Abstract
The expansion of the social work field in Kazakhstan led to the emergence of the social pedagogues profession. New technologies have become social-therapeutic technologies and social activities. Purpose of the Study:is to develop design principles of social and therapeutic technologies and teaching methods, the comparison of the use of technology and social-therapeutic work of social workers and university teachers. Research Methods: is a survey of practicing social pedagogues, as well as university teachers who teach the future social pedagogues. Analysis, generalization of approaches to social therapy, simulation technologies, comparison and search work. Findings: According to the results of questionnaires and self-evaluation of teachers, 30% of social pedagogues and 70% of university teachers, training future social workers use social and therapeutic work technology. Teachers often use art-therapy techniques (75% of teachers and 80% of social pedagogues). 40% of social pedagogues use art therapy mainly for stress relief in children, 23% for the aggression removal. Conclusions: A theoretical model of the technology design of social-therapeutic activity of the social pedagogues has been elaborated. The research work on the study of the social experience of practicing teachers has been carried out. The method of learning social-therapeutic technologies which was tested in the educational process of the university has been worked out.
Keywords: Social WorkersSocial PedagoguesSocial-TherapeuticTechnologies
1.Introduction
universities started in 2010. The development of modern society and socio-pedagogical practice enhances
tools of modern social pedagogues. The existing problems of social adaptation and socialization of
students, the interaction processes tension creates the conditions for the actualization of therapeutic
techniques for working with students.
2.Problem Statement
The expansion of the social work field in Kazakhstan led to the emergence of the social
pedagogues profession. New technologies have become social-therapeutic technologies and social
activities.
3.Research Questions
How active practicing social pedagogues use social-therapeutic technologies in their professional
activities? What is the technique of training future social pedagogues to social-therapeutic work?
4.Purpose of the Study
Is to develop design principles of social and therapeutic technologies and teaching methods, the
comparison of the use of technology and social-therapeutic work of social workers and university
teachers.
5.Research Methods
- Is a survey of practicing social pedagogues, as well as university teachers who teach the future
social pedagogues. Analysis, generalization of approaches to social therapy, simulation technologies,
comparison and search work.
The role of the social teacher as a social therapist includes "the assistance of the person in contact
with the relevant experts, aid in the conflict resolution (Ovcharova R.V., 2001). Psychotherapeutic
function of the social teacher according to T.A Shishkovets comprises:
- Child care for mental equilibrium;
- The establishment of a trusting relationship with the child, a teenager, an adult;
- Assist in resolving interpersonal conflicts, removing the doldrums;
- Assist in changing the relationship of the child, teenager, adult to life, to the environment, to himself;
- The organization of the child, the adult "success situations " (Shishkovets T.A., 2005; Basov N.F.,
2007).
37
It is important to teach future social teachers to new technologies, including social and therapeutic
work. To do this, we will develop design principles of social and therapeutic technologies, compare how
social pedagogues and teachers of the university use technology of socio-therapeutic work in training
future social pedagogues and also work out technology of socio-therapeutic work with pupils. It became
the purpose of our study. Let's start with a concept definition.
6.Concept definition
The technology and social-therapeutic work concept may have several options of formations:
1) Technology → pedagogical technology→ socio-pedagogical technology + social therapy =
socio-therapeutic work technology;
2) (Social Therapy + (technology → pedagogical technology)) + socio-educational activity ═
socio-pedagogical work technology.
The "social-therapeutic work technology " concept is a pedagogical category, because its
construction is based on the concepts of "pedagogical technology" and "social and educational activity".
That is, a priori, we start from the educational component of human activity.
Having studied the "educational technology", "social -pedagogical activity", "social therapy"
concepts we have defined the concept of "socio-therapeutic work technology" as "a set of organization
procedures and implementation of social therapy in the socio-educational activities." The very
of socialization, the development of their socio-cultural experience and to create conditions for self-
realization in society.
Activating the use of the term "therapy" in psychology and sociology connected with the direction
of society humanization, the emergence of the humanistic psychology and humanistic education areas.
Translated from the Greek word "therapy" literally means "care, treatment." Social therapy is a set of
decisions, procedures, measures and actions aimed at solving social problems of various levels of
organization (N.F. Basov, 2007).
7.Three theories as a basis for the social and therapeutic work technology
design
Theoretical basics of socio-therapeutic work technologies design are the following theories:
- "Pedagogical accompaniment" (G. Bardier, I. Romazan, T. Cherednikova, V.V. Kashelev, R.J.
Zhumazhanova);
- "Pedagogical support" (G.V. Kornetov), facilitation (Carl Rogers, R.S. Dimuhametov, Sh.U.
Tasbulatov, V.T. Tikhomirova);
- "Helping relationships" (O.S Gazman, G.M.Kodzhaspirova, V.V. Shahgulari).
38
These concepts are considered as three interrelated models of psychologist and social teacher work
in educational institutions and referred to as a " psychological and pedagogical support model", "support
model" and the "model of care" in studies of V.G. Maralova, T.P. Maralova, V.V. Khromov (2001).
All three models belong to the humanist pedagogy, environmental approach; Existentialism is a
philosophical base. Let us consider them briefly in succession.
The term "psycho-pedagogical support" of pupils means a system of professional activity of the
educational process (teachers, psychologists) aimed at creating a social, psychological and pedagogical
conditions for successful learning and personal development of children, improve the pedagogical skill of
the teacher, the formation of interpersonal relations. It is important to have educational and psychological
competent interaction with students having competent modern scientific bases.
O.S. Gazman determined the "pedagogical support" direction as a pedagogy of freedom, which
aims to develop tools for the formation of freedom able personality (O.S. Gazman, 1998). The concept
emanating from the recognition that, for any human characteristic expectation of support or willingness to
provide it, entails a change in teacher position. G.M. Kodzhaspirova (2004), pedagogical support is
regarded as a system of pedagogical activity which reflects the human personality potential, including
assistance in overcoming social, psychological, personal difficulties. The process with the child to
determine its own interests, goals, possibilities and ways of overcoming obstacles to save his own dignity
and achieve the desired results in education, self-education, communication, lifestyle.
The word
Introduced by C. Rogers. Educational facilitation is a kind of
the child is aware of its intrinsic value, the desire is supported for
cooperation. He involves students in the work, creates a work environment where learners feel
comfortable (physically and mentally), provides assistance and support; centers on the objectives of
training and education; promotes dialogue (G.M. Kodzhaspirova, 2004). The word "facilitation" is
derived from the English verb to facilitate, assist, promote. It was introduced by Rogers. Educational
facilitation is a kind of educational activity in the process of which, the child is aware of its intrinsic
value, supported by the desire for self-development, self-actualization, self-improvement, the disclosure
of abilities. Facilitator is a specialist, who escorts group processes, training cooperation. He involves
students in the work, creates a work environment in which learners feel comfortable (physically and
mentally); He provides assistance and support; centers on the objectives of training and education;
promotes dialogue (G.M. Kodzhaspirova, 2004).
"Helping relationship” pedagogy is seen in the works of Kazakhstani scientist V.V. Shahgulari
(2007). He proceeds from K. Roger’s thesis that "helping relationship" is a "relationship, in which at least
one of the parties intends assist the other side in personal growth, development, the best of life, the
development of maturity, the ability to get along with others", relations characterized by "honesty and
transparency of ones true feelings, the warm acceptance and appreciation of the other person as an
individual." V. Shahgulari in his work "The essence and content of " helping relationship " pedagogy
compares the С.Roger’s helping relationship and Gestalt approach and finds in them both common and
distinctive features. He said that one of the common features, "allowing the client to determine the value
39
of his experience and through this to be able to answer for himself, and the same perception of the client's
life as his as a basis for future changes." The differences, according to V.Shahgulari, "concerns the
relationship to the phenomenon of empathy." In Roger’s approach empathic understanding leads to the
mutual satisfaction of the therapist and the client, and in the Gestalt approach, empathy in its extreme
form is viewed more as an obstacle to the true contact " (V.V. Shahgulari, 2007).
Also, the author dwells on the fact that Gestalt pedagogy (and Gestalt approach) has no concept of
a helping relationship, there is the concept of Gestalt therapeutic action and reflection, that the learning
process is focused, in particular, on authority respect, competence in relationships and work with
proximity and distance, sympathy and antipathy in them.
Based on the models, these theories suggest the following principles for the design of social and
therapeutic work of social educator:
1) The principle of creating a favorable pedagogical, social and therapeutic environment
2) -The principle of creation and development of student creativity;
3)-The principle of facilitation;
4)- The principle of positive thinking and ensure a positive development of the environment;
5)- Student-centered approach
8.Findings
8.1 Results
social therapy, psycho-pedagogical, correctional help to the individual in order to protect his mental,
physical and moral health and it deals with the prevention and overcoming negative phenomena.
We design
pedagogue:
- Diagnostic phase it is diagnosis of personality problems, the determination of the need for
therapeutic intervention, identification of social worker criteria and indicators of the results of social and
therapeutic activities;
- Direct socio-pedagogical therapy is setting a goal of therapeutic activity, the use of social and
pedagogical treatment methods, training work;
- Development of positive thinking and creativity as a consolidation of therapy phase, positive
results;
- Evaluation and self-evaluation of the results of socio-pedagogical treatment of the individual.
It is necessary to have knowledge and master methods of therapy in order to design and implement
social and therapeutic work technology.
After studying the theory and methods of therapy, we have developed a theoretical model of the
design technology of social and therapeutic work (see Figure
40
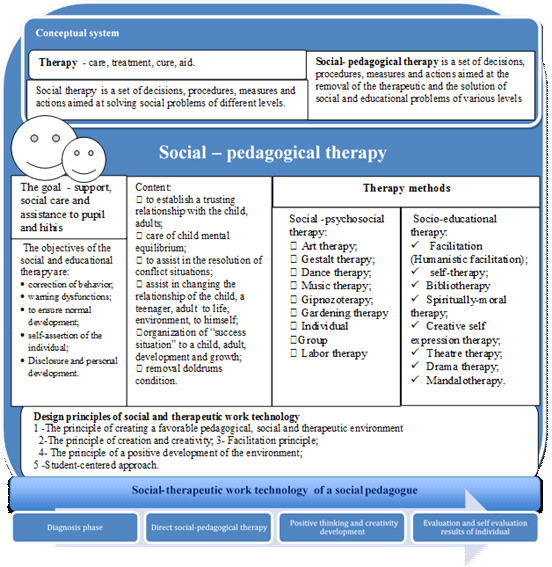
It contains conceptual apparatus, principles, methods, technology itself. On this basis a training
course for teaching techniques of social and therapeutic work will be developed. Next, we’ll consider
how social workers and university teachers actively use the social and therapeutic technologies in practic.
8.2Discussion
We have selected a group of respondent specialists from practical social workers of Almaty as
experts and university professors in accordance with the objectives of the study. University teachers
conduct psychological and pedagogical subjects at the university, including the specialties "Pedagogy
and Psychology", "Social pedagogy and self-knowledge." 51 people took part in the survey, including 2
men and 49 women, 30 school social workers, 21 teachers of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University .
Teachers responded that 70% of university teachers, 30% of practical social workers use the above
mentioned technology, when asked about the use of technologies of social and therapeutic work.
Teachers basically answered to the question "How do you understand a technology of socio-
therapeutic work at school?" They said that this technology means the removal of the depressed
41
state (university teachers 30%, social workers 35%), to assist in conflict resolution (university
professors 30%, social workers 40%), concern about the child's mental balance (40% of high school
teachers, social workers 25%).
The results of answers to the question "Which of the following areas of treatment as a social
teacher you use in your work?". Basically, teachers use art therapeutic techniques (75% teachers,
80% - social teachers); play therapy (15% teachers, 10% of practicing social teachers); Fairy tale
therapy (5% of the teachers, 7% of practicing social teachers);art therapy (3% of teachers and 3%
practicing social teachers); mandalo therapy (2% of high school teachers).
Conflicting results in the answers to questions of social and therapeutic work technologies
application (general question) and detailed responses (selection response on therapy type) used
therapies, in our opinion, due to the fact that teachers did not recognize the term "technology and
social - therapeutic work " specific methods at the start of the questionnaire.
However, the choice of answers to clarifying questions, detailed answer enabled us to
identify the most used therapies by the facilitation teachers. This allows, on the one hand, to refine
the results and to see the readiness of teachers to use the new social and therapeutic technologies. On
the other hand, such a result, in our opinion, firstly, shows the lack of knowledge in an explicit form
for this type of activity at 30% of high school teachers and 70% of practicing social teachers.
Secondly, based on this, yet it demonstrates below average degree of activity of the application of
therapeutic techniques. Because if the teacher does not think about the purpose of their use, he does
not track the effectiveness of their application and, accordingly, technology management is actually
dispersed.
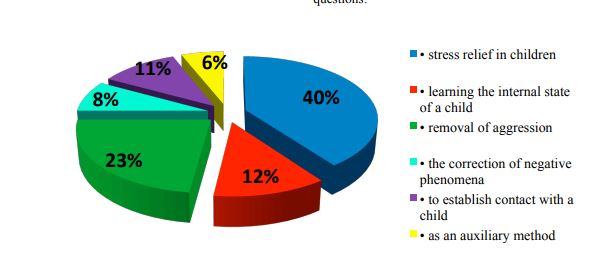
80% of the interviewed social teachers practice art therapy method to solve the following
problems: stress relief in children (40%); learning the internal state of a child (12%); removal of
aggression (23%); the correction of negative phenomena (8%); to establish contact with a child (11%); as
an auxiliary method (6%) (Figure
80% of social pedagogues use art therapy method to solve the following
children, on their inclusion in the positive social relationships, to develop the habit of self-control,
discipline, organization, culture, communication, self-control. Inclusion in the joint exercise of art,
based on the interest and attention to each other, allows children to be "liberated", to acquire the
skills companionship.
9.Conclusion
9.1 Teaching students to social and therapeutic work technology
We have developed as part of our study methods of teaching the use of technology and social-
therapeutic work. It includes the steps of: diagnostic, training, evaluation.
On the first stage the diagnosis of creative abilities of students of a specialty "Social pedagogy
and self-knowledge" was held. We supposed, if social teachers have a high level of creativity, they
will be able to apply successfully art therapeutic techniques in their professional activities. This is
especially true for art therapy methods. Therefore, on the first phase of the training introduction we
offered to future social teachers to check their level of creative development potential and
creativity. Also, this step contributes to the actualization of knowledge and creative qualities of
future teachers.
program is as follows: a lecture-training sessions 1 "Impact of art therapy on the psycho-emotional state
of students' - 2 hours; lecture-training sessions 2 "Technologies of socio-therapeutic work of a social
teacher" 2 hours; lecture-training sessions 3, "Creating a positive mindset," 3hours. Totally 7 hours.
Training objective: to acquaint students with the technology of social and therapeutic work.
therapeutic work (20 questions). The technique has been tested in the classroom for "Deviancy" specialty
5B012300 - Social pedagogy and self-knowledge. Students showed positive results. According to the
self-esteem of students, they were satisfied with the training, learnt about the art therapy concept, social
therapy technologies. According to the results of the survey 100% of the students want to go through a
deeper course on socio-educational therapy, art therapy techniques.
9.2Conclusion
Modern pedagogical practice requires the introduction of new methods and technologies of social
and educational work of social teachers. Development and widespread use of new educational
technologies and a scientific basis is necessary. Technologies specifics is the complexity of its
construction, as opposed to using the methods with research and reflexive component of the social
teacher work, maintenance of the technology structure (procedure enforcement) for its productive
use. Socio-therapeutic work technology is a new kind of social and pedagogical technologies. They
are based on the principles of humanistic and person-centered pedagogy
43
References
- Basov N, F. (2007). Social teacher: introduction to the, Academy. , profession. Moscow
- (), P.28.
- Dimuhametov R, S. (2005). Update scientific bases of teacher training: the principle of.
- (), facilitation. Almaty, RIPI SO press. P. 115.
- Gazman O, S. (1998). Education and educational support for children. National education. #6
- Kodzhaspirova G, M. (2004). Pedagogy: Textbook for students of educational establishments.
- (), vocational education. Moscow, Vlados press. P. 320.
- Maralova V, G.Maralova TP& Khromova V, V. (2001). Psychodidactic principles of.
- (), training. Education and science in Cherepovets: History-experience-perspective. Vologda. P. 10-11.
- Mynbayeva A& Seilkhanova , M. (2013). Technologies for social-therapeutic work: pedagogical.
- (), designing and use in practice. KazNU Bulletin "Pedagogical science" series. V.39(2).
- Ovcharova, R. V. (2001). Reference book of the social, P.34. , teacher. Moscow
- Rogers, C. (2012). On becoming a person: A therapist's view of psychotherapy. Houghton Mifflin
- (), Harcourt.
- Shahgulari V, V. (2008). The essence and content of "helping relationship". , pedagogy. KazNU
- (), Bulletin "Pedagogical science" series. #2. P.154-160
- Shishkovets T, A. (2005). Directory of the social P.25. , teacher. Moscow
- (), Social technologies: Explanatory dictionary Moscow. P. 277.
- (), 44
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
27 January 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-019-8
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
20
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-283
Subjects
Child psychology, developmental psychology, occupational psychology, industrial psychology, ethical issues
Cite this article as:
Mynbayeva, ., Seilkhanova, M., & Akshalova, B. (2017). Social-Therapeutic Technologies In Professional Work Of Social Pedagogues. In Z. Bekirogullari, M. Y. Minas, & R. X. Thambusamy (Eds.), Cognitive - Social, and Behavioural Sciences - icCSBs 2017, January, vol 20. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 36-44). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.01.02.5

