The Impact of the Training Programmes Over the Teacher`s Performance and Professionalism in the Pre-University Education
Abstract
The human resources competitiveness from the pre-university education represents a strategic priority of the Ministry of the National Education and Scientific Researches for Romania in 2016. The favourable background provided by the training schemes/programmes developed by the Sectorial Operational Programme in the Human Resources Domain allowed a numerous attendance of teachers at training courses, which had an impact over the improvement of the educational system and an increasing of its adaptability to the labour market requirements, promoting lifelong learning and acquiring competences for personal and professional development. This research presents the most important results referring to the impact of the training programmes, developed for the last five years in the South Muntenia Region, targeting the teachers’ performance and professionalism. The figures were obtained by questionnaires applied to a number of teachers from the pre-university education system of South Muntenia Region. These teachers develop their activity in theoretical, technological and vocational high schools. These figures provided a general overview of the today’s training system of teachers (suppliers, duration, costs, certificates, organisation, and strengths, improving aspects) and also details referring to motivation, the quality of the training programmes, facilities, their impact over the teaching process, future training needs, needs adapted to the specialised culture, methodic and pedagogic activity.
Keywords: Training programmespre-university educationteaching careerprofessionalismlifelong learning
Introduction
Both at European level and nationwide, one may note the importance attached to professional
development of teaching staff in post-secondary education. The strategic priorities of the National
Ministry of Education and Scientific Research in Romania and the sectoral action plans for 2016
regarding development of teaching career have as strategic initiative “Launching a Strategic Project
Using European Funds with a view to Making Teaching/Education and Ongoing Professional
Development Master Operational”.
The improvement programs for teaching staff in post-secondary schools are oriented on developing
new skills to enable adaptation to educational needs, curriculum and requirements on the job market. In
the past five years the post-secondary school teaching staff have benefited by a large range of
professional development programs both in their specialization and in psycho-pedagogy and methods-
related training.
Materials and Methods
The endeavour to investigate the impact of professional development programs in South Muntenia
Region combines both quantitative and qualitative research methods. In terms of methods and
techniques used to collect information, documentary analysis has been made of legislative regulations
regarding post-secondary school teaching staff training, statistical analyses of INSSE, ongoing
professional development methodology for post-secondary school staff, priorities of the Ministry of
Education and the sectoral action plans for 2016, press file of the Ministry of Education on the high
school leaving examination results over the past five years. The hypotheses which provided the basis of
the questionnaire regarding the analysis of the impact of teaching staff development in South Muntenia
Region on the growth of performance and the professionalization of teaching careers are related to the
fact that the professional development programs are partially adapted to the teaching staff’s needs
whereas the improvement system is sometimes deficient as regards strategies, methods and
organization.
Results
The programs and activities in the field of the development of scientific, psycho-pedagogical and
didactic training are permanently adapted to the dynamics of the educational processes and systems.
Both South Muntenia Region and other regions in Romania have seen a real enhancement of the
quality of education following multiple professional development programs implemented in the past
five years.
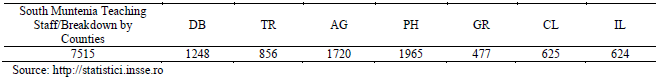
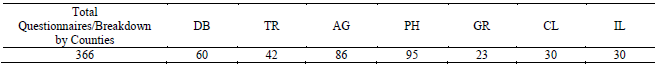
The post-secondary school teaching staff sample in South Muntenia Region selected with a view to
conducting the questionnnaire survery consists of a number of 366 teachers out of 7515 in total. This
was established on the basis of a representative sample at county level, comprising the seven counties
in the region, as shown in Table
3.2.Sample Breakdown
The sample breakdown by age criterion shows similarities with the seniority criterion and is similar
to the breakdown by age groups in the total of teaching staff for the region, as indicated in Table
In this sample a higher weight is covered by the teaching staff in the urban areas that carry out their
activities in vocational schools and high schools; most of these educational establishments are situated
in cities, as shown in Table
Most teaching staff selected for this survey (over 89%) have reached a high level of professional
training (first level teacher certification – 60.3% and second level teacher certification - 23.5%, PhD
5.6%).
In the selection of teaching staff by county, account has been taken of the curricular area and the
number of high schools, vocational schools and post-secondary technological schools in the area was
kept in balance, as shown in Table 5.

Discussion
At European level teaching staff’s professional development is different from country to country.
France, Holland, Sweden, Island consider that teaching staff development is a
Poland, Luxemburg teaching staff development is closely related to career evolution and financial motivation. The credits obtained are taken into consideration upon career advancement. In Romania,
teaching staff and management, supervision and auditing staff in post-secondary schools attend
professional development programs every five years. Such programs ensure them a minimum of 90
transferable professional credits every five years (Methodology of ongoing training of teaching staff in
post-secondary schools, 2009). Table 6 shows the teaching staff’s reasons relating to their ongoing
professional development.
According to the Education Law the teaching staff’s professional development is a right of the
teachers. Starting from the professional development-related activities set forth in the legislation the
respondents have ticked various choices regarding forms of conducting such development activities, as
shown in Table 7.
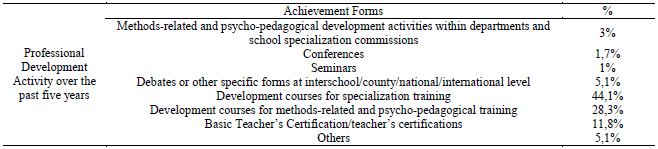
Participation of teaching staff interviewed to professional development programs was completed in
different manners, as indicated in Table 8.

We can summarize the Muntenia South teaching staff’s participation to specialization programs over
the past five years as prioritized for mathematics, economics, history, geography, Romanian language,
physics, chemistry, biology, teacher’s certifications, master’s degrees. As for methods-related and
psycho-pedagogical development, teaching staff have chosen courses for specialization didactics and
basic discipline methods, mentoring, curricular qualification, assessment. The desire to develop in
terms of educational management has boosted the participation to courses which enable the access to
management, supervision and auditing positions, implementation of educational policy measures at
organizational level. For South Muntenia development of IT skills outlines an evolution from initiation
to the domain to use of educational platform in the didactic undertaking.
A gratifying element is the number of professional development programs presented in Table 9 to
which respondents have participated over the past five years.
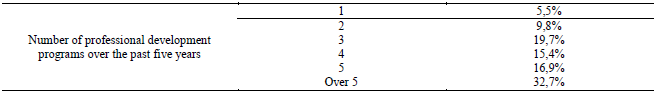
We may notice the teaching staff’s interest in professional development; the high attendance to such
activities which mainly have an impact on the evolution and the adaptability to newness.
With regards to training providers, most of them belong to the public sector; however, the private
providers have a rather high weight, probably due to the attractive offer which constitutes a genuine
interest for the teaching staff.

In case of respondents, the choice of a professional development program has been influenced as
shown in Table
The credits system is appreciated by the teachers interviewed, however the decision to choose a
professional development program is influenced by the trainer, duration and facilities offered upon
courses completion.
The aspects requiring improvements in relation to professional development programs to which
teaching staff have taken part refer to training program/timetable/duration, themes approached and
degree of newness, adaptability to target group, costs, bureaucracy in filling documents, practical
applicability, logistics, certificate issuance, selection of trainers, sustainability, seminar materials,
modern methods adapted for children with special educational needs.
For the following years teaching staff interviewed target professional development courses focused
on: specialization development, linguistic refinement in an international language, ICT, assessment,
inter/transdisciplinarity, specialist research, counselling, educational management, integration of
children with special educational needs, modern teaching/assessment methods. The impact of the professional development programs conducted over the past 5 years in South
Muntenia region is explained in Table
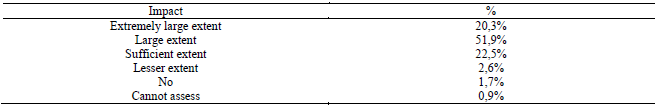
The changes in the teaching career as a result of the professional development programs completion
are presented below:
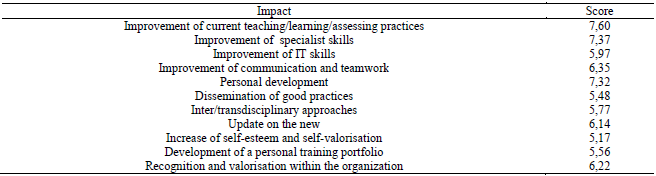
The score obtained indicates an improvement of key competences, a learning development, an
acquisition of expertise and an adaptation to what is new in the specialist’s domain.
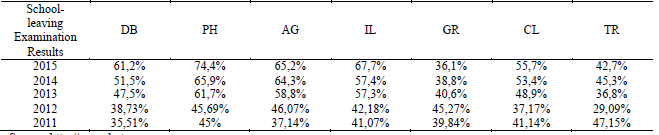
As a consequence of the professional development programs for the post-secondary schools in
South Muntenia Region, the quality of the teaching act has seen actual improvements and the results
have been visible in the performances of the pupils in the school-leaving examination, except Giurgiu
and Teleorman counties.
Conclusions
With regards to professional development programs and their impact on teaching careers one may
observe the need for a development of training providers market so that there is a productive
competition in their offers. At local level the Teaching Staff House (CCD) is the most important
training provider; however, the quality of the courses does not always stand up to expectations. The
universities should meet the needs of post-secondary teachers halfway especially through development
programs in specialization and research. Private providers offer mainly non-disciplinary internships, short-term qualifications requested as
part of some projects/programs financed by European funds and the costs are generally high compared
to the quality of the programs.
The teaching staff’s motivation to participate to professional development programs is triggered by
their desire to personally develop, to be in line with what is new and to be competitive in their
profession. The borderline between motivations concerning professional sphere and those concerning
personal sphere is difficult to distinguish, development of specialist competences as well as key or
transversal competences constitutes an active side of lifelong learning program. The quick and
profound transformations occurred in the learning process over the past years impose ongoing
development of teaching staff, their adaptation to new and change of one side and needs of the job
market of the other side.
The participation of teaching staff in South Muntenia Region to professional development courses
reaches high values; the teachers attend not only obligatory development programs conducted through
the public sector but also attractive development courses offered by private providers. The intention to
professionally improve is closely followed by the desire to personally develop, the recognition of their
position within their own educational establishment, the integration into a modern and top-of-the-class
educational system.
Author Contributions
Constanța Popescu and Antoaneta Roxana (Georgescu) Surcel conceived and designed the research,
Constanța Popescu and Antoaneta Roxana (Georgescu) Surcel distribute the questionnaires, Constanța
Popescu and Antoaneta Roxana (Georgescu) Surcel analyzed the data, Constanța Popescu and
Antoaneta Roxana (Georgescu) Surcel wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
MENCS – Ministry of National Education and Scientific Research
CNDIPT – National Centre for Professional and Technical Education Development
ISE – Institute for Educational Sciences
CNCEIP – National Center for Curriculum and Assessment in Post-Secondary Schools Education
DPPD – Department of Teaching Staff Training
CCD - Teaching Staff House
ISJ – County School Inspectorate
ONG – Non-Governmental Organizations
DB, TR, GR, PH, AG, CL, IL – counties in South Muntenia Region – Dâmbovița, Teleorman, Giurgiu,
Prahova, Argeș, Călărași, Ialomița
CES- Special Education Needs
References
- *** (2008). CHAPTER 4: Continuing Professional Development – Requirements and Opportunities. In Levels of autonomy and responsibilities of Teachers in Europe, Eurydice, 2008, page 47.
- *** (2009). Methodology of ongoing training of teaching staff in post-secondary schools.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
04 October 2016
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-014-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
15
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1115
Subjects
Communication, communication studies, social interaction, moral purpose of education, social purpose of education
Cite this article as:
Popescu, C., & (Georgescu) Surcel, A. R. (2016). The Impact of the Training Programmes Over the Teacher`s Performance and Professionalism in the Pre-University Education. In A. Sandu, T. Ciulei, & A. Frunza (Eds.), Logos Universality Mentality Education Novelty, vol 15. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 784-791). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2016.09.99

