Abstract
Now in each preschool institution in CIS countries, and in Kazakhstan there are innovative pedagogical transformations connected with introduction of new programs and technologies. In 2007-2008 academic year Aktobe regional experiment named as "Technology of the Portfolio as a form of an assessment of pupils’ personal achievements in the preschool organizations" has been started. The purpose of research was investigation of expediency of application Portfolio technology in the preschool organizations. In total 90 pupils of the preschool organizations of education took part in experiment. The objects of research were children of preschool age (4-7 years). The main forms of diagnostics of personal changes of children is a supervision, conversation, a subject and role-playing game, the analysis of products of activity, questionnaires and psychological tests. During selection of diagnostic tasks we proceeded from the accounting of features of preschool age children. At the beginning of the conducted research consultation "experiment in the preschool organization» we investigated teachers’ level of readiness for novelty (according to V. I. Andreyev), and also provided theoretical education. Educational work with pupils’ parents for the purpose of formation of positive relation on experiment was organized in parallel. The pupil Portfolio consists of the following sections: the medical, for three years of work of experiment all postponed diseases of the child are fixed (chronic, catarrhal, etc.) frequency of child’s visit, physical and anthropological data, psychological, personal and cognitive development, the social and organizational work.
Keywords: Portfolio, Preschool organizations, Children, Education
Introduction
Now in each preschool institution as CIS countries and in Kazakhstan there are innovative transformations connected with introduction of new programs and technologies, obtaining the new status, search of effective models of the organization of the pedagogical process focused on identity.
Implementation of experimental activity promotes formation of participants research culture, i.e. comprehension and perception of the pedagogical facts, phenomena, processes, results, judgment of regularities, theories, and on this basis to a reconstruction of own system of innovative activity. These processes demand reorientation of teacher activity to the new values adequate to nature of experiment that, in turn, highlights one of the main problems increasing of professional competence – formation of research culture. In 2007-2008 academic year regional experiment on "Technology of the Portfolio as a form of an assessment of personal achievements of pupils in the preschool organizations" where the preschool organizations No. 2, 9, 10, 16, 19, 25 of Aktobe, Alginsky preschool of the Aktyubinsk area of the Republic of Kazakhstan entered began. The total number of participants was 90 children.
Problem Statement
In psychology and pedagogical literature questions of use of a portfolio at comprehensive school are actively discussed. Most often there is an idea about the Portfolio of the pupil or teacher (Ayukasova, 2008). On that idea the pedagogical technologies developed and introduced in an education system prevailing at the school level are accented. Often, considering age features of the early and preschool childhood, experimental work bears changeable character. The working group approved experimentally technology of the Portfolio for pupils of 3-6-year age, having transformed it under their psychological and age features. The analysis of psychology and pedagogical literature also doesn't contain the wide range of application of techniques and technologies in teaching and educational process except for a technique of M. Montessori recognized around the world. Advantage of application of this technique is that the Portfolio allows reflecting as much as possible early process of formation of the child as comprehensively developed personality coordinates and regulates her separate parties for successful socialization (Evgrafova, 2010).
Research Questions
Introduction of new forms of personal achievements estimation for preschool age children is supposed to be carried on the platform of organization previous, and also include professional experience of tutors and other perspective pedagogical technologies, innovative processes in education.
In experimental research we had to organize the following steps: - formation of the working group of teachers, definition of bases of researches, distribution of control and experimental groups, working off of mechanisms of completing and instructing;
- psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of all participants;
- the analysis of psychology and pedagogical literature on Portfolio’s technology, systematization of the obtained data, drawing up the maintenance of Portfolio for preschool age children;
- diagnostic and correctional work.
Purpose of the Study
Main objective of the made experiment is studying of expediency of application of technology of the Portfolio as forms of an assessment of personal achievements of pupils in the preschool organizations.
Research Methods
The main forms of diagnostics of personal changes of children – supervision, conversation, creative tasks, picture tests, the analysis of products of activity, poll. We used the indexed cards for diagnostics of the contents and methods of education and training in the main directions of educational process: development of game activity, speech development of the child, formation of elements of mathematical representations, acquaintance with children's fiction and world around, skills of designing and manual skills, familiarizing with the musical and fine arts.
Main directions of experiment: psycho diagnostics, psycho correction, professional consultation, support of the corresponding subject developing space in group, psychology and pedagogical education.
Findings
There are various approaches to definition of the concept "portfolio" (Novikova, 2006). Despite differences in understanding of concept, all researchers agree in opinion that the Portfolio, first of all, it’s a way of fixation, accumulation and an assessment of individual achievements for a certain period.
It’s main sense – "to show everything, on what you are capable". This technology helps to develop skills of reflexive and estimated activity, to form ability to make goals, to plan and organize design activity of the teacher.
Essential difference of the maintenance of the Portfolio of the child of preschool age is existence of the following sections: - the medical: for three years of experimental work all postponed diseases of the child are fixed (chronic, catarrhal, etc.); visit by the child of the preschool organization; physical and anthropological data; - the psychological: changes on personal and mental indications are considered (norm – not norm, prevalence level, etc.); - the social: it is fixed communicative and personal orientations of the child – his relation in system: the child – the parent; the child – the child; the child – the tutor; - the organizational: all information about child’s educational and organizational activity are fixed.
The analysis of program assimilation for kinds in three years allowed to allocate the maximum results by the end of experiment. According to a state program of "Balapang" recommended for use by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the maximum point makes 3,0 points.
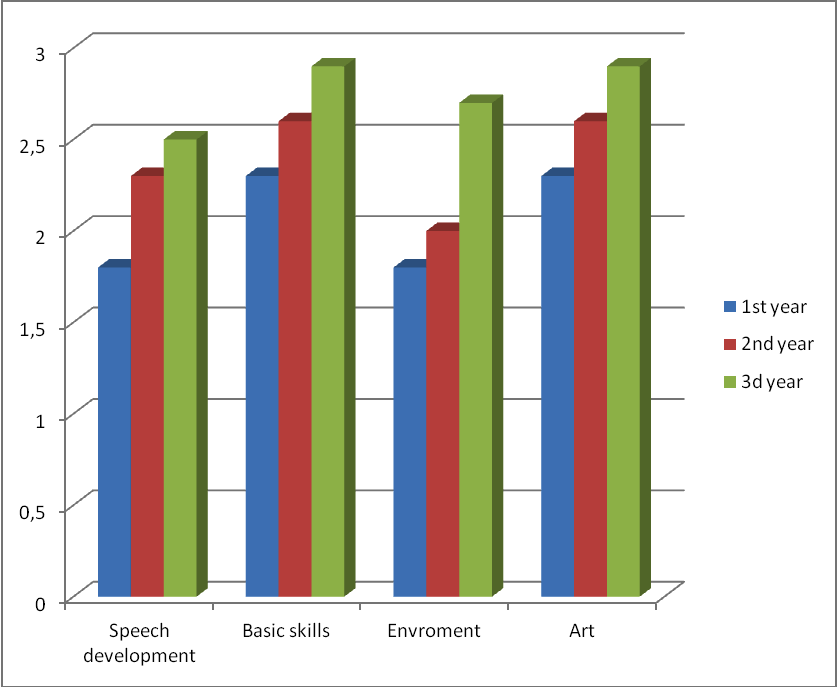
During all three stages of experiment tutors conducted pedagogical diagnostics of assimilation of the program by children, participating in experiment (fig. 1). Diagnostics provides feedback, gives the chance to design educational process, proceeding from a real level of development of children, success of development by each child of this or that section of the program. Game character of tasks, the fairy tale characters putting the child in a problem situation which demands use of social experience I defused emotional tensions as the child could test it, feeling that it is checked. All tasks joined in regime processes (a morning, evening interval of time, walk, part of occupation) without breaking the usual organization of life of children.
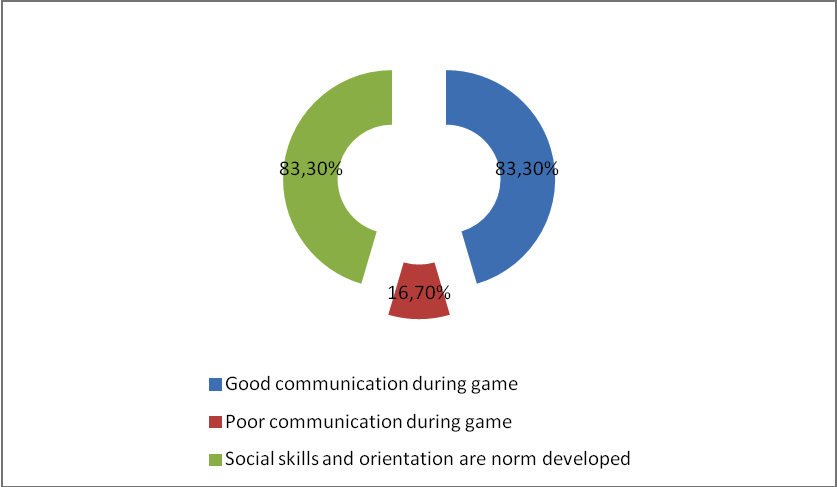
The figure of 2 indicators of social development of children of experimental group shows that 83,3% of children well communicate during game and social skills are created. At 16,7% of respondents – the specified indicators carry low result as children who are only in a family or the having enough adult parents enter this category. These children are taken on personal control by psychologists, individual consultations with the recommendation – to involve their children in circles on interests were held with parents.
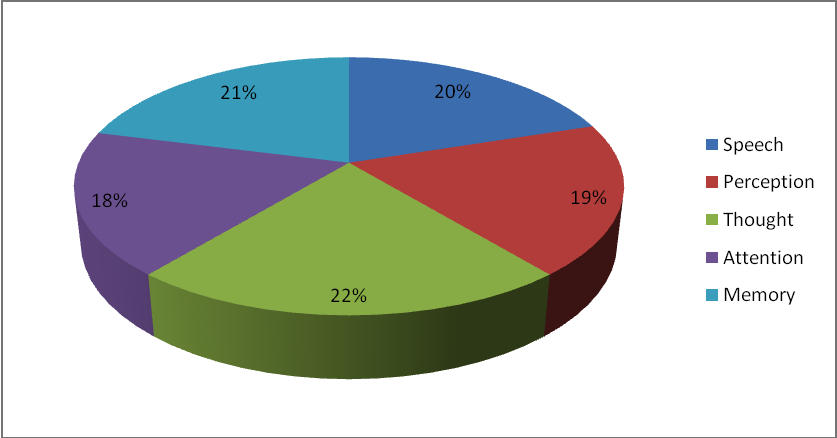
The comparative analysis of indicators of mental development and assimilation of the program of children for three stages of the course of experiment show dynamics in development. The decisions made taking into account application of the special techniques corresponding to preschool age led to improvement of organizational and methodical work, promoted improvement of quality of education and development.
Throughout all stages of experiment the consultations training and methodical seminars, round tables, psychological trainings with the tutors working during research were held. The work mechanism with the parents of children who gave the consent that their child will be was especially carefully developed is in experimental group. All carried-out work had open character where parents could see work of the child, his activity. For parents organizational and methodical events for the purpose of their education were also held.
Conclusions
As a basis of teaching and educational activity we considered the process of formation of the identity of the child. Work of the preschool organizations in the experimental mode causes systematic improvement of the contents and methods of education and training of preschool children, professional development of teachers, and also the organization of psychology and pedagogical education of parents. In process of work techniques "Were applied find differences" and "Find and delete"; imagination – a technique "Drawing"; memory – techniques "Remember pictures" and "Remember words"; thinking – techniques "Establish sequence", "nonsenses", "Call in a word" and others. The decisions made taking into account these techniques led not only to improvement of organizational and methodical work, but also promoted education improvement of quality.
Everything without exception parents want to have as little as possible problems upon transition of the child to comprehensive school, there is a wish that the child was prepared for training at school. They need to see results of educational work of the preschool organization for own calm and confidence in development of the child. Teachers are firmly sure that this technology helps them, and the first stage, to the child to be guided in so unstable world.
References
Ayukasova, H. (2008). Management of process of development and deployment of model of a portfolio. Peddiagnostika, No. 2. 145, 150.
Evgrafova T. (2010). I Learn Myself portfolio. School psychologist, No. 24, 219, 37.
Novikova, Of This Year, Pinskaya M. A., Prutchenkov A.S. (2006). A portfolio in profile training: method. recommendations about maintenance of work with a portfolio of pupils. Library of the Metodist magazine, No. 10. – 172, 32.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 January 2015
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-001-3
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
2
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-218
Subjects
Educational psychology, education, psychology, social psychology, group psychology, collective psychology
Cite this article as:
Naurzalina, D., Tolegenova, A., Doszhanova, S., Kubiyeva, V., Izmagambetova, R., & Almurzayeva, B. (2015). Portfolio as a form of an assessment of preschool child personal achievements. In Z. Bekirogullari, & M. Y. Minas (Eds.), Cognitive - Social, and Behavioural Sciences – icCSBs 2015 January, vol 2. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 130-136). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2015.01.15

