, 34% of the second- and third-year students and 42% of the fourth-year students, future undergraduate students, exhibit the basic components of social competencies (indifference to the problems of quality of life, products, and service; ability to behave responsibly; formation of partnerships with classmates; ability to predict the possible consequences of activity or inactivity in relation to other people; independence in decision making). According to 59% of teachers surveyed, students are not responsible and independent, they are indifferent to social life aspects (including the problems of quality).
Social changes that are taking place in society: the growth of individualistic consciousness, interpersonal disunity causes difficulties in the formation of social competencies. However, in psychology and pedagogy, striving of an individual for interpersonal relationships is considered as one of the basic desires for adequate development of the personality, therefore, the organization of subject-subject relationship between the participants of the educational process was chosen by the teachers and students as the second condition for the formation of social competencies. The subject-subject relationship is the one based on the primacy of dialogue, cooperation, respect, and trust. It is formed during work on the scientific and educational product (art, project, research, etc.) (Belousov, & Yanushevskaya, 2015). The teachers of the department (about 68%) noted the importance of this condition and emphasized that in practice this condition is difficult to implement due to lack of time as the teachers are reoriented for fulfilment of the effective contract.
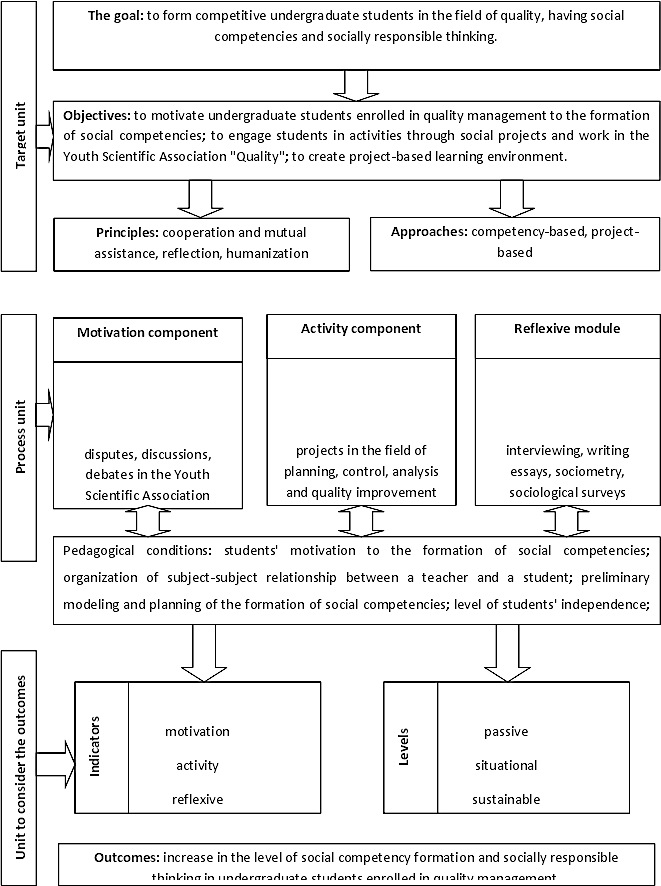
Modelling and planning of the process of the formation of social competencies is the third organizational and pedagogical condition (Smolyaninova, 2014). The model designed by the authors consists of interrelated components: target, technological and productive units (Fig. 1). The target unit includes the goal, objectives and principles of the model. The goal is achieved through the following objectives: to motivate undergraduate students to the formation of social competencies; to engage students in activities through social projects and work in the Youth Scientific Association "Quality"; to create project-based learning environment. The process unit consists of the motivation, activity and reflexive components. They imply specific forms of work defined by the model. The unit to consider the outcomes includes criteria, indicators and levels of the business and analytical competencies development. The level of students’ independence can be evaluated through testing. We have conducted the research to analyze the specifics of independent work of students at the Department of Quality Control Physical Methods and Equipment, TPU to identify the pedagogical conditions for the organization of students’ independent learning (Redko, & Sivitskaya, 2015).
Project-based learning environment, an important pedagogical condition for the formation of social competencies in the academic process, is realized through participation of students in project activities. The curriculum of the undergraduate students enrolled in quality management includes the discipline "Creative Project" studied in the 1st year. It orients the students to the formation of the indicators and characteristics of social competencies and socially responsible thinking such as readiness to be involved in the issues of quality of life, products and services; ability to behave responsibly (to take responsibility for development and outcomes of the project); ability to make decisions, etc. (Redko, & Sivitskaya, 2015). Creative project development is monitored by the teacher, which does not negate the student self-control. The students regularly interact with the teacher to discuss the interim results. Twice a semester, during the conference week, the students present their project results to a team of experts, teachers of the department. After that, the project course can be either corrected or considered completed.
The main expected outcome of the project is students’ motivation to the formation of social competencies: capability of self-learning activities, self-discipline and perfectionism, ability to assign responsibility, willingness to take the initiative, and persistence. The other expected outcome is experience gained by students: choice of methods to achieve the goal; work planning and organization; teamwork coordination, conflict resolution; independent logical completion of the work; analysis of the results (reflection), development of proposals to improve the performance of future projects.
We provide the description of social and creative projects developed by the first-and second-year students.
A textbook called "Entertaining Quality for Children of School Age". The idea of this project directly affects the development of socially responsible thinking in future undergraduates. It explains younger children what the quality is and why we need to think about the quality of products and services. The target audience of the textbook, schoolchildren, is chosen since the explanation with no specialized terminology used requires a high degree of understanding of the subject. As a result of this project, the students developed textbook content, selected and reworked materials and used bright pictures to illustrate the book.
This project is socially orientated. The students had a need for sharing information about the quality, its essence and role in modern life. The term "quality" today means not only the quality of products and services; it is increasingly common in the phrase "quality of life". "Quality of life" is a complex, comprehensive concept that includes both objective and subjective components, for example, health, consumption, affordable education, social activities and others.
Social-creative project "Consumer Memo." This project aims to inform the juvenile consumers about the quality characteristics of various products; about their rights during various operations with goods. The target audience is children of school age. The students developed the layout of the memo, chose groups of products most relevant for schoolchildren and described the quality indicators for each group. The memo contains information on the point of contact in case of defective products purchased and any disagreement with the seller arisen. The students chose the illustration techniques for the memo: illustrations for visualization, bright font, italics/bold text; adaptation for text simplicity, replacing complex words by simpler ones; gathering information about consumer rights and necessary qualitative characteristics of the goods for analysis (Plotnikova, & Redko, 2015).
Conclusion
The research revealed the following organizational and pedagogical conditions for the formation of social competencies and socially responsible thinking of the future undergraduates trained in quality management:
Motivation of students to the formation of social competencies.
Organization of subject-subject relationship between a teacher and a student.
Preliminary modelling and planning of the process of the formation of social competencies.
Level of students’ independence.
Project-based learning environment.
The analysis of the motivational conditions indicated that almost all the students show positive attitude toward the formation of social competencies, but they are not sufficiently motivated to this process, especially in the first year of study. Half of the students are not ready for responsible and independent decision making, which is an essential indicator of the high level of the formation of social competencies.
The analysis of the results of the organization of subject-subject relationship between a teacher and a student showed friendly environment for a dialogue between the students and the teachers of the department. However, the teachers had an impression that students are not always ready to take responsibility for their professional future, for transformation and enhancement of quality of life in the team and in the country.
The social and creative projects provided the experience in the formation of social competencies of students in the course of training.
This research contributes to the scientific evidence base and confirms that the formation of social competencies of students is an important psychological and pedagogical problem (Raykhlina, 2009). Its solution involves ideological and conceptual issues of society and education. The educational target under changing socio-economic conditions is not only to provide a certain level of knowledge and skills in basic sciences, but to ensure the ability and preparedness to live in a modern super complex society, to efficiently interact and achieve socially important goals, and to solve life's problems (Volgunova, & Nikolaeva, 2015; Khromov, & Gulyaeva, 2015).
Despite the problems occurring, much attention is paid to the formation of social competencies in the undergraduate students enrolled in quality management at the Department of Quality Control Physical Methods and Equipment, Tomsk Polytechnic University. This process is estimated as an efficient one since almost 100% of the undergraduates of the department are working in the professional field after graduating from the university; the students participate in conferences, contests and competitions and become winners. The graduates keep in touch with the department; they participate in social programs to improve quality of life in their organization and in Russia.
References
- Belousov, A.M., Yanushevskaya, M.N. (2015). Project management based on standard AS 9100. Gaudeamus Igitur, 4, 27–28.
- Khromov, S.S., Gulyaeva, N.A., Zelenetskaya, I.S. Minakova, L.Yu., & Sheketera A.L. (2015). An algorithm for the integration of information and communication technologies in teaching languages for special purposes. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 200, 224-229.
- Plotnikova, I.V., Redko, L.A., & Yanushevskaya M.N. (2015). Creative Project (TPU experience). Higher education in Russia, 4,155–159.
- Raykhlina, Ye. L. (2009). Pedagogical conditions of integration of educational and extra-curricular activities of students as a means of forming their citizenship. Bulletin of the Moscow State University of Culture and Arts, 6, 173–177.
- Redko, L. A., Sivitskaya, L.A., & Frantsuzskaya, E.O. (2015). Organisation of Independent Work of Students of a Technical University in Field-Specific Disciplines: Instructional Commitment of a Lecturer. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6, 142–150. Retrieved from DOI:
- Redko, L.A., Sivitskaya, L.A., & Yanushevskaya, M.N. (2015). Pedagogical conditions for organization of students’ independent learning in an administering sub-department of a technical university. Vocational training of students of a technical college in a foreign language: theory and practice: proceedings of the All-Russian scientific-methodological seminar on April 23–24, 112–115.
- Russian Federation Youth Development Strategy for the Period until 2025 (2016, May 5). Access mode: https://fadm.gov.ru/mediafiles/documents/document/98/ae/98aeadb5-7771-4e5b-a8ee-6e732c5d5e84.pdf
- Smolyaninova, O.G. (2014). Development and evaluation of social competencies of students of High Pedagogical School by Means of e-Portfolio. Modern problems of science and education, 1, 35–43.
- Volgunova, G.A., Nikolaeva, N.O. (2015). The development of social competence as a condition for formation of citizenship in students. Young scientist, 13, 610–613.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 January 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-018-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
19
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-776
Subjects
Social welfare, social services, personal health, public health
Cite this article as:
Belousov, A. M., Redko, L. A., Tichonova, E. V., & Yanushevskaya, M. N. (2017). Formation of Social Competencies and Socially Responsible Thinking of Students. In F. Casati, G. А. Barysheva, & W. Krieger (Eds.), Lifelong Wellbeing in the World - WELLSO 2016, vol 19. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 728-734). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.01.96

