Abstract
The article deals with social problems of higher education sector’s significance as a factor for long-term economic development and human well-being from the position of its ability to compete in the labor market after graduating from university. With the increasing availability of higher education in the Russian Federation due to the emergence of paid training, quality of education had deteriorated and resulted in necessity to toughen requirements to universities and introduce criteria for effectiveness of their activities. Under these circumstances it became urgent to conduct self-study of universities for compliance with new criteria. The paper presents results of marketing research of education’s quality in the Ural state economic university using SERVQUAL method and graphical method of analysis “importance- execution”. According to the survey, it was revealed that all indicators of students' expectations have not been met fully. Most successfully the university fulfills a social role in the development of personality, volunteerism and patriotic education. The study revealed that professional development: competences of teachers, employment for graduates and cooperation with employers became a priority for the university.
Keywords: Human developmenthigh educationquality of educational servicesSERVQUAL method
Introduction
The educational system is closely intertwined with the economic, cultural, scientific and technological spheres of social life. For one thing, education as a social institution promotes the development of every individual, educational organization creates the conditions for the disclosure of the potential student opportunities: intellectual, creative, cultural, sports. For another thing, higher education programs allow a person to get professional competencies needed to effectively build a future career. According to the editorial board of the magazine “Academy of Management Learning & Education” (Benos, 2010), education needs to the transition to a new paradigm based on human well-being. It is noted that higher education gives an individual a healthy understanding of humanistic culture. Universities should teach students not only the professional knowledge and skills, but also the principles of social equity and humanism, engaging them in social and volunteer activities to benefit all sectors of society. Benos (2010) confirmed that human capital accumulation has been identified as a fundamental source of long-run growth and income inequality in modern economies. In some countries there is a significant public intervention in education, while in others there is extensive private financing of the education sector (e.g. United States). N. Benos comes to conclusion that welfare was the highest under following conditions: education-inclined altruism is strong; human capital sensitivity is low; human capital elasticity with regard to private and public education expenditures is either very low or very high and intergenerational human capital linkages are strong. Czarnecki (2014) considers that welfare policy is organized in accordance with certain principles according to which social services are provided. Mostly important these principles determine to what extent the market, state and family are held responsible for satisfying social needs. K. Czarnecki examined the relationship of different national approaches to higher education participation and funding with welfare regimes. The strong relationship with a given welfare regime (social-democratic, liberal or conservative) has been confirmed. At the same time one cannot identify the existence of a distinct “post-communist” welfare regime. The importance of education in the formation of personal potential is enshrined in the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”. Introducing the a process of upbringing and training of public benefits, created in interests both individuals and the nation as a whole, the law defines the main purpose of education as intellectual, moral and spiritual, creative, physical, and professional development of the person (Federal law, 2012). Thus, the education is designed to develop human, not only as a person but also as a citizen of their country and future employee. According to the long-term forecast of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030, one of the most important guidance should be increasing accessibility and quality of education; number of students enrolled in the process should four times increase by 2030 at the leading universities of the country - from 5% to 20 % (Forecast, 2015). One of the conditions of accessibility of higher education is a sufficient number of educational institutions offering training. Table
Kochkina & Molokova (2016) point out the intensity and chaos of institutional reforms in the Russian system of higher education in the transformation period and come to the conclusion that: -rejection of the planned system in the period from 1990 to 2008 led to the emergence of excess number of universities, the emergence of commercial education, accessibility of higher education by those who wish to reduce the quality of educational services; -unwillingness and inability of the emerging market economy of Russia to form an order in higher education system on demanded training resulted in misbalance of humanitarian and engineering professions. Some reduction in number of universities that has occurred over the past five years (Table
The application of SERVQUAL method
In the framework of this article SERVQUAL method was focused on offered by V. Zeytaml, L. Berry and A. Parasuraman in 1985. Alongside such advantages as simplicity, clarity of presentation of the results, a clear definition of those areas in which you need to improve performance, this method has disadvantages– lack of comparison values (or at least as a threshold in the monitoring of the Ministry) and some confusion for respondents (Fadeeva, 2012). The method allows evaluating the difference in expectations of future students and the real perception of the quality of educational services provided, taking into account the degree of importance of each criterion for consumers. Students were asked to complete a questionnaire using 5 point “Likert scale” where is 1- strongly disagree, but 5 - completely agree. The survey questions were developed by the authors in accordance with the five basic parameters of service quality:
Tangibility of (material elements): material technical and information equipment of the university,
Reliability: implementation of the promises given to the consumer,
Responsiveness of staff: professionalism and discipline of teaching staff,
Staff competence: courtesy and tactfulness of staff, high standard of knowledge, confidence and attentiveness to students,
Empathy (sympathy): an individual approach, understanding of students’ needs, taking care of them.
The criterion “tangibility” is represented by four questions, the criterion “reliability” - five questions, the criterion “responsiveness of staff” - four issues, “staff competence” - four questions, “empathy” - five questions. Students responded for three parts of the questionnaire. The first part of the questionnaire records the expectations of consumers regarding five groups of proposed criteria. Students were asked to express their expectations about the best educational institutions by 22 positions, distributed according to five criteria described above. The second part by the same scale records the perception of the quality of educational services by students of the Ural state university of economics and assumes their assessment of its compliance with the expectations by the same 22 items. The third part of the questionnaire records the importance of the following criteria in assessing the quality of educational services. Students expressed an opinion about how each of the proposed 22 sub-criteria is important to them in assessing the quality of educational services. Survey results were processed by calculating the average rating on all three parts of the questionnaire. Following ratings were calculated: consumer expectations, consumer perception of the quality and importance of each criterion. The digital expression of the quality status for each criterion is the quality factor Q. Quality factor Q is calculated as the difference of perception and expectations of ratings for each of the 22 sub- criteria.
(1)
Where
- a quality factor to
For the analysis and graphical presentation of the results of marketing research of the quality of education method of analysis “importance-execution” was used , which analyzed the results of the study in two-dimensional form using two axes: the y axis-R “rating of importance” and the axis x-Q “coefficient of quality”. It should be noted that for the measurement of satisfaction with the quality of educational services is insufficient application of a technique considered. It is useful to supplement the modification SERVQUAL evaluation of perceived value and other indicators of customer satisfaction. Additional indicators proposed by, in particular, Lamben (2014) include: overall assessment of satisfaction and future intentions of consumers, such as the willingness to recommend the service to friends and intention to refuse the services of the company.
The results of marketing research
Based on the 22 coefficients of average quality coefficients, five quality coefficients are calculated for each of the five criteria and a global quality factor (Table
Satisfactory results are considered to be quality factors maximally approached to zero value. All five quality coefficients obtained as a result of research on five criteria and a global quality factor are close to zero, but have negative value. The results obtained are that students' expectations of quality training performance are slightly higher than their actual perception of the university. It is worth highlighting the criterion “staff competence” as the most important for respondents when evaluating the quality of educational services organizations, it received the lowest score, and quality factor has the greatest deviation from zero value. Results of research in a three-dimensional shape using two axes: the axis y - R “rating of importance” and the axis x - Q “quality factors” are shown in Fig.
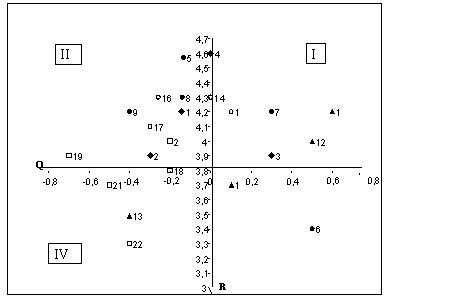
Rating factors / Quality criteria:
♦ - Tangibility (material elements)
simplicity and convenience of obtaining of the necessary information
a pleasant interior of corridors and classrooms (color scheme, lighting)
teachers appearance should comply with their activities
availability of modern classrooms, equipped with modern facilities
- Reliability:
assistance to graduates ‘ employment,
organization of healthy food at affordable prices
presence an environment of interesting student life (competitions, construction brigades, trainings)
graduates demand in the labor market
availability and provision of dormitories to nonresident students
▲ - Reactivity of staff:
classes are conducted in a timely manner, on schedule, on time
quality of classroom depends on the availability of a scientific degree of teachers (PhD, Dr.)
involvement in conducting of classroom teachers - practitioners (working at specific enterprises)
interaction of teachers with students on teaching issues and outside classrooms (portal, e-mail)
□ – Staff competence:
high level of knowledge of the theory and practice of taught material
teachers should create conditions motivating the students to study
teachers should conduct their classes lively
courtesy and goodwill in relation to the students by teachers of the university
□ – Empathy:
student voice is significant at the university and his opinion is always heard
the willingness of teachers to spend consultations for students
teachers provide students with tasks of different levels of complexity
availability of organization at the university which would help the students to protect their rights
teachers adhere to the individual approach to a student
Minimum and maximum values of “importance” and “quality factor” are displayed according to the marketing research. Criteria that fall into the first quadrant are positive and characterized by high level of importance and high quality assessment. This means that the high expectations of students according to criteria are fully justified and coincided with the level quality of services provided by the educational institution. As regards the quality of these parameters it is necessary to adhere to supporting action: regular monitoring in order to prevent loss of quality. So, students evaluate the quality of teaching highly enough as a guest practitioners and teachers of the educational organization. The level of confidence is higher if a scientific degree the teacher has. In addition, the expectations of students regarding student life are fully meet. It can be concluded that in the Ural state economic university the basic conditions for human well-being of each student are created. Criteria that fall in the third and fourth quadrants are not particularly important for consumers who participated in the survey. At the same time, they characterize the quality of educational services organizations. It is necessary to do additional research, involving more than a representative sample in order to determine exactly the importance of these criteria. The study revealed the most problematic parameters characterizing the quality of educational services - criteria that fall in quadrant II. It is important for students’ characteristics that do not meet their expectations. They require immediate action by the educational organization, so consider them in more detail: Criteria relating to "empathy" parameter”: research results showed that students expect from teachers a greater willingness to provide advice. At the same time, research has shown that opportunity to communicate with teachers via the Internet, e-mail, and social networking is regarded by students as a criterion of little importance. From this, we can conclude that the increased use of the opportunities offered by the virtual Internet environment for the younger generation, in matters of communication with teachers and students is still conservative and needs face-to-face contact. Results of the research showed that students expect individual approach to the opportunities in compiling tasks of different difficulty levels to test knowledge. Undoubtedly, the features and capabilities of each individual are the basic conditions for development of human well-being. Therefore, teachers of the educational organization should perform it creating jobs for the practical work. Criteria characterizing the “competence of the personnel”: students expect more interesting activities, as well as a friendly and courteous attitude of teachers. In a complex of marketing services the staff played the most significant role: in addition to the high professionalism, he has to be open in communication with consumers. In educational institutions such behaviour is a necessary condition which will enable students to feel confident and free and thus reveal their personal abilities. Material elements of quality of educational services: many students do not like the interior of an educational organization, as well as difficulty in obtaining information related to the educational process. Due to the complex structure of educational organization, as well as the information richness of the learning process, indeed, such a problem is possible. It is necessary to make structure of information for students, to minimize its duplication, the use of various means of its dissemination. Criteria “reliability”: during research deceived expectations of students were identified regarding the promise to provide hostel to all non-resident, which undoubtedly, can lead to the formation of a negative image of educational organization not fulfilling its promises. Considering the fact that a high percentage of applicants come from the Sverdlovsk region and there is a need of a hostel, this situation requires more in-depth research and solutions. The showed results are example that the students are not assured of the future: doubt in employability, future employment. Thus students expect from an educational organization more active facilitation measures in employment. This is, perhaps, one of the most disturbing findings. Educational organizations have a serious mission - to increment each individual as future highly skilled workers by means of disclosure of his creative and intellectual potential. Doubts about future of employment among students indicate that they know little about the career success of graduates of the Ural state economic university. Thus the educational organization should be in the habit of meeting students and graduates, as well as to engage them and develop a system to facilitate the employment of university graduates.
Conclusion
Based on the results of marketing research we can conclude that SERVQUAL method made it possible to identify and focus on the most important quality characteristics of educational services. The lowest score among the parameters of quality of education students “stuff competence” was received ,which was alarming and indirect evidence that the prestige of the university teaching profession is reduced, which can be attributed to chronic underfunding of higher education, insufficient attention to the advanced training of academic and teaching staff. Eventually it can adversely affect the quality of the labor force and the rate of economic development of Russia over the long term. Market research has allowed determining in what areas should be directed the limited resources of the university to enhance its effectiveness and competitiveness, as well as the value of social institution. The expectations of students regarding student life diversity and conditions for the development of their social and creative potential were fully meet. It can be concluded that in the Ural state economic university the whole educational process and learning activities of students were organized so as to allow training future employers in the context of the paradigm of education based on human well-being.
References
- Benos, N. (2010). Education policy, growth and welfare. Economic education, 18 (1), 33–47.
- Czarnecki, K. (2014). The higher education policy of “post-communist” countries in the context of welfare regimes. Poznań University of Economics Review, 14(2), 43-62. (in Polish)
- Fadeeva, N.V. (2012). Methodology for assessing the quality of services .Vestnik of ТGТU, 2( 8), 484-491. (in Russian)
- Federal Law of December. (2012). № 273-FZ. On Education in the Russian Federation, 2 (1), 2. (in Russian)
- Gaidukova, G.N. (2013). Sociological monitoring consumer satisfaction with the quality of educational services. Modern problems of science and education, 1, 463-470. (in Russian)
- Ketova, N.P. (2014). Educational services Russian universities: the trend of development, quality management principles, evaluation, ways of improving . Vestnik of Adygeya State University, 4(151), 219-227. (in Russian)
- Kochkina, E.M., & Molokova E.L. (2016). Retrospective evaluation of the intensity of the dynamic changes of the national higher education system. Upravlenez, 1, 59. (in Russian)
- Lamben, J.J. (2004). Management, market-oriented. Strategic and Operational Marketing.
- Long-term forecast of the Russian Federation of socio-economic development for the period up to 2030. (2015, April 15). Retrieved from http://economy.gov.ru/minec/activity/sections/macro/prognoz/doc2013032
- Nabokov, V.I., & Kravtsova, O.A. (2015). Marketing approach to quality management of the university educational services. Agricultural Magazine of Urals, 7(137), 86-90. (in Russian)
- The data of Federal Service of State Statistics. (2015, March 23). Retrieved from http://www.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat_main/rosstat/ru/statistics/population/education
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 January 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-018-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
19
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-776
Subjects
Social welfare, social services, personal health, public health
Cite this article as:
Kapustina, . M., Jadko, E. A., Izakova, N. B., & Yakimenko, E. V. (2017). Market Research of Education’s Quality in the University as indicator of Human Well-being. In F. Casati, G. А. Barysheva, & W. Krieger (Eds.), Lifelong Wellbeing in the World - WELLSO 2016, vol 19. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 714-721). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.01.94

