Abstract
In this paper a novel algorithmic scheme for differential evolution is proposed with two populations and new mutation strategies. The populations contain latest and best individuals, and the sizes of these populations are controlled independently. The LL-NADE algorithm uses the parameter adaptation scheme proposed in L-SHADE, and the sizes of both populations are reduced at the same time. The experiments described in the paper are performed on the CEC 2022 benchmark suite. The total standard score is used for comparison of different algorithms on a set of benchmark problems. The experiments are performed with six different mutation strategies, which utilize individuals from both populations. The most efficient mutation strategy utilizes directed search from newest to top individuals. It is shown that LL-NADE is capable of demonstrating results comparable with state-of-the-art algorithms. Comparison on various test functions and dimensions have shown that LL-NADE performs in a way that is not similar to other differential evolution algorithms, achieving better results on some problems, but worse on other.
Keywords: Differential evolution, population size, parameter adaptation
Introduction
The development of modern optimization methods is one of the important directions of computational intelligence research nowadays, as such methods are often utilized in other learning or search algorithms. The heuristic optimization, which includes evolutionary algorithms (EAs), focuses on black box optimization, including single-objective, multi-objective, constrained and other types of problems (Sloss & Gustafson, 2020). The differential evolution (DE) (Price et al., 2006) today represents a popular family of approaches, which are relatively simple and easy to implement, and at the same time very efficient in many scenarios. This can be seen by the success of the DE-based algorithms in optimization competitions in the last several years, such as Congress on Evolutionary Computation competition on single-objective numerical optimization, where DE is taking leading places (Škvorc et al., 2019).
One of the problems of DE is the sensitivity to parameter values, which lead to numerous studies on parameter adaptation schemes, with SHADE being one of the most popular approaches (Tanabe & Fukunaga, 2013). However, few attempts have been made in changing the basics of the DE algorithmic scheme. A recent study on Unbounded DE (UDE) (Kitamura & Fukunaga, 2022) has shown that it is possible to apply specific selection mechanisms with infinitely growing population to achieve competitive results.
In this paper the dual population algorithm is proposed, which further develops the ideas of UDE. LL-NADE (Linear and Linear populations sizes reduction Newest and top Adaptive Differential Evolution) maintains the newest population, which contains recently discovered solutions, and top population, that keeps the best solutions throughout the whole search process. The numerical experiments are performed on the CEC 2022 benchmark problems (Kumar et al., 2021). The main features of the proposed algorithm are the new mutation strategies, combining top and newest solutions, and the novel selection (replacement) scheme for the population of newest individuals.
Problem Statement
This paper is focused on the problem of developing new algorithmic schemes for differential evolution for solving numerical optimization tasks. Most known algorithmic schemes rely on a single population and an archive, while other possibilities should be discovered.
Research Questions
The problem statement raises a set off questions, including the following. First of all, is it possible to develop an algorithmic scheme with more than one population and find an efficient control strategy. Secondly, if the first population contains new individuals, and the second keeps the best, what should be the mutation strategies in such design? In third place, what would be the performance of such approach compared to the state-of-the-art algorithms?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to propose a new efficient differential evolution algorithm and estimate its efficiency on a set of benchmark problems compared to the best known alternative approaches.
Research Methods
Differential evolution
The differential evolution algorithm was proposed by Storn and Price 1995. The differential evoltuion is a population-based heuristic for numerical optimization. The algorithm begins with initialization of a set of individuals where is the dimensionality of the search space:
Here rand is a uniformly distributed random number in , and are the lower and upper boundaries of variable .
The main search operator of DE algorithm is the difference-based mutation. There are several popular mutation strategies, with current-to-pbest being one of the best:
,
where is called mutant vector, , is the value from current population, j-th coordinate of the i-th solution, the indexes i, r1 and r2 are different from each other, and is the scaling factor parameter, chosen from , pbest is the index of one of the pb*100% individuals, sorted by fitness, and different from i, r1 and r2.
The most widely used crossover operator in DE is the binomial crossover, which is applied after mutation:
,
where is the crossover rate, and is a randomly chosen index from , required to make sure that at least one index is taken from the donor vector, is called trial vector.
After applying bound constraint handling method, such as midpoint-target, the fitness value of the trial vector is calculated, and the selection step is applied:
The greedy selection in original DE allows it to always increase the average fitness of the population or at least to keep it at the same level.
Proposed approach
As mentioned above, the main idea of LL-NADE, namely the usage of newest and top individuals, is inspired by UDE, which has shown that proper selection strategies in combination with the whole search history could be helpful in achieving better performance. The LL-NADE algorithm first initializes a population of individuals , . After that, the individuals in this population are evaluated and sorted by their fitness values, individuals are copied to the newest population , and individuals are copied to the top population . The parameter should be set larger than both and . The LL-NADE uses variants of the mutation strategy used in JADE, SHADE and L-SHADE, i.e. current-to-pbest mutation strategy. LL-NADE also applies adaptation of parameters proposed in the SHADE algorithm, however the archive is not used. The modified mutation strategies use individuals from both populations and work as follows:
- r-new-to-ptop/t/t: vi,j=xr1,jnew+F×xpbest,jtop-xi,jnew+F×xr2,jtop-xr3,jtop
- r-new-to-ptop/t/n: vi,j=xr1,jnew+F×xpbest,jtop-xi,jnew+F×xr2,jtop-xr3,jnew,
- r-new-to-ptop/n/t: vi,j=xr1,jnew+F×xpbest,jtop-xi,jnew+F×xr2,jnew-xr3,jtop,
- r-new-to-ptop/n/n: vi,j=xr1,jnew+F×xpbest,jtop-xi,jnew+F×xr2,jnew-xr3,jnew,
- r-new-to-pnew/n/n: vi,j=xr1,jnew+F×xpbest,jnew-xi,jnew+F×xr2,jnew-xr3,jnew,
- r-top-to-ptop/t/t: vi,j=xr1,jtop+F×xpbest,jtop-xi,jtop+F×xr2,jtop-xr3,jtop
Here r-new and r-top mean that for a target solution a random individual will be chosen from the population of newest solutions or the population of top solutions. Next, pnew and ptop mean that one of the individuals, sorted by fitness, will be chosen from either newest or top population. Finally, t/n stands for using top or newest individuals in the last difference. Unlike most DE algorithms, here the target vector is chosen randomly, instead of being the i-th vector from the population.
For the parameter the following control scheme is used: at the start the value is set to , and it is decreased to by the end of the search linearly as follows:
,
where is the generation number. Note that if the or , value, depending on the mutation strategy drops to 1, then it is set to 2, so there is always a choice between two best solutions.
One other important feature of the LL-NADE algorithm is the new selection (replacement) mechanism. The selection used in the algorithm depends on the chosen mutation strategy, i.e. if the target vector is from newest or top population. If the newly generated vector is better than the target vector, it is saved to the newest population. The place for the new solution is saved is determined by index , which is iterated from 1 to , and is incremented only if there is a successful solution. The replacement mechanism in LL-NADE works as shown below:
,
where for the target vector means that it can be chosen from newest population or top population. The new solutions, which replace old ones in the population, can be used for generating other vectors in the same generations. Besides, successful vectors are stored in , a temporary population. At the end of each generation and are joined, sorted, and only solutions are copied back to . This ensures that the top population always contains the best solutions from the whole search process. LL-NADE also uses linear population size reduction, same as in L-SHADE algorithm (Tanabe and Fukunaga, 2014), however here it is used for two populations, newest and top, at the same time.
Findings
The computational experiments with LL-NADE were performed on the CEC 2022 benchmark suite, developed for the Single Objective Bound Constrained Numerical Optimization Competition (Kumar et al., 2021). The benchmark contained 12 functions, defined for 10D and 20D, 30 independent runs were required for each of them. The algorithm was developed in C++ and ran on OpenMPI-powered cluster. For the first set of experiments the population sizes and changed from 5D to 60D with a step of 5D, and 6 mutation strategies were considered. This resulted in a total of 864 experiments. To compare the efficiency, the Mann-Whitney rank sum test with tie-breaking and normal approximation was applied with significance level of 0.01. In addition, the total standard score, summed over 12 functions, was calculated to compare a pair of approaches. The parameters of LL-NADE used in the experiments are the following: . For the first set of experiments the NL-SHADE-LBC algorithm (Stanovov et al., 2022) was chosen as the baseline approach, as it is announced to be second best algorithm in CEC 2022 competition. Figures 1 and 2 show the total standard score of comparing LL-NADE with NL-SHADE-LBC with different population sizes and strategies. Lighter areas mean better results, i.e. larger total score.
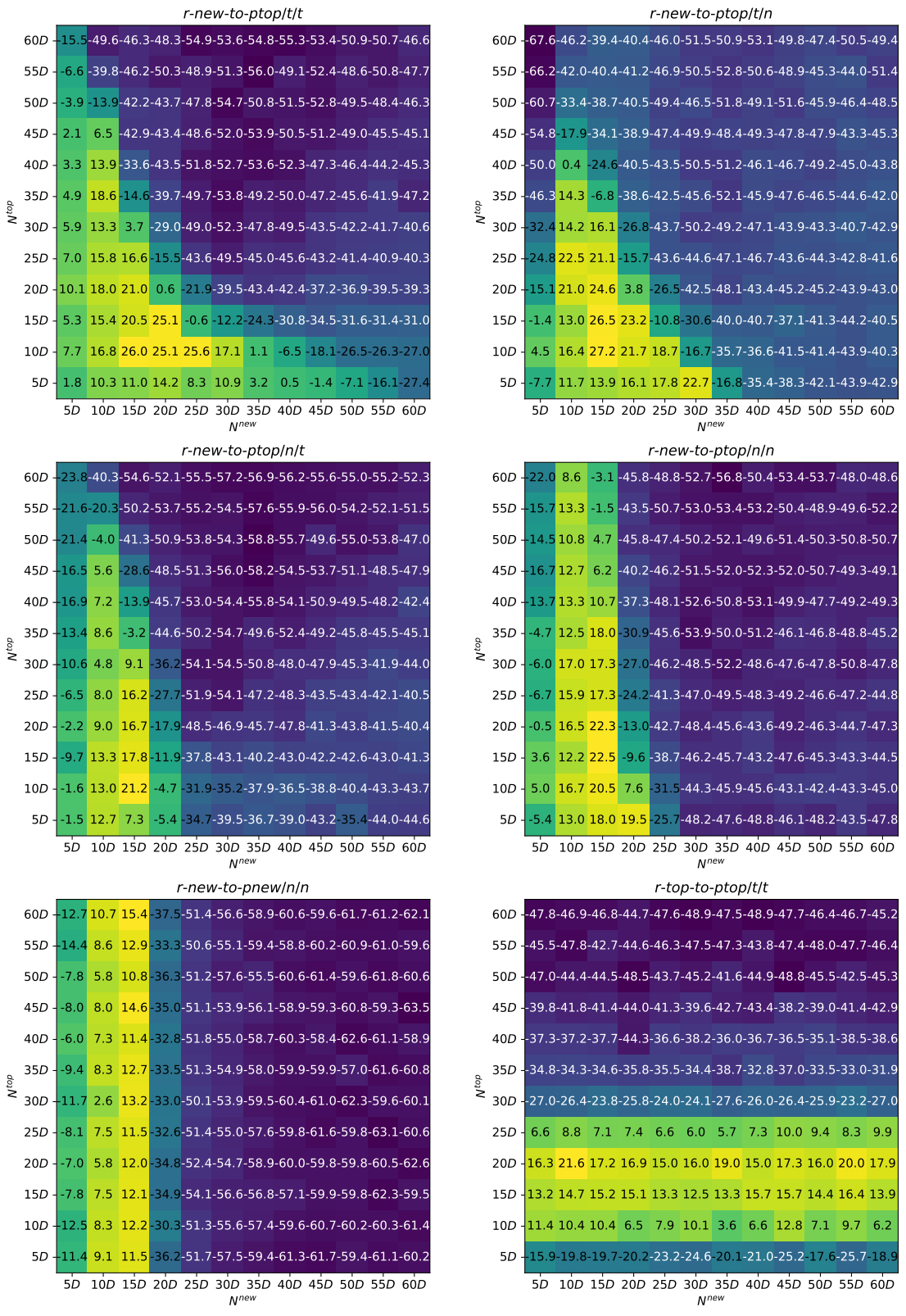
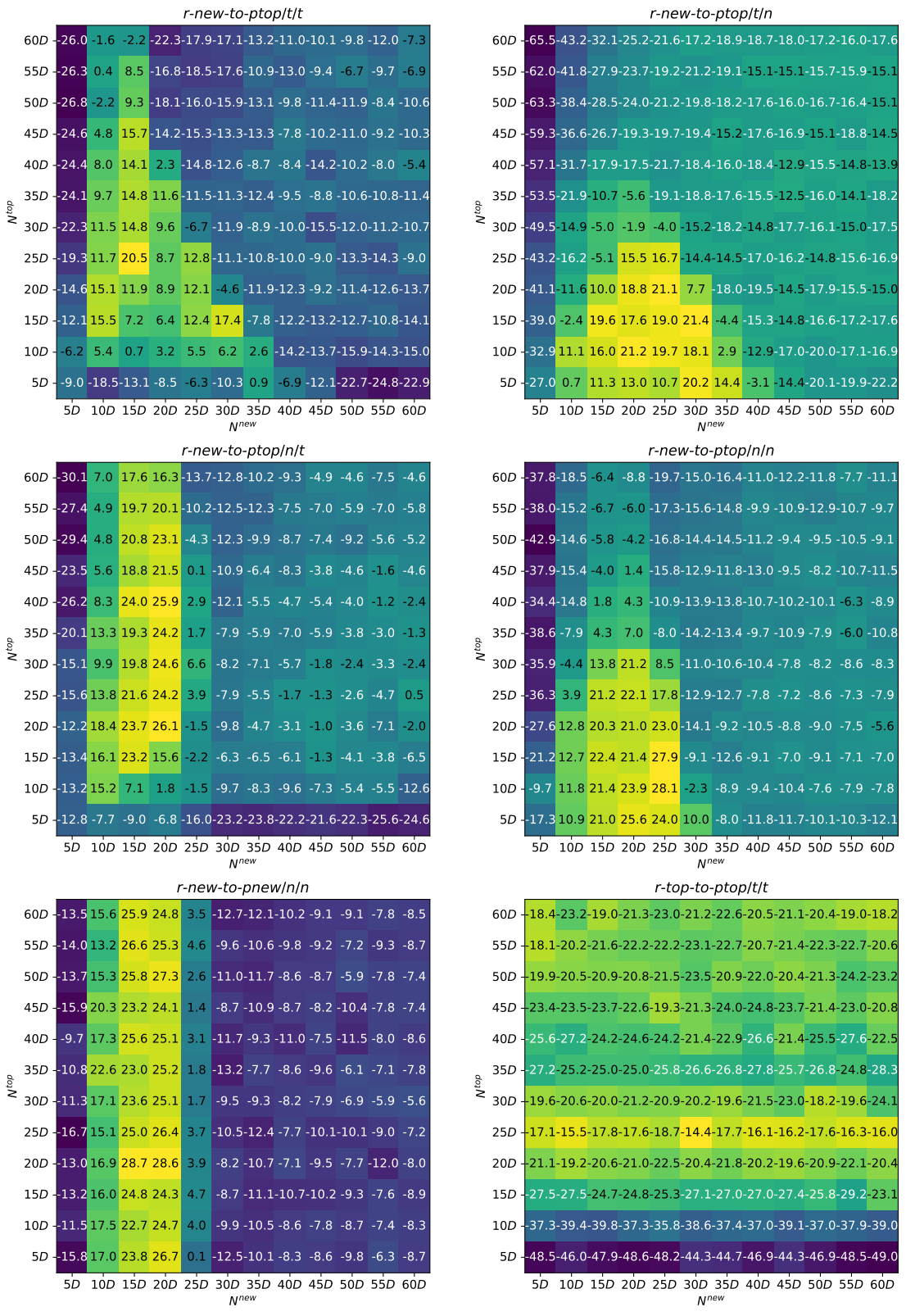
Considering the results in Figures 1, it can be concluded that for all mutation strategies for 10D functions the area of highest efficiency is around 15D or 20D for both and . For r-new-to-ptop/t/n and r-new-to-ptop/t/t there is a clearer dependence of two populations sizes, while r-new-to-ptop/n/t and r-new-to-ptop/n/n are characterized by smaller influence of . Speaking of the efficiency of the proposed algorithms, LL-NADE is able to outperform NL-SHADE-LBC using all mutation strategies except the last one, r-top-to-ptop/t/t. The efficiency of r-new-to-pnew/n/n is also lower compared to the strategies which use both populations.
Figure 2 shows similar results, i.e. total standard score of Mann-Whitney tests is larger than 0 for population sizes of around 20D. An important difference compared to 10D case is that the strategy using only newest vectors r-new-to-pnew/n/n may have the same level of efficiency compared to strategies using both populations. Also, increasing the population size significantly decreases the efficiency of the algorithm, probably because the convergence speed is also considered.
To conclude the experiments section, we provide the comparison of LL-NADE using r-new-to-ptop/n/t strategy and with best participants of CEC 2022 competition, the results are shown in Table 1. The top 3 algorithms are EA4eig (Bujok & Kolenovsky, 2022) combining several DE variants and CMA-ES, mentioned earlier NL-SHADE-LBC (Stanovov et al., 2022) and NL-SHADE-RSP-MID (Biedrzycki et al., 2022), an advanced version of the NL-SHADE-RSP with k-means algorithm. The numbers in Table 1 are the numbers of wins/ties/losses over 12 tested functions.
The results in Table 3 show that LL-NADE has comparable or even better performance against the top 3 methods of the recent CEC competition, which shows that the proposed approach can be promising.
Conclusion
In this paper a new differential evolution algorithm was proposed, which used a new algorithmic scheme with two populations and novel mutations. The experiments performed in this study have shown that the proposed algorithm LL-NADE is highly competitive compared to the best methods in the CEC 2022 benchmark, especially on complex functions. One of the disadvantages of LL-NADE is that it requires more parameters to be set compared to known alternatives. The LL-NADE is a non-hybrid method, and it does not increase the computational complexity compared to modern DE variants, and it can be improved by implementing modifications, developed for other DE algorithms.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, Grant No. 075-15-2022-1121.
References
Biedrzycki, R., Arabas, J., & Warchulski, E. (2022, July). A version of nl-shade-rsp algorithm with midpoint for cec 2022 single objective bound constrained problems. In 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE. DOI:
Bujok, P., & Kolenovsky, P. (2022, July). Eigen crossover in cooperative model of evolutionary algorithms applied to cec 2022 single objective numerical optimisation. In 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE. DOI:
Kitamura, T., & Fukunaga, A. (2022). Differential Evolution with an Unbounded Population. In 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE. DOI:
Kumar, A., Price, K., Mohamed, A. K. A. A., & Suganthan, P. N. (2021). Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2022 Special Session and Competition on Single Objective Bound Constrained Numerical Optimization. Technical Report Nanyang Technological University, Singapoure.
Price, K., Storn, R. M., & Lampinen, J. A. (2006). Differential evolution: a practical approach to global optimization. Springer Science & Business Media.
Škvorc, U., Eftimov, T., & Korošec, P. (2019). CEC real-parameter optimization competitions: Progress from 2013 to 2018. In 2019 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC) (pp. 3126-3133). IEEE. DOI:
Sloss, A. N., & Gustafson, S. (2020). 2019 Evolutionary Algorithms Review. In W. Banzhaf, E. Goodman, L. Sheneman, L. Trujillo, & B. Worzel (Eds.), Genetic Programming Theory and Practice XVII. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation (pp. 307-344). Springer, Cham. DOI:
Stanovov, V., Akhmedova, S., & Semenkin, E. (2022). NL-SHADE-LBC algorithm with linear parameter adaptation bias change for CEC 2022 Numerical Optimization. In 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC) (pp. 01-08). IEEE. DOI:
Tanabe, R., & Fukunaga, A. (2013). Success-history based parameter adaptation for differential evolution. In 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (pp. 71-78). IEEE. DOI:
Tanabe, R., & Fukunaga, A. (2014). Improving the search performance of SHADE using linear population size reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, CEC (pp. 1658-1665). DOI:
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License
About this article
Publication Date
27 February 2023
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-960-3
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
1
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-403
Subjects
Hybrid methods, modeling and optimization, complex systems, mathematical models, data mining, computational intelligence
Cite this article as:
Stanovov, V., Akhmedova, S., & Semenkin, E. (2023). Adaptive Differential Evolution With Two Populations of New and Best Individuals. In P. Stanimorovic, A. A. Stupina, E. Semenkin, & I. V. Kovalev (Eds.), Hybrid Methods of Modeling and Optimization in Complex Systems, vol 1. European Proceedings of Computers and Technology (pp. 102-110). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epct.23021.13

