Abstract
The safety of all workers such as those working in the construction industries is paramount as long as success is desired to be achieved in any project. Each piece of work in project execution is having relevance that is incomparable to one another. Problems relating to health and safety were greatly said to be the responsibility of construction firms in terms of their approach to work and how important safety is being considered by the firm. Most Nigeria workers in the built industry and other developing countries suffers from occupational injury with relative high degree of occurrence making the sector unsafe. So many factors can contribute to that, Parties involve (including government agencies) in the Nigerian construction industries are not given much priority to issues concerning safety during construction process, based on that, this paper tends to highlights issues relating to health and safety from the perspective of Nigerian construction industries with aim of mitigating the problems identified. Descriptive research approach was used to solve this problem and a qualitative data was used as a primary data of the study, the result obtained was discussed and analysed be using descriptive method of analysis. Lack of frequent site visit by government agencies was found to be the major issue to safety of workers in the Nigerian construction industries and therefore recommended that, passing the national building code in to bill and making sure of its implementation and compliance by all stakeholders in the country is the only way out.
Keywords: Construction industry, safety, issues, building code
Introduction
Construction firms are being considered to be one of the economic sectors that rapidly boom the economy of any nations (Isah, 2018). The safety of workers in the built industry should be considered to be of great importance for achieving a successful project delivery. Though Each piece of work in project execution is having relevance that is incomparable to one another, as state by Chucks and Uchenna (2013).
Scope and limitation
The research is for all Nigerian construction industries by making random selection of some construction industries to represent the entire population of the study. However, construction industry is one of the largest business sectors in both developed and developing countries with so many issues facing it, the research will only forecast on the on the issues relating to health and safety.
Problem Statement
There are many sectors that booms the economic status of both developed and developing countries, construction industry is said to be one of the most important sector that helps to raise the economic status of any nation in terms of their contribution to gross domestic product (GDP), the sector is not only important in boosting economy, but also equally important in terms of infrastructural development (Yoon et al., 2017). Nigeria like all other countries, countries is generating GDP from its construction section with an increase from 2.0% to 3.2% in the last quarter of year 2018 (CBN, 2019). According the national bureau of statistics, Nigerian industries accounts for 27.36% among which construction industries provide nothing not less than 18% between the year 2014-2017 (NBS, 2018). Nigeria such as other developing countries is generating GDP from its construction section with an increase from 2.0% to 3.2% in the last quarter of year 2018 (CBN, 2019).
Unfortunately for the sectors, it plays a negative effect to life and safety of the people happened to be the employees of such sector. Most workers in the construction industries agonized from simple or complex injuries leading to fatality almost every year due to the nature of their work; some of them undergo ill health, such as burning, loss of finger or leg, permanent deformation. In the absence of good and proper site controlling, this problem will not only have occurred to the workers on site but if care not taken, this can also affect passer-by especially children as well as other people working around them (Williams, 2006). Unsafe act and unsafe working conditions referred to be the major causes of accidents happening in the construction sites and that, construction workplaces hazards were said to be impossible to be identified and eliminated always Patel, Barot and Shah (2008).
Construction industries in most developing nations are performing far lower than what is expected when it comes to issue of safety, the situation in Nigeria is also the same as per the provisions made by the National Building Code approved by the national executive council in the year 2006 which is yet to be enacted and enforced effectively till date. Idoro (2011) said that most Nigerian construction companies doesn’t give much attention to safety during construction like all other developing countries but rather it is being considered as a burden. Proper records of accident injuries in most developing countries are usually poor (Huang & Hinze, 2006). Based on this problem, there is need to undertake a research towards solving safety issues in the Nigerian construction. Nyirenda, Chinniah, and Agard (2015) said that, providing good and sound policies, health and safety plans can be a yardstick of having rapid advancement of employees, their progress, and a maintained workplace that is considered to be free from real construction hazard that can cause injury to employees.
Research Questions
- What are the issues relating to health and safety in the Nigerian construction industries?
- What is the proper solution towards improving the working condition and safeguarding the lives of workers in the construction industries?
Purpose of the Study
- To reduce the rate of occupational injuries happening in the Nigerian construction industries and the world at large.
Research Methods
A quantitative research approach was used to elucidate data used for this research using questionnaire and a checklist. Five indigenous construction sites operating in Katsina state were visited and workers available on sites were considered as the research respondents. However, percentages and mean of the result obtained was presented in a tabular form followed by a clear discussion of the result found.
Findings
Table 1 has shown that all the questionnaire distributed were filled and retrieved by the researcher with 94% valid and 6% as invalid and this shows that the researcher was able to get the minimum response of 62.4% and 37.6% attrition rate as stated by Baruch and Holtom (2008).
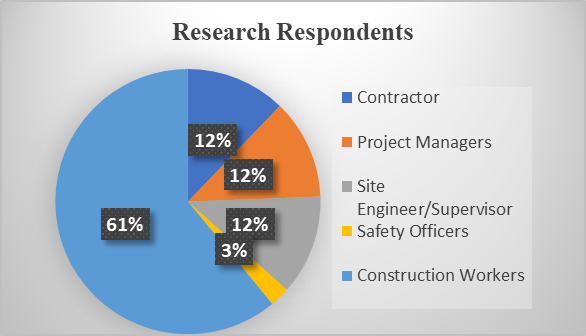
The chart in Figure 1 show five different respondents were used as the research participants both playing a specific task, the result shows that construction workers were the highest participant in the research with 61% while safety officers were the lowest with 3% only. This shows that, there is likely going a numerous case of accident most of the construction sites visited.
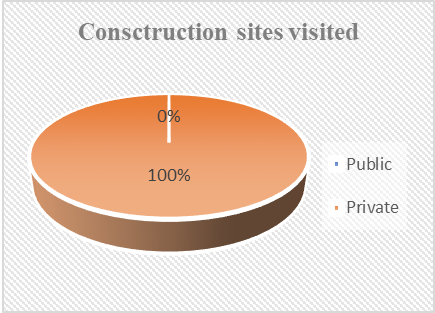
The chart in Figure 2 show that 100% of the construction sites visited were own by private companies not government and this can have negative effect of taking high risk of medical care of the workers injured and eventually this can make the construction workers to shun away from this responsibility while public companies gives the opportunity to spread any risk among the large company owners (Suopajärvi et al., 2016).
Safety Issues in Nigerian Construction Sites
Where by SA= Strongly Agree (5), A= Agree (4), N= Neutral (3), SD = Strongly Disagree (2) and D= Disagree (1)
Table 2 above shows the responses of the research participants using Likert scale. From the table, on the issues of government agency visit to the construction sites, the response strongly disagrees with statement and this implies that, contractors can handle projects using their own traditional ways as such could lead to so many accidents as there is no check and balances as the main role of government agencies in construction projects is to check the activities of contractors for compliance as mentioned in the national building code 2006.
However, on the issue of providing the necessary safety facilities, the result shows that, the respondents also strongly disagree with the statement, as this coincides with what the researcher found on ground as items such as rain gear, hoisting equipment, scaffold and ladder protections were not provided in all the sites visited by the researcher, these issues are a great problem to worker’s life and health this was also available in the appendix.
On the issues of personal protective equipment (PPE), the result also shows that the respondents strongly disagree with the statement saying that, each worker is provided with PPE, during the field work survey, the researcher observed that some workers were even working on site mixing concrete barefooted without hand gloves and helmet. This means that the workers are not safe at all as any slight accident can cause injury.
So also, on the issues of first aid box, the result shows that the respondents agree with statement saying that, the company has first aid box fully equipped with first aid drugs and tools and this is recommendable as first aid box helps to reduces the risk of injury and saves life to some extent, lack of first aid box can worsen situation in the event of accident.
But on the other hand, the result shows that, most of the companies don’t have a professionally trained health and safety officers as the respondents disagree with the statement saying, the company has a professional and trained safety officers. The importance of safety officer in each hazardous and dangerous working place is paramount but this is not the case in the Nigerian construction sites, health and safety officers helps to minimize the level of accident by preparing and planning a comprehensive health and safety plan to suite the current work situation.
As construction sites are well known to be a great source of hazards that were leading to the injuries and death to workers in some, therefore, workers on sites needs to aware of the hazards they are facing so as to avoid them.in this regards, employers need to warn workers of hazards throughout the sites in form of clear, appropriately visible signage (Cutforth, 2019). The Table 2 above also presents the result obtained on the issues of using warnings sings whereby the respondents agree with the statement saying that, the company always fixed safety sings and warnings, this normally happened as money is always given in the bill of quantities for preliminaries which normally the clients doesn’t take-off their face from, they make sure that such money is fully utilized in providing such signs.
There is all sort of risk associated with construction projects, it is the role of the employer to ensure himself and his employee are protected with the required type of insurance coverage as stated by (All-West Crane, 2018). to reduce the risk of accident damages and loss of lives, workers are normally insured by health insurance company to cut off the medical expenses to be paid by the victims in the event of accident and other illness, respondents strongly disagree with the statement saying that, Workers are insured by health insurance company despite the importance of health insurance mentioned, this can be a serious issues that need to be address and enforced to all construction company workers and their alike.
On the job training improves the performance of workers and his skill, a skilled worker always faced less injury incidents than the unskilled one, but this is not the case in the context of Nigerian construction sites as the respondents also strongly disagree with the statement saying that, workers are being sent to safety training programs.
From the result discussed, it can be clearly seen that, safety issues in the Nigerian construction industries is not recommendable as the basic safety issues were not rated good by the research participants. Among the major issues rated poorly was the inability of government to visit construction sites frequently, this issues can lead to improper use of poor construction tools and equipment, improper or not use of PPE and noncompliance to safety rules, this can be said to be the remote cause of almost all injuries on construction sites except that occurred as a result of act of God and negligence. Other issues rated poorly includes; lack of providing safety facilities including PPE, unprofessionally trained safety personnel, lack of good health insurance coverage and development capacity trainings. These and many more were enough to make any working place to be so dangerous and hazardous.
Conclusion
Based on the result found, the research concludes that, no construction work can progress without having healthy workers, therefore, life and health of all workers shall be given due consideration by having close supervision by both site engineers and government agencies during all work operations to control the rate of injuries, however, all construction workers shall be covered by a good health insurance scheme that will take care of their health in the event of any injury.
From the findings of the research, the research recommends that:
- All workers in the construction industry must be insured with a good insurance health insurances coverage to take care of their medical expenses in the event of incidents.
- The National Building Code 2006 bill passed by legislative house should be blessed by the federal executive council as a law.
No contractor shall be given any sort of project until his health and safety planned is approved by the concerned government body and closely be monitored for maximum compliance.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND) Nigeria and Hassan Usman Katsina Polytechnic and Universiti Sains Malaysia.
References
All-West Crane, 2018 Crane safety tips for your construction project https://www.allwestcrane.com/blog/2018/02/crane-safety-tips-for-your-construction-project/
Baruch & Holtom (2008). Sample size and distributed questionnaire retrieved on 7/7/ 2019 from www.researchgate.net/podt/sample_size_and_distributed_questionnaire/amp
Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN). (2019). National Growth Rate Data. Retrieved from www.tradeeconomics.com/Nigeria/gdp-growth-annual
Chucks, O. K., & Uchenna, O. P. (2013). Appraising the influence of cultural determinants of construction worker’s safety perception and behavior in Nigeria.
Cutforth, P. (2019) Importance of warning signs on building sites published by construction white card Australia (online) retrieved on 9/7/2019 from www.whitecardaustralia.com
Idoro, G. I. (2011). Effect of mechanisation on occupational health and safety performance in the Nigerian construction industry. Journal of Construction in Developing countries, 16(2), 27-45.
Huang, X., & Hinze, J. (2006). Owner’s role in construction safety. Journal of construction engineering and management, 132(2), 164-173.
Isah, H. (2018). The influence of language proficiency on occupational safety of foreign workers, in the Construction Industry Student’s Work University Sains Malaysia.
National bureau of statistic (2018). Annual report retrieved from https://nigerianstat.gov.ng/page/data-analysis
Nyirenda V., Chinniah, Y., & Agard, B. (2015). Identifying Key Factors for an Occupational Health and Safety Risk Estimation Tool in Small and Medium-size Enterprises. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5462637/ on 31/08/2019
Patel, R., Barot, U., & Shah, K. (2008). Accident on construction site: Identification & mitigation: A literature survey. International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science and Management.
Suopajärvi, L., Poelzer, G.A., Ejdemo, T., Klyuchnikova, E., Korchak, E. & Nygaard, V. (2016). Social sustainability in northern mining communities: A study of the European North and Northwest Russia. Resources Policy, 47, 61–68.
Williams, S. (2006). Health and safety in construction. United Kingdom: Crown Publishing.
Yoon, S. J., Lin, H. K., Chen, G., Yi, S., Choi, J., & Rui, Z. S. (2017). Effect of Occupational Health and Safety Management System on Work-Related Accident Rate and Differences of Occupational Health and Safety Management System Awareness between Managers in South Korea's Construction Industry Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5462637/ on 31/08/2019
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
26 December 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-950-4
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
2
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-882
Subjects
Technology, smart cities, digital construction, industrial revolution 4.0, wellbeing & social resilience, economic resilience, environmental resilience
Cite this article as:
Isah*, H. (2017). Health And Safety Issues In The Nigerian Construction Industries: Prevention And Mitigation. In P. A. J. Wahid, P. I. D. A. Aziz Abdul Samad, P. D. S. Sheikh Ahmad, & A. P. D. P. Pujinda (Eds.), Carving The Future Built Environment: Environmental, Economic And Social Resilience, vol 2. European Proceedings of Multidisciplinary Sciences (pp. 733-739). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epms.2019.12.74
